- JDK in Java
- The Java Development Kit is an implementation of one of the Java Platform:
- Contents of JDK
- Most Popular JDKs:
- Set-Up:
- Compile and Run Java Code using JDK:
- Java
- The Jar component:
- Important Components of JDK
- Переменная окружения JAVA_HOME
- Что такое JAVA_HOME
- Какие программы используют JAVA_HOME
- Ошибки, связанные с JAVA_HOME
- Как установить переменную окружения JAVA_HOME в Windows
- Резюме
- How to Set JAVA_HOME Linux
- Prerequisites
- JDK vs. JRE
- Environment variables
- JAVA_HOME
- Setting up JAVA_HOME
- Setting JAVA_HOME globally
- Final thoughts
- About the author
- Sidratul Muntaha
JDK in Java
The Java Development Kit (JDK) is a cross-platformed software development environment that offers a collection of tools and libraries necessary for developing Java-based software applications and applets. It is a core package used in Java, along with the JVM (Java Virtual Machine) and the JRE (Java Runtime Environment).
Beginners often get confused with JRE and JDK, if you are only interested in running Java programs on your machine then you can easily do it using Java Runtime Environment. However, if you would like to develop a Java-based software application then along with JRE you may need some additional necessary tools, which is called JDK.
JDK=JRE+Development Tools
The Java Development Kit is an implementation of one of the Java Platform:
Contents of JDK
The JDK has a private Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and a few other resources necessary for the development of a Java Application.
JDK contains:
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE),
- An interpreter/loader (Java),
- A compiler (javac),
- An archiver (jar) and many more.
The Java Runtime Environment in JDK is usually called Private Runtime because it is separated from the regular JRE and has extra content. The Private Runtime in JDK contains a JVM and all the class libraries present in the production environment, as well as additional libraries useful to developers, e.g, internationalization libraries and the IDL libraries.
Most Popular JDKs:
- Oracle JDK: the most popular JDK and the main distributor of Java11,
- OpenJDK: Ready for use: JDK 15, JDK 14, and JMC,
- Azul Systems Zing: efficient and low latency JDK for Linux os,
- Azul Systems: based Zulu brand for Linux, Windows, Mac OS X,
- IBM J9 JDK: for AIX, Linux, Windows, and many other OS,
- Amazon Corretto: the newest option with the no-cost build of OpenJDK and long-term support.
Set-Up:
Setting up JDK in your development environment is super easy, just follow the below simple steps.
Installation of JDK
- Go to this Oracle’s official Download Page through this link
- Select the latest JDK version and click Download and add it to your classpath.
- Just check the JDK software is installed or not on your computer at the correct location, for example, at C:\Program Files\Java\jdk11.0.9.
Set JAVA_HOME for Windows:
- Right-click My Computer and select Properties.
- Go to the Advanced tab and select Environment Variables, and then edit JAVA_HOME to point to the exact location where your JDK software is stored, for example, C:\Program Files\Java\jdk11.0.9 is the default location in windows.
Java maintains backward compatibility, so don’t worry just download the latest release and you will get all the old and many new features. After Installing the JDK and JRE adds the java command to your command line. You can verify this through the command prompt by the java -version command. In some cases, you need to restart your system after installing the JDK.
Compile and Run Java Code using JDK:
You can use the JDK compiler to convert your Java text file into an executable program. Your Java text segment is converted into bytecode after compilation which carries the .class extension.
First, create a Java text file and save it using a name. Here we are saving the file as Hello.java.
Java
After that just simply use the javac command, which is used for the compilation purpose in Java. Please don’t forget to provide the full path of your java text file to the command line else you will get an error as “The system cannot find the path specified”,
Your command should be similar to the given below example where Hello is the file name and the full path to the file is specified before the file name. The path and javac.exe should be inside the quotes.
“C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-11.0.9\bin\javac.exe” Hello.java
You can notice now that the Hello.class file is being created in the same directory as Hello.java. Now you can run your code by simply using the java Hello command, which will give you the desired result according to your code. Please remember that you don’t have to include the .class to run your code.
C:\Users\Pinaki\Documents>java hello_world
(Output:) Hello Geek!
