- HTML Video
- Example
- The HTML Element
- Example
- How it Works
- HTML Autoplay
- Example
- Example
- Browser Support
- HTML Video Formats
- HTML Video — Media Types
- HTML Video — Methods, Properties, and Events
- Example: Using JavaScript
- HTML Video Tags
- HTML5 Video Player: How It Works in 6 Definitive Steps
- 1: What defines an HTML5 Video Player?
- 2: How an HTML5 Video Player interacts with your workflow
- 3: How different API factors affect the stream
- 4: Are all features and capabilities necessary?
- 5: Metrics to measure your stream
- 6: SDKs and Testing
- The big picture
HTML Video
The HTML element is used to show a video on a web page.
Example
The HTML Element
To show a video in HTML, use the element:
Example
How it Works
The controls attribute adds video controls, like play, pause, and volume.
It is a good idea to always include width and height attributes. If height and width are not set, the page might flicker while the video loads.
The element allows you to specify alternative video files which the browser may choose from. The browser will use the first recognized format.
The text between the tags will only be displayed in browsers that do not support the
HTML Autoplay
To start a video automatically, use the autoplay attribute:
Example
Note: Chromium browsers do not allow autoplay in most cases. However, muted autoplay is always allowed.
Add muted after autoplay to let your video start playing automatically (but muted):
Example
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the element.
| Element | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.0 | 9.0 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 10.5 |
HTML Video Formats
There are three supported video formats: MP4, WebM, and Ogg. The browser support for the different formats is:
| Browser | MP4 | WebM | Ogg |
|---|---|---|---|
| Edge | YES | YES | YES |
| Chrome | YES | YES | YES |
| Firefox | YES | YES | YES |
| Safari | YES | YES | NO |
| Opera | YES | YES | YES |
HTML Video — Media Types
HTML Video — Methods, Properties, and Events
The HTML DOM defines methods, properties, and events for the element.
This allows you to load, play, and pause videos, as well as setting duration and volume.
There are also DOM events that can notify you when a video begins to play, is paused, etc.
Example: Using JavaScript
Play/Pause Big Small Normal
Your browser does not support HTML5 video.
For a full DOM reference, go to our HTML Audio/Video DOM Reference.
HTML Video Tags
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
| Defines a video or movie | |
| Defines multiple media resources for media elements, such as and | |
| Defines text tracks in media players |
HTML5 Video Player: How It Works in 6 Definitive Steps
An HTML5 Video Player, in regards to the overall technology stack (on the streaming service side), sits at the end of the workflow, providing audiences with playback. It’s usually the last thing you think about as it’s the final piece to the puzzle, however, whether you stream Live or On-Demand, an HTML5 video player plays (pun intended) an important role in what you do and how your audience engages with your content. Since it’s such an essential piece, let’s go through the six different layers of a player, how it fits in the technology chain and how device support, available APIs, and playback testing can help you extend your reach with better quality of experience.
1: What defines an HTML5 Video Player?
When speaking with people in the streaming industry, the way they define what a player is can vary significantly due to their experience and the initiatives of the company they are a part of. Streaming services normally take a holistic view and see the player as everything that interacts with their users, which can include UI controls, recommendations, and more. However, solution vendors or development teams tend to take the opposite approach and believe the player has many layers, with UI controls and other aspects being a part of different pieces of the player stack.
At the base of those layers, is the core framework of the player. It is an essential piece and one that can be packaged into a Software Development Kit (SDK) to make it easier for developers to integrate into the application they are working on. Along with the framework, APIs are another layer that helps integrate many different components and enable a vast amount of integrations. APIs allow applications to control the playback experience by instructing the player or listening for player events, which require decisions to be made. A few examples are:
- Play/Pause
- Seek (Scrub or jump)
- Subtitle settings
- Video timing events to determine when to insert an ad
- DRM configurations to ensure authorized users can see content
On top of those layers, there’s another that contains the UI aspects of the player, such as the buttons, menus, and options for viewers to control playback. Last but not least, an additional layer affects the business logic behind it all, which makes decisions such as:
- Allowing users to skip ads
- Select the best subtitle language for the viewer’s location
- Automatically loading the next video when the viewer finishes their current stream.
2: How an HTML5 Video Player interacts with your workflow
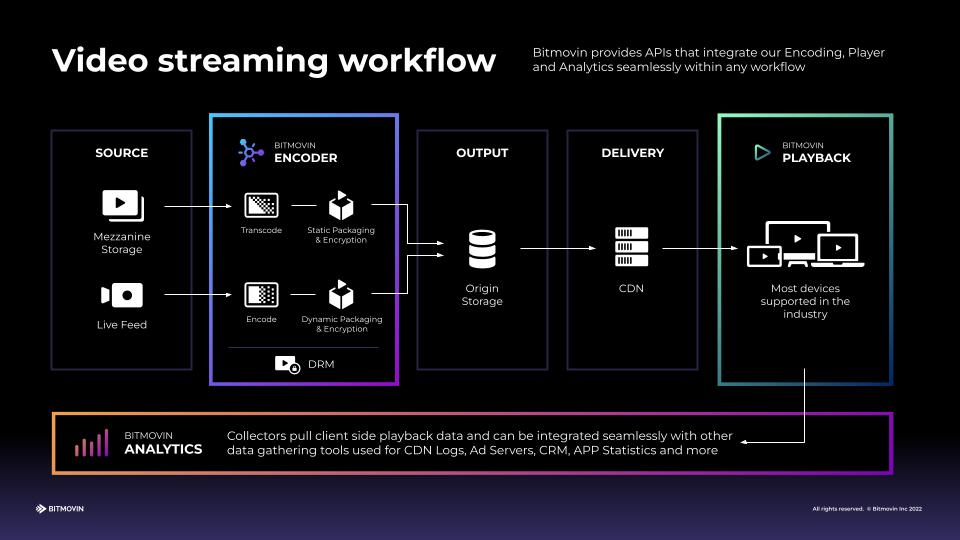
The player also plays an important role in the end-to-end workflow and even though it is the last part, all requests for content stem from it. It is affected by all of the other pieces before and after, meaning it needs to have the correct configuration settings to work along with what you’ve put together. The video viewed by users for VOD workflows will be a compressed version of the original file that is normally stored on a local or cloud storage, while live video will be ingested from the point where the stream originated from. To cut down the size of the original file for VOD, the encoder steps in to compress it, and to make sure it can meet the needs of network conditions on the viewer’s end, it can apply a bitrate ladder to it, making it available in different qualities to cover a range of viewing environments.
