- How to Make JavaScript Execute After Page Load
- The onload Method
- The window.onload Method
- Window: load event
- Syntax
- Event type
- Examples
- Live example
- HTML
- JavaScript
- Result
- Specifications
- Browser compatibility
- See also
- Found a content problem with this page?
- MDN
- Support
- Our communities
- Developers
- What is the Window onload event in JavaScript?
- Window.onload Event in the head section of HTML
- Onload Event in the body section of HTML
- Window Onload Event in the body section of HTML
- Output of Console
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Shehroz Azam
- JavaScript Window Onload Function Call
- window.onload Functionality Usage With Example in HTML
- Examine the Given HTML Code in Few Steps
- Alternative Way to See the Same Results
How to Make JavaScript Execute After Page Load
It’s important to be sure that JavaScript doesn’t run before the page load. In this tutorial, you will get the right answer to your question of making the JavaScript run after the page load. Here are the two methods which can help you get the work done correctly.
The onload Method
The onload event occurs after the element has finished loading. This can be used with the body element to run a script after the webpage has thoroughly loaded:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> head> body onload="loadFunction()"> h1>Welcome to W3Docs h1> script> function loadFunction( ) < alert("Page is loaded"); > script> body> html>The window.onload Method
The onload property with the window element is used to run a script after the webpage has thoroughly loaded. The onload property fires the function as soon as the webpage has been loaded:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.5.0.min.js"> script> head> body> h1>Welcome to W3Docs h1> script> function loadFunction( ) < alert("Window is loaded"); > window.onload = loadFunction(); script> body> html>Window: load event
The load event is fired when the whole page has loaded, including all dependent resources such as stylesheets, scripts, iframes, and images. This is in contrast to DOMContentLoaded , which is fired as soon as the page DOM has been loaded, without waiting for resources to finish loading.
This event is not cancelable and does not bubble.
Note: All events named load will not propagate to Window , even with bubbles initialized to true . To catch load events on the window , that load event must be dispatched directly to the window .
Note: The load event that is dispatched when the main document has loaded is dispatched on the window , but has two mutated properties: target is document , and path is undefined . These two properties are mutated due to legacy conformance.
Syntax
Use the event name in methods like addEventListener() , or set an event handler property.
addEventListener("load", (event) => >); onload = (event) => >;
Event type
Examples
Log a message when the page is fully loaded:
.addEventListener("load", (event) => console.log("page is fully loaded"); >);
The same, but using the onload event handler property:
.onload = (event) => console.log("page is fully loaded"); >;
Live example
HTML
div class="controls"> button id="reload" type="button">Reloadbutton> div> div class="event-log"> label for="eventLog">Event log:label> textarea readonly class="event-log-contents" rows="8" cols="30" id="eventLog">textarea> div>
body display: grid; grid-template-areas: "control log"; > .controls grid-area: control; display: flex; align-items: center; justify-content: center; > .event-log grid-area: log; > .event-log-contents resize: none; > label, button display: block; > #reload height: 2rem; > JavaScript
const log = document.querySelector(".event-log-contents"); const reload = document.querySelector("#reload"); reload.addEventListener("click", () => log.textContent = ""; setTimeout(() => window.location.reload(true); >, 200); >); window.addEventListener("load", (event) => log.textContent += "load\n"; >); document.addEventListener("readystatechange", (event) => log.textContent += `readystate: $document.readyState>\n`; >); document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", (event) => log.textContent += `DOMContentLoaded\n`; >);
Result
Specifications
Browser compatibility
BCD tables only load in the browser
See also
Found a content problem with this page?
This page was last modified on Apr 8, 2023 by MDN contributors.
Your blueprint for a better internet.
MDN
Support
Our communities
Developers
Visit Mozilla Corporation’s not-for-profit parent, the Mozilla Foundation.
Portions of this content are ©1998– 2023 by individual mozilla.org contributors. Content available under a Creative Commons license.
What is the Window onload event in JavaScript?
With the new advancements in web development, JavaScript is even evolving in different frameworks, which makes life easy for developers. Talking about its use, as of now many famous websites are built on JavaScript which depicts how reliable this language is.
JavaScript has a window onload event to launch certain functions whenever a web page is loaded. The onload event is also used for verification of type and version of visitor’s browser. Further cookies can also be checked through the onload attribute.
The attribute of onload triggers when the object is loaded in HTML. This is to launch the script whenever the associated element loads. In simpler words, we can say that the window onload event is triggered whenever a web page is launched successfully.
Onload event is used with to run a script once its substance (which includes CSS files, images, and scripts) of the page is triggered completely. However, you do not always need a tag. It can be used with other Html elements.
The download.onload launches before the images and external contents, triggered just before the window.onload. Whereas, window.onload starts after the page is completely loaded including CSS, script files, images, and many more.
If you want to manipulate load event in JavaScript, then you need to register event listener through method of addEventListener() as shown in the example below:
window. addEventListener ( ‘load’ , ( event ) => {
You can also handle the load event through the property of the window object i.e. onload. The example below shows how to use onload property:
Window.onload Event in the head section of HTML
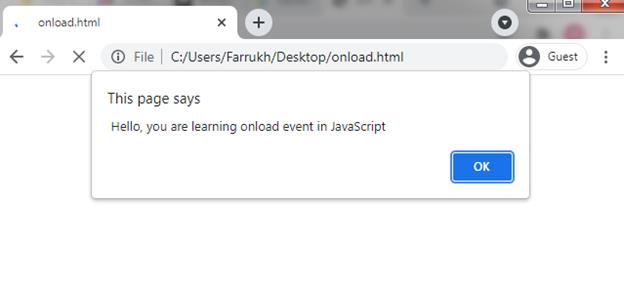
First of all, we are going to present a simple example of a window.onload event. In this example, we simply display an alert message whenever a page is loaded.
alert ( » Hello, you are learning onload event in JavaScript» ) ;
window. onload = js_onload_code ( ) ;
Onload Event in the body section of HTML
Content can be displayed in the body section of HTML. Whenever the webpage is loaded then the event which occurred at that time is named onload event. We can use the onload event in the body section so that we can execute the script.