The Jar component:
JDK contains many useful tools and among them, the most popular after javac is the jar tool. The jar file is nothing but a full pack of Java classes. After creating the .class files, you can put them together in a .jar, which compresses and structures them in a predictable fashion. Now, let’s convert our Hello.class to a jar file.
Before proceeding, please note that you should be in the same directory where the Hello.java file was saved. Now type the command given below in the command line.
Creating a .jar file
C:\Users\Pinaki\Documents>”c:\Program Files\Java\jdk-11.0.9\bin\jar.exe” –create –file Hello.jar Hello.class
Now you can notice that Hello.jar file had been created in the same directory using Hello.class file and jar.exe. You can use the jar file by adding it to your classpath and executing the program inside it. Here the -cp stands for classpath which helps to add the jar to the same classpath.
Executing the .jar file
java -cp hello_world.jar hello_world
Important Components of JDK
Below there is a comprehensive list of mostly used components of Jdk which are very useful during the development of a java application.
Переменная окружения JAVA_HOME
Во многих статьях в интернете, документации к инструментам для разработки на Java и в книгах зачастую упоминается JAVA_HOME. Что же такое JAVA_HOME?
Что такое JAVA_HOME
JAVA_HOME это переменная окружения, указывающая на директорию с установленным JDK (Java Development Kit, комплект разработчика Java). JAVA_HOME это соглашение, используемое во многих программах из экосистемы Java.
Какие программы используют JAVA_HOME
- Intellij IDEA, Eclipse, NetBeans
- Apache Maven, Apache Ant, Gradle
- Apache Tomcat
- Jenkins
Некоторые игры, написанные на Java (например, Minecraft), тоже могут требовать установленной переменной JAVA_HOME.
Ошибки, связанные с JAVA_HOME
Если переменная окружения JAVA_HOME не определена, некоторые программы могут выдавать следующие ошибки:
- Переменная среды java_home не определена
- Cannot determine a valid Java Home
- JAVA_HOME is set to an invalid directory
- JAVA_HOME is not defined correctly
- JAVA_HOME environment variable is not set
- JAVA_HOME command not found
- JAVA_HOME not found in your environment
- JAVA_HOME does not point to the JDK
При появлении таких ошибок просто установите переменную JAVA_HOME
Как установить переменную окружения JAVA_HOME в Windows
Сперва вам нужно установить JDK или JRE.
- Установите JDK, если вы занимаетесь разработкой программ на Java
- Установите JRE, если вам нужно только запустить прикладную программу на Java
После установки JDK либо JRE запишите путь установки, он понадобится.