The packager then “packages” the encoded video into standard protocols that are supported by devices such as HLS, DASH. Content security measures, such as DRM (Digital rights management), can be applied at the packager layer to the specific protocols. Once the content is done being processed, it is then stored in the origin where the CDN will request it from and deliver it to the player on the end user’s device. Lastly, Analytics will play a crucial role in monitoring the playback experience of your viewers as it collects data and helps you identify if any issues are happening with your stream.
3: How different API factors affect the stream
Along the workflow described in the previous paragraph, APIs can and will be a big piece of each step in the streaming flow, especially when it comes to the player & device. They can be configured to manipulate the behavior parameters and allow applications to instruct the player to perform certain actions such as selecting a specific audio track or video quality. The Player APIs typically allow applications to control player functionality in:
- Core Playback (Ex. subtitles, play, pause, & buffer levels)
- Advertising (Ex. ads to play, inclusion of CT URLs, ad timing & restrictions)
- DRM (Ex. type, provider, URL & persistence)
- Network (Ex. manipulations of requests & responses)
During playback, the APIs can also be configured to send events to the applications, which helps trigger business logic that has been implemented and can base decisions on the metrics provided by the player. Events can be:
- The start or end of an ad-break
- The beginning or end of a live casting session
- Download of progress updates
- Video quality changes
- Playback errors
These events are critical for applications as it gives them the ability to apply dynamic viewing experiences to interactions made by the viewer and adapt the playback quality to meet network requirements. The ability to change qualities has to do with the stream having adaptive bitrates (ABR) available. When content is requested, the player starts by identifying the current network conditions & device/OS type so that it knows the best quality and bitrate to request content in. It will also understand the available buffer, so if there are any network interruptions, it won’t immediately affect the viewer and give the steam time to reconnect.
4: Are all features and capabilities necessary?
For all of the APIs and the features they enable, not everything is important for every workflow. The more features you add to your player, the heavier it is and that’s why
load time truly depends on the number of items your user’s device/browser needs to load up when trying to access your content. To give viewers the best experience without having to have every feature enabled, modular player structures are required.
Player modules help prioritize the features you want to enable for your viewers during their viewing experience and will directly have an impact on decreasing load time. A good example of this is DRM protection. If a stream is DRM protected, it can include a DRM module on the player but if the stream is not protected, there is no need for this module to be a part of your player. An additional item to this is that players can also offer specific modules for specific devices, such as Smart TVs. These device-specific modules help alter the behavior of the player.
5: Metrics to measure your stream
The features you’ve implemented for your player are necessary, however, one of the most important pieces is the analytics that will help you monitor the playback from your streams as mentioned above. Analytics are essential and give you the ability to optimize and grow your streaming capabilities with the data from your audience viewing your content, ultimately enabling you to offer a greater quality of experience. The data provided from the playback you’re monitoring can be measured by multiple metrics and used to create a composite score that reflects what is important to your business goals and model. For example, if you’re streaming live content, the metrics you care about will be different from a company that streams only VOD content.
To show you what the metrics might look like, some common metrics are:
- Quality of experience on the streaming session (per device) –
- Video startup time
- DRM load time
- Buffer percentage
- Playback errors
- Playback Failures
- Average bitrate
- Resolution played in
6: SDKs and Testing
Media isn’t always available or viewable on every device and to guarantee a good quality of experience for viewers, the player has to support the device it’s being streamed on. To make it easy for developers to utilize an HTML5 video player, they focus on increasing the number of devices that can stream content smoothly and boost the playback quality, through SDKs (Software Developer Kits). The SDK is essentially the player written in the programming language the developer uses allowing them to quickly integrate it into their application and is usually provided for iOS, Android, Roku, or other programming environments. These SDKs are essential, as they enable developers to support devices faster and have more time to focus on creating feature-rich applications. As these SDKs are built to make it work seamlessly with the platform, they also make it have a better, more stable end-to-end experience for viewers.
Supporting more devices is a necessity, but not always feasible as it depends on the amount of time you and your team can devote to implementing the SDKs. This is where testing becomes essential and can help save a team time as they can see how the playback of their stream is acting on devices they’d like to support next. At Bitmovin, we’ve implemented this to our system through Stream Lab, which enables anyone to test active streams on actual devices to see how the stream functions in a real streaming environment. It’s our latest update and one that will help empower developers to have an easier time deciding which SDKs they would like to implement next.The big picture
From this blog, I hope you’ve come away with some good pointers. I hope you now have a clear picture of what goes into an HTML5 video player and why it is one of the most important pieces of your workflow. APIs will essentially be your best friend in implementing the viewing experience you want to offer, the metrics you want to track, and the devices you’d like to support. Even though each part of your streaming workflow is important, the player is what connects you to your user and can ultimately play a big part in avoiding churn.