- HTML Form Validation
- HTML Form Validation
- 1. Using HTML5 built-in functionality
- 2. Using JavaScript
- Conclusion- HTML Form Validation
- Recommended Articles
- Data Validation – How to Check User Input on HTML Forms with Example JavaScript Code
- What are the different types of form validations?
- What data should be validated?
- How to set up client side validation
- How to set up validation with HTML5 functionality
- How to set up validation using JavaScript
- Inline validation using JavaScript
- HTML5 Constraint validation API
- Don’t forget server side validation
- Form Validation best practices
HTML Form Validation
HTML form validation is a process of examining the HTML form page’s contents to avoid errored-out data being sent to the server. This process is a significant step in developing HTML-based web applications, as it can easily improve the quality of the web page or the web application. There are two ways to perform the HTML form Validation, and they are by Using HTML5 built-in functionality and by Using JavaScript.
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
HTML Form Validation
There are mainly two ways by which HTML form validation can be performed,
1. Using HTML5 built-in functionality
HTML5 provides this feature of form validation without using JavaScript. Form elements will have validation attributes added, which will enable the form validation for us automatically. Validation attributes allow us to specify various kinds of rules on our form elements. They allow us to set the length of the data, set a restriction on the values of the data, etc.
Let’s see one simple example of HTML form validation using built-in form validating elements and will then proceed further for HTML form validation using JavaScript.
Form Validation using HTML5 validation attribute – In this example, we will use the form validation tag required, which will cause data in that field to be mandatory to be entered; otherwise, the form will not be submitted. Below is the code snippet for the same, along with some styling of a web form.
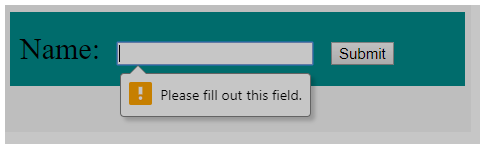
.formData < padding-top: 20px; padding-bottom: 20px; padding-left: 10px; background-color: darkcyan; >form < font-size: 30px; >form input Name: So we have a very simple web form along with only one input data field as “Name”. Please note that we have used the required keyword in the input tag element.
Let’s try to submit the form without entering any value in the name field. Upon submitting, you will get the error message as “Please fill out this field”, and the form will not be submitted.
Output with blank data:
So it can be seen that the error message is not added by us and is provided by HTML itself.
Like the required attribute provided by HTML, there are various form tags available to use. Below is the list of some form validation tags,
- minlength: Used to set the required minimum length of an element
- maxlength: Used to set the required maximum length of an element
- pattern: Used to define a regular expression
2. Using JavaScript
JavaScript is used widely for HTML form validation as it provides more ways to customize and set the validation rules; also, some of the tags provided in HTML5 are not supported in the older versions of Internet Explorer. JavaScript is being used for a long time for form validation.
In JavaScript form validation, basically, we define functions to validate the data before submitting it to the server. We can implement any logic required for achieving the validation rules. JavaScript is more flexible in this way because there is no restriction on defining rules. But it is necessary to know JavaScript to implement this compared to form validation using built-in tags.
Let’s see the example of form validation using JavaScript. We will implement the same example of the form with only one input as the name element.
.formData < padding-top: 20px; padding-bottom: 20px; padding-left: 10px; background-color: darkcyan; position: absolute; width: 100%; >form < font-size: 30px; >form input < margin-left: 10px; font-size: 15px; >.errorMessage < background-color: white; width: 143px; padding-left: 10px; padding-right: 10px; padding-top: 5px; padding-bottom: 5px; margin-left: 107px; visibility: hidden; border-radius: 10px; position: relative; float: left; >.errorMessage.top-arrow:after Name: From the previous example, we have removed the required tag from the form element “name”. Instead, we have added one tag onsubmit in the form element. As mentioned before, we will be writing a function for validation for which the tag is added.
We have written a function named validateForm() which will do the validation. We are implementing the same rule of checking whether the entered data in the name field is blank or not. The logic to check this is upon a click of the submit button, this function will be called, and the entered value will be checked whether it is null or either blank. The function will return true in case of data is not null or blank, but if the data is blank or null, then the error message is displayed to the user.
If we try to submit the form without entering any data, we should get the error message on the screen. As can be seen from the example, we have designed the error message in the same way possible.