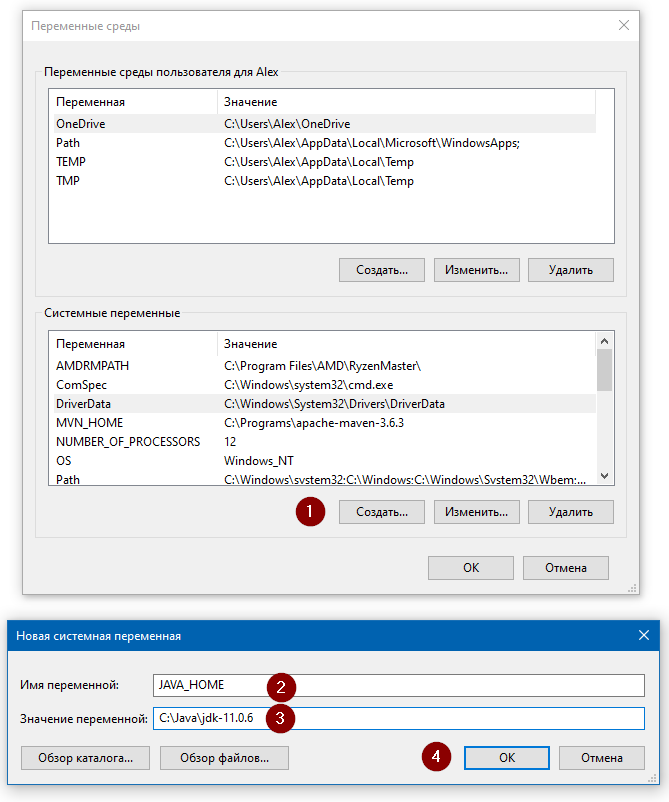
Теперь щёлкните правой кнопкой на «Мой компьютер» → «Свойства» → «Дополнительные параметры системы» → «Переменные среды…». В разделе «Системные переменные» нажмите кнопку «Создать…» и укажите следующие данные:
| Имя переменной | JAVA_HOME |
| Значение переменной | Путь к директории JDK / JRE, например: C:\Java\jdk-11.0.6 |
Сохраните изменения, кликнув «OK». Теперь выберите в списке переменную окружения Path и нажмите «Изменить…». В конце списка добавьте строчку со значением «%JAVA_HOME%\bin«
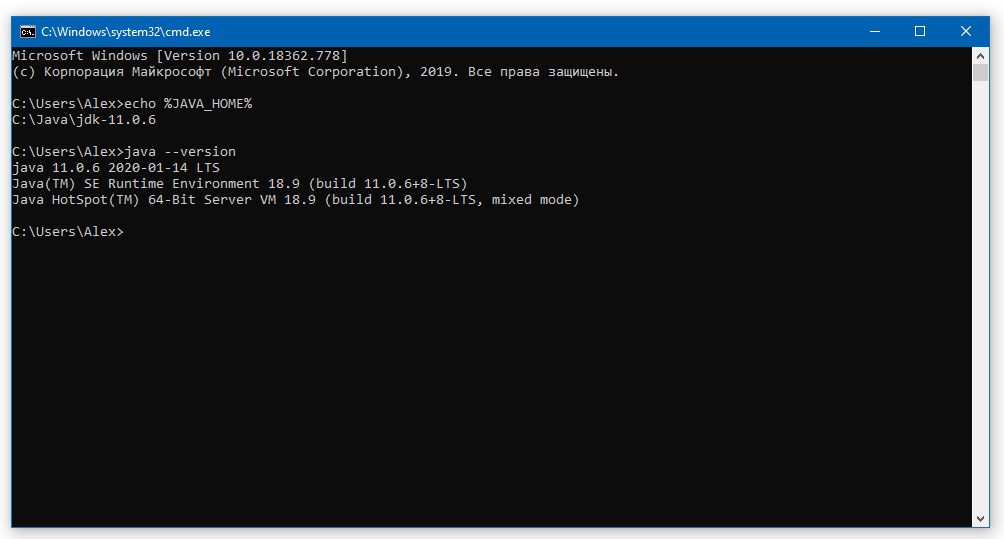
Для проверки откройте консоль (Win+R, cmd) и укажите последовательно укажите две команды:
Если вы правильно установили JDK/JRE и правильно установили переменные окружения, вы увидите вывод наподобие этого:
Это будет служить результатом того, что переменная JAVA_HOME установлена правильно и Java работает из командной строки.
Резюме
В данной статье мы рассказали вам, что являет собой переменная окружения JAVA_HOME, где она используется и как её корректно указать.
How to Set JAVA_HOME Linux
Java is one of the most influential and popular programming languages. Originally released by Sun Microsystems in 1995, Java is a cross-platform language that is now a part of almost every aspect of technology. You will find Java everywhere – banking, financial services, big data, stock market, mobile (Android), and more. It easily ranks among the top programming languages and is likely to remain so for at least a decade.
In this guide, we’ll showcase one of the basic and crucial steps of configuring Java on your system – setting up the JAVA_HOME environment variable in Linux.
Prerequisites
Before diving deeper, let’s quickly refresh on various concepts and keywords.
JDK vs. JRE
If you’re interested in Java, you are probably already familiar with them. JDK stands for “Java Development Kit.” It contains the necessary tools and libraries to build and run (using JRE) Java apps. If you’re interested in learning or working on a Java project, JDK is the option to choose.
JRE stands for “Java Runtime Environment.” This package contains the tools and libraries needed to run a Java application. It’s a must-have to run any Java program on the system.
Note that JDK comes bundled with JRE by default. So, you don’t have to install JRE separately if you already have JDK installed.
Environment variables
In Linux, environment variables hold various system info available to apps. The info can be about how apps run on the environment, different system behaviors, etc.
Depending on the accessibility of the variables, we can divide them into 2 categories.