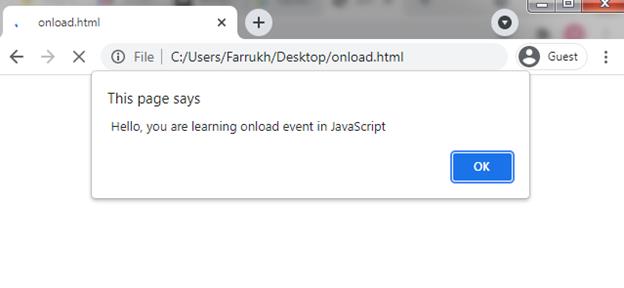
If you want to use an onload event within the body section then run the following code.
alert ( » Hello, you are learning onload event in JavaScript» ) ;
Window Onload Event in the body section of HTML
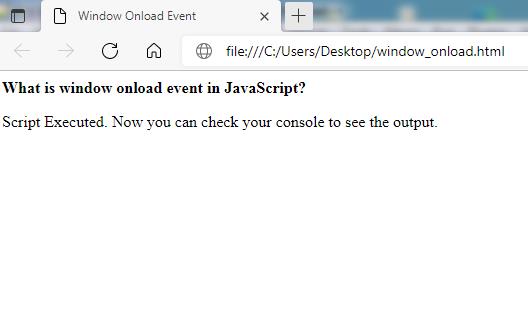
The object of the onload window represents the window of the browser. Whenever all the operations are completely loaded then onload property processes the load event. The function which we want to execute is allocated to the handler function of the onload property. Whenever the webpage gets loaded then the function will be executed. We have provided you with an example below.
window. onload = function functionName ( ) {
< b >What is window onload event in JavaScript ?
< p >Script Executed. Now you can check your console to see the output.
window. onload = function your_function_name ( ) {
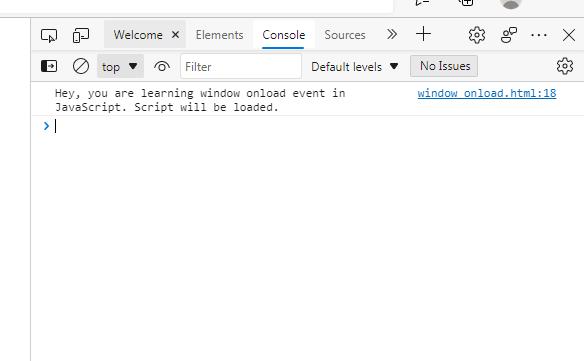
console. log ( ‘Hey, you are learning window onload event in JavaScript. Script will be loaded.’ ) ;
Output of Console
If you want to see the output of the console then you have to open devTool by pressing the shortcut keys i.e. CTRL+SHIFT+ I. After opening the Devtool, you will be able to see the console’s output screen as shown below.
Conclusion
We have learned about what window.onload() event is and also learned the syntax of onload event. We briefly discussed several methods of how to write onload events in JavaScript along with an example. To recap, window.onload() event triggers after the web page has been loaded. We also see that the onload event is useful to set the version of browsers and also used to observe the cookies of a web page.
About the author
Shehroz Azam
A Javascript Developer & Linux enthusiast with 4 years of industrial experience and proven know-how to combine creative and usability viewpoints resulting in world-class web applications. I have experience working with Vue, React & Node.js & currently working on article writing and video creation.
JavaScript Window Onload Function Call
- window.onload Functionality Usage With Example in HTML
- Examine the Given HTML Code in Few Steps
- Alternative Way to See the Same Results
This article explains the purpose of the window.onload method in JavaScript by an example. The window.onload function executes to perform a task once the page on the browser finishes loading.
window.onload Functionality Usage With Example in HTML
The window.onload method is triggered when the page is entirely loaded on the browser (as well as all images, style, scripts, and CDN). Here you can see an example of HTML page source code that uses the window.onload method for auto-execution to display an alert box.
html> head> title>(Window.onload function in HTML)title> script type="text/javascript"> function code() alert(" Alert inside code function Window.onload"); > window.onload=code(); script> head> body> h1> Graphic Designer Firm h1> p1> A craft of creating visual content to communicate messages.p1> br> img src = "Graphic-Design.png" height="500px" width="500px" > br> hr width="800"> body> html> In the above HTML page source, you can see the tag that uses JavaScript in doctype html. In the next step function code() is declared inside of the tag.
The function code() is called window.onload . It displays a default alert dialogue when a web page loads completely with images and text content.
Examine the Given HTML Code in Few Steps
Follow these four easy steps and get a clear understanding of the window.onload method.
Create a text document. You can utilize notepad or any other text editing tool.
Paste the given code in the created text file.
Save that text file with the extension of .html and open it with any default browser.
You can see an alert box that pops up right after the complete page load.
Alternative Way to See the Same Results
You can achieve the alert message results by using an alternative onload event via a body tag. Here is an example of a body tag that uses auto-execution to call a function code containing an alert box:
script type="text/javascript"> function code() alert(" Alert inside code function"); > script> body onLoad="code()";> In both examples, onLoad of body tag and window.onload have the same functionality to execute the statements after completing page load.
Copyright © 2023. All right reserved