Working with JAR and Manifest files In Java
Whenever a developer wants to distribute a version of his software, then all he want is to distribute a single file and not a directory structure filled with class files. JAR files were designed for this purpose. A JAR file can contain both class files and other file types like sound and image files which may be included in the project. All the files in a JAR file are compressed using a format similar to zip.
Creating a JAR file – more Options
A jar file is created using jar tool. The general command looks somewhat like this:
jar options jar-file [manifest-file] file1 file2 file3 .
- jar – file : name of jar file on which you want to use jar tool.
- file1, file2, file3 : files which you want to add inside a jar file. manifest-file is the name of file which contains manifest of that jar file, giving manifest-file as an argument is entirely optional.
- c : Creates a new or empty archive and adds files to it. If any of the specified file name are directories, then the jar program processes them recursively.
- C : Temporarily changes the directory.
- e : Creates an entry point in the manifest.
- f : Specifies the JAR file name as the second command-line argument. If this parameter is missing, jar will write the result to standard output (when creating a JAR file)or read it from standard input(when extracting or tabulating a JAR file).
- i : Creates an index file.
- m : Adds a manifest file to the JAR file. A manifest is a description of the archive contents and origin. Every archive has a default manifest, but you can supply your own if you want to authenticate the contents of the archive.
- M : Does not create a manifest file for the entries.
- t : Displays the table of contents.
- u : Updates an existing JAR file.
- v : Generates verbose output.
- x : Extract files. If you supply one or more file names, only those files are extracted Otherwise, all files are extracted.
- 0 : Stores without zip compression.
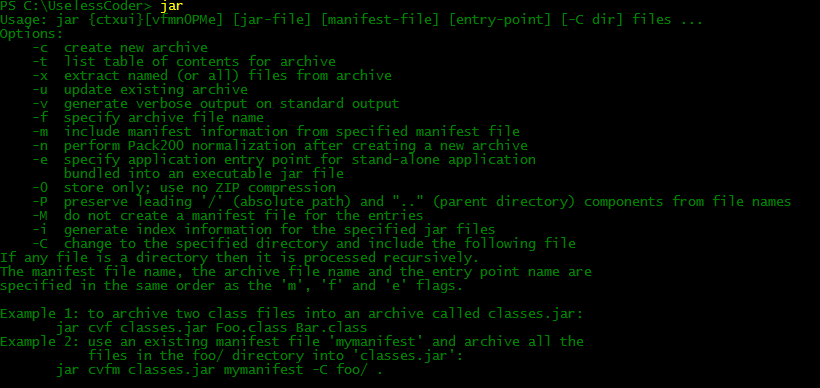
The options of jar command are almost similar to that of UNIX tar command. In windows you can also get help about various options of jar command just by typing jar in cmd and then pressing enter, the output will be somewhat similar to this:
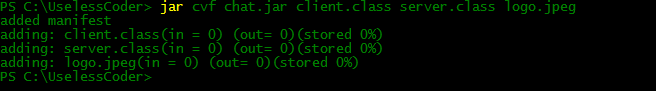
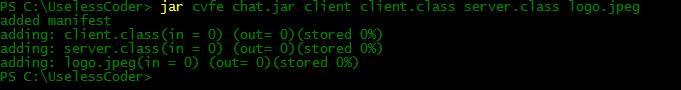
For creating a JAR file which have two classes server.class and client.class and a Jpeg image logo.jpeg, one need to write following command :
jar cvf chat.jar server.class client.class logo.jpeg
The output of above command will be somewhat like this:
It’s a better practice to use -v option along with jar command as you will get to know how the things are going on.
Manifest File
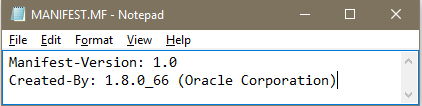
Each JAR file contains a manifest file that describe the features of the archive. Each JAR file have a manifest file by default. Default manifest file is named as MANIFEST.MF and is present in the META-INF subdirectory of archive. Although the default manifest file contains just two entries, but complex manifest files can have way more. Here, is what a default manifest file looks like –
The entries of manifest files are grouped into sections. Each section have two entries section name and its value. We will see a bit later how these sections can really help us in controlling the properties of our archive. Manifest file can also be updated by using the m option of jar command. But there are certain things which need to kept in mind while updating manifest file otherwise you may get the following creepy message.
java.io.IOException: invalid manifest format
Things to keep in mind while handling Manifest files:
- You should leave space between the name and value of any section in manifest file, like Version:1.1 is in valid section instead write Version: 1.1 that space between colon and 1.1 really matters a lot.
- While specifying the main class you should not add .class extension at the end of class name. Simply specify the main class by typing:
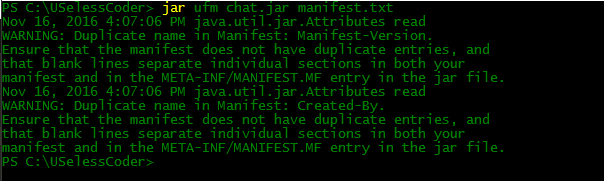
Now let’s come back and update the contents of our chat.jar archive. To update the manifest file we simply need to write the following command:
jar uvfm chat.jar manifest.txt
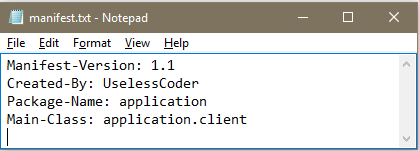
Here manifest.txt is the new manifest file, which has following contents:
The output of above command will be somewhat like this:
Here we are getting two warnings because we are trying to overwrite to previously present entries.