- Local environment variables: These variables are set on a per-user basis. Only the specific user can use them in their sessions.
- Global environment variables: These variables are accessible by everyone on the system.
JAVA_HOME
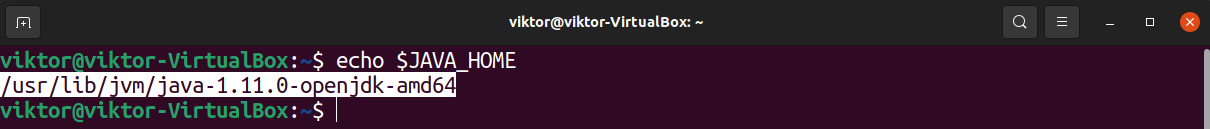
The JAVA_HOME is an environment variable. It holds the location of the Java binaries. Many applications rely on this environment variable to locate the Java binaries and libraries.
It can be set both on a local or global basis.
Setting up JAVA_HOME
Now that we understand what JAVA_HOME is, it’s time to learn how to set its value.
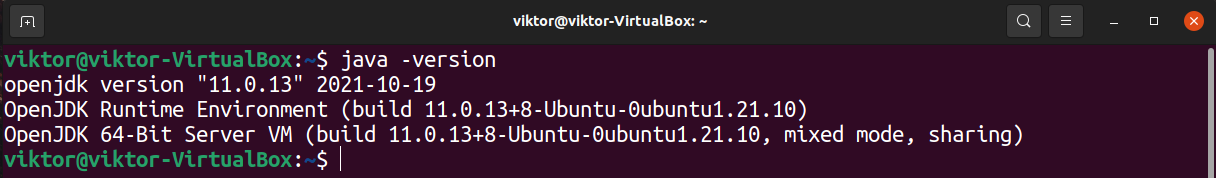
First, figure out the version of Java installed. This version number is often linked to the Java binary path.
If Java was installed globally, then the installation is likely stored at the following location.
This directory contains the Java binaries and libraries. Check the content of the directory.
In my case, I have OpenJDK 11 installed on Ubuntu (more on installing the latest Java on Ubuntu). From the output, we can see entries like “default-java” and “java-1.11.0-openjdk-amd64” are symlinks of “java-11-openjdk-amd64”.
We’re going to set the value of JAVA_HOME to java-1.11.0-openjdk-amd64 (recommended).
Note that this environment variable will only last for the current shell session. Once restarted, you have to set the value once again manually. To solve this issue, most shells come with a configuration file that contains codes and commands the shell must run whenever it launches. In the case of bash, it’s called bashrc (for zsh, it’s zshrc, etc.).
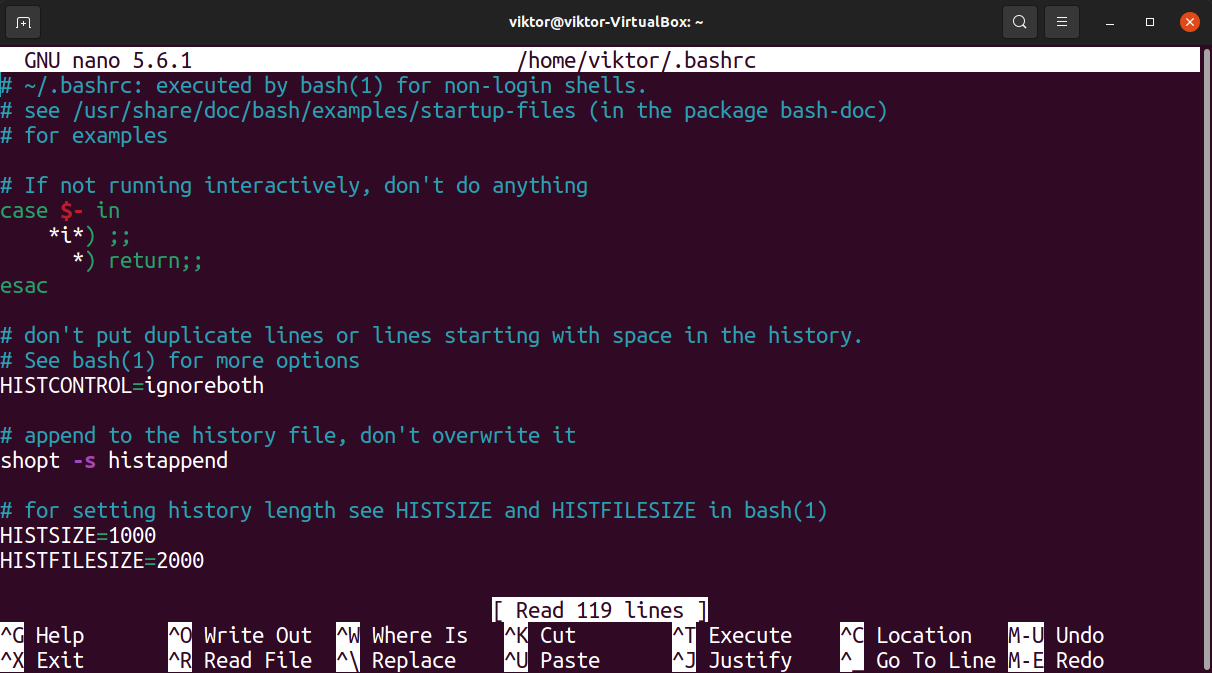
Open the file in a text editor.