Output with blank data:
Conclusion- HTML Form Validation
So we have seen a very simple example of form validation at the client side. Mainly there are two ways to perform HTML form validation. The first is using the built-in functionality provided in HTML5, and the second is by using JavaScript. Using the first method, we don’t need to write extra code.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to HTML Form Validation. Here we discuss the overview and two ways of HTML Form Validation by which they can be performed. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –
89+ Hours of HD Videos
13 Courses
3 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
97+ Hours of HD Videos
15 Courses
12 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
HTML & CSS Course Bundle — 33 Courses in 1 | 9 Mock Tests
125+ Hours of HD Videos
33 Courses
9 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
Data Validation – How to Check User Input on HTML Forms with Example JavaScript Code
Shruti Kapoor
Forms are ubiquitous in web applications. Some apps use forms to collect data to sign up users and provide an email address. Others use them to fulfill online transactions to facilitate a shopping experience.
You might use some web forms to apply for a new car loan, whereas you’ll use others to order pizza for dinner. So it’s important that the data collected from those forms is cleaned, formatted correctly, and devoid of any malicious code. This process is called form validation.
We need form validation anytime we are accepting user input. We must ensure that the data entered is in the correct format, lies within a valid range of data (such as for date fields), and does not contain malicious code that could lead to SQL injections. Malformed or missing data can also cause the API to throw errors.
What are the different types of form validations?
Form validation can happen on the client side and the server side.
Client side validation occurs using HTML5 attributes and client side JavaScript.
You may have noticed that in some forms, as soon as you enter an invalid email address, the form gives an error «Please enter a valid email». This immediate type of validation is usually done via client side JavaScript.
In other cases, you may have noticed that when you fill out a form and enter details such as a credit card, it may show a loading screen and then show an error «This credit card is invalid».
Here, the form made a call to its server side code, and returned a validation error after performing additional credit card checks. This validation case where a server-side call is made is called server side validation.
What data should be validated?
Form validation is needed anytime you accept data from a user. This may include:
- Validating the format of fields such as email address, phone number, zip code, name, password.
- Validating mandatory fields
- Checking the type of data such as string vs number for fields such as social security number.
- Ensuring that the value entered is a valid value such as country, date, and so on.
How to set up client side validation
On the client side, validation can be done in two ways:
How to set up validation with HTML5 functionality
HTML5 provides a bunch of attributes to help validate data. Here are some common validation cases:
Link to JSFiddle Here we have two required fields — First Name and Last Name. Try this example in JSFidle. If you skip either of these fields and press submit, you’ll get a message, «Please fill out this field». This is validation using in-built HTML5.
How to set up validation using JavaScript
- What is defined as «valid» data? This helps you answer questions about the format, length, required fields, and type of data.
- What happens when invalid data is entered? This will help you define the user experience of the validation — whether to show an error message inline or at the top of the form, how detailed should the error message be, should the form be sumitted anyways, should there be analytics to track invalid format of data? And so on.
You can perform JavaScript validation in two ways:
Inline validation using JavaScript
const submit = document.getElementById("submit"); submit.addEventListener("click", validate); function validate(e) < e.preventDefault(); const firstNameField = document.getElementById("firstname"); let valid = true; if (!firstNameField.value) < const nameError = document.getElementById("nameError"); nameError.classList.add("visible"); firstNameField.classList.add("invalid"); nameError.setAttribute("aria-hidden", false); nameError.setAttribute("aria-invalid", true); >return valid; > #nameError < display: none; font-size: 0.8em; >#nameError.visible < display: block; >input.invalid
In this example, we check for required fields using JavaScript. If a required field is not present, we use CSS to show the error message.
Aria labels are modified accordingly to signal an error. By using CSS to show / hide an error, we are reducing the number of DOM manipulations we need to make. The error message is provided in-context thereby making the user experience intuitive.
HTML5 Constraint validation API
The required and pattern HTML attributes can help perform basic validation. But if you want more complex validation or want to provide detailed error messaging, you can use the Constraint Validation API.
Some methods provided by this API are:
The following properties are useful:
In this example, we will validate using HTML5 inbuilt methods such as required and length in conjunction with the Constraint Validation API to provide detailed error messages.
const nameField = document.querySelector("input"); nameField.addEventListener("input", () => < nameField.setCustomValidity(""); nameField.checkValidity(); console.log(nameField.checkValidity()); >); nameField.addEventListener("invalid", () => < nameField.setCustomValidity("Please fill in your First Name."); >); Don’t forget server side validation
Client side validation is not the only validation check you should do. You must also validate the data received from your client on the server side code to ensure that the data matches what you expect it to be.
You can also use server-side validation to perform business logic verifications that should not live on the client side.
Form Validation best practices
- Always have server side validation, since malicious actors can bypass client side validation.
- Provide detailed error messages in-context with the field that produced the error.
- Provide an example of what the data should look like in case of an error message, such as — «Email did not match format — test@example.com»
- Avoid using single error pages that involve redirection. This is bad user experience and forces the user to go back to a previous page to fix the form and lose context.
- Always mark required fields.