Executable Jar Files
You can use the e option of jar command to specify the entry point of your program, ie. class which you normally want to invoke when launching your Java application.
To create chat.jar file having client class as main class you need to write following command –
jar cvfe chat.jar client client.class server.class logo.jpeg
The output of above command will be somewhat like this:
Remember not to add .class extension after the name of class which you want to set main class.
Alternatively you can add a Main-Class entry in the manifest file and then update it. For the above example you just need to add this entry:
With main class being set one can simply run a jar program by writing following command –
Depending on operating system configuration, users may even be able to launch application by double clicking the JAR file icon.
Package Sealing
Finally, we are going to discuss about package sealing in Java. We can seal a package in Java to ensure that no further classes can add themselves to it. You may want to seal a package if you use a package visible classes, methods and fields in your code. Without package sealing, other classes can add themselves to the same package and thereby gain access to package visible features.
- To achieve package sealing all one need to do is to put all classes of that package into a JAR file.
- By default the packages in a jar file are not sealed but one can change the global default by adding few lines in manifest file.
- Let’s again consider the case of our chat.jar archive, now the package of classes client.class and server.class is application and we want to seal this package all we need to do is to add following line in the manifest file and update it.
Name: application Sealed: true
This is all from my side on how to work with JAR files. Stay Tuned!!
This article is contributed by Abhey Rana(UselessCoder). If you like GeeksforGeeks and would like to contribute, you can also write an article using contribute.geeksforgeeks.org or mail your article to contribute@geeksforgeeks.org. See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks main page and help other Geeks.
Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.
How to Work With a JAR Manifest File in Java
Developer.com content and product recommendations are editorially independent. We may make money when you click on links to our partners. Learn More.
In the Java programming language, a manifest file is a text file that contains metadata related to files contained in a programmer’s JAR archive. This metadata can range from information relating to package information to attributes of security properties.
A program can only have one manifest file in its JAR archive, so it is important for developers to understand how to work with these manifest files and how to use them properly. In this Java tutorial, you will learn how to work with a JAR manifest file in your Java applications.
Default Manifest Files in Java
When you create a JAR file, a default manifest file is also created with it. This file initially contains two fields relating to the manifest version and the JDK version. For example, here is a typical manifest file’s contents:
Manifest-Version: 1.0 Created-By: 11.0.3 (Oracle Corporation)
The default manifest is always located in the path META-INF/MANIFEST.MF of your JAR file.
How to Modify a Manifest File in Java
Developers can either modify a manifest file manually or by using the m option at the creation of a JAR file. Manually modifying the file means directly adding entries to it.
As you may have noticed from the previous section, JAR files contain header:value pairs. You can also add an entry for your desired header:value pair. However, it is important to note that, after the last entry, programmers should add a new line character. Otherwise, the last entry will not be parsed properly.
Alternatively, coders can also use the m option to modify JAR manifest files, as shown below:
jar cfm ArchiveName.jar add-to-manifest.txt files-to-include
The m option specifies that you intend to merge certain information from a text file (such as add-to-manifest.txt) to your existing JAR manifest file.
It is important for developers to note that the order in which the f and m options appear should match that of their respective arguments. You also need to ensure that your text file ends with a new line character.
The next two sections describe some particular use cases that you can apply with your JAR file.
JAR Files and Java Application Packaging
JAR files are sometimes used to package Java applications. When you decide to run an application in a JAR file, programmers need to specify the entry point to use. An entry point is the class in which your main() method is defined. To define your application’s entry point, use the Main-Class header.
For example, if your entry point is ClassName in the package PackageName, then you should include the following entry in your manifest file:
Main-Class: PackageName.ClassName
To run the application in your JAR archive, you can now use the command below:
You can also set the entry point for your application using the e option of your JAR tool. It is important to note that this option overrides the Main-Class header in your manifest file.
The Java code example below creates an archive named ArchiveName.jar with the entry point set to MyClass.class:
jar cfe ArchiveName.jar * MyClass.class
You can also use the e option when updating your JAR archive. If your entry point is in a directory (say MyDirectory), then you can use the forward-slash ‘/’ when specifying it in the command line:
jar cfe ArchiveName.jar * MyDirectory/MyClass.class
How to Add Classes to JAR Classpath
When packaging your applications, programmers may place different classes in several jar files. A good example here would be if an applet packaged in a JAR archive has dependencies packaged in different JAR archives.
To ensure that classes in another JAR archive are loaded into your JAR file when you run it, you need to add their classpath in your calling JAR file.
Simply do this by setting the path in the Class-Path header in your manifest file. For example, if the JAR file to be loaded is in the same directory as your calling JAR file, you could use the following:
Class-Path: Other-JAR-File.jar
Final Thoughts on Java Manifest Files
A manifest file allows developers to describe information relating to files in their JAR archive. As previously mentioned, always remember to end the modifying text file of your JAR file with a new line character.