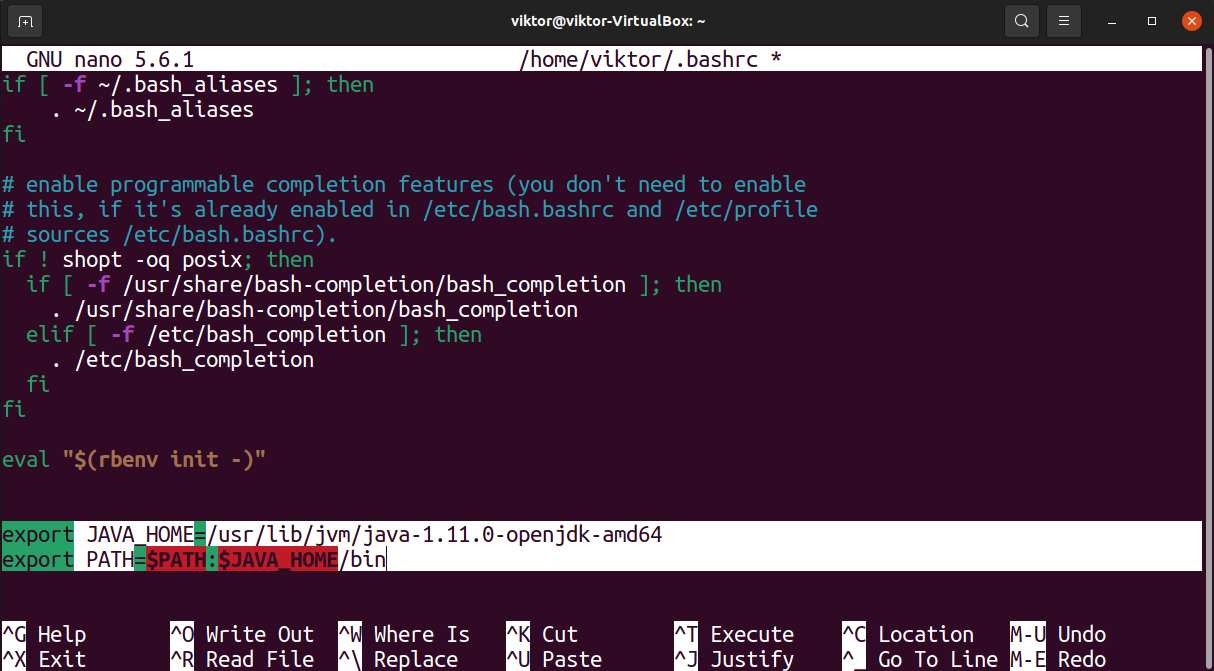
Now, add the following line at the end of the file. It will mark the environment variable accessible to all shell sessions and the binaries available directly from the PATH variable.
$ export JAVA_HOME =/ usr / lib / jvm / java — 1.11.0 — openjdk — amd64
$ export PATH = $PATH : $JAVA_HOME / bin
Save the file and close the editor. To take the changes into effect, reload the bashrc file.
Setting JAVA_HOME globally
The previous section demonstrates setting up JAVA_HOME on a single user account. It’s a good practice because each user may prefer different configurations. Some may even use a completely different Java version or Java flavor.
Bash comes with a global bashrc file that every shell session in the system must load, irrespective of the user. By declaring the location of JAVA_HOME there, we can make it available for all users in the system. Note that it’s not recommended and should be used only in specific situations.
Open up the global bashrc file in a text editor. Note that it requires sudo privilege to tweak this file.
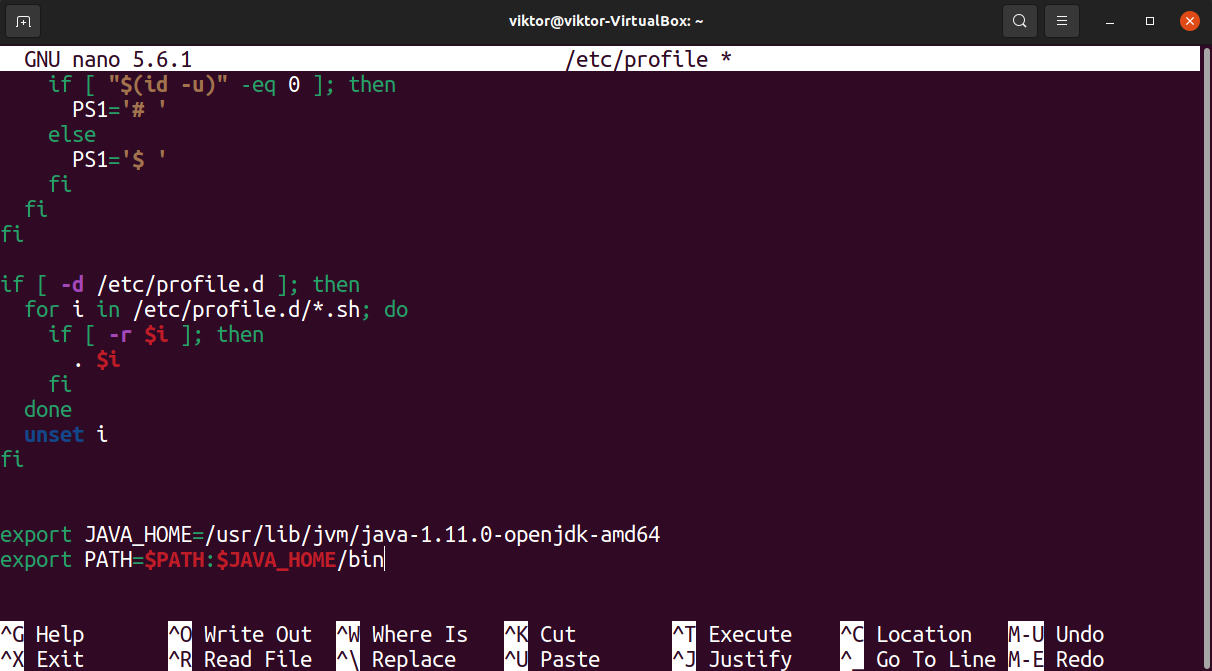
Now, update the values of JAVA_HOME and PATH.
$ export JAVA_HOME =/ usr / lib / jvm / java — 1.11.0 — openjdk — amd64
$ export PATH = $PATH : $JAVA_HOME / bin
Save the file and close the editor. Reload the file into the bash shell to take the changes into effect.
Final thoughts
In this guide, we’ve explored various concepts like environment variables and demonstrated how to set JAVA_HOME as a local or global environment variable. Numerous development apps like NetBeans, Eclipse, Maven, ANT, Apache Tomcat, Android Studio, and more depend on JAVA_HOME to function properly.
Note that if the variable was set globally, then the location must be accessible to all users in the system. Otherwise, it will cause many issues, leading to severe headaches. To solve file permission conflicts, Linux comes with a built-in tool: chown. Learn more about chown and how to use it.
About the author
Sidratul Muntaha
Student of CSE. I love Linux and playing with tech and gadgets. I use both Ubuntu and Linux Mint.