- Выравнивание содержимого тегов
- text-align
- Try it
- Syntax
- Values
- Accessibility concerns
- Formal definition
- Formal syntax
- Examples
- Start alignment
- HTML
- CSS
- CSS Text Align – Centered, Justified, Right Aligned Text Style Example
- Table of Contents
- Basic Syntax
- Values of the text-align Property
- The left Value
- The center Value
- The right Value
- The justify Value
- The inherit Value
- Conclusion
Выравнивание содержимого тегов
Как я и обещал ранее, в этом уроке вы узнаете как можно выровнять по горизонтали содержимое любого HTML-тега на странице не используя устаревший атрибут align . Как вы возможно уже догадались, мы опять будем использовать стили (CSS), а точнее наш любимый атрибут style .
Итак, чтобы выровнять содержимое HTML-элемента, необходимо атрибуту style присвоить одно из следующих значений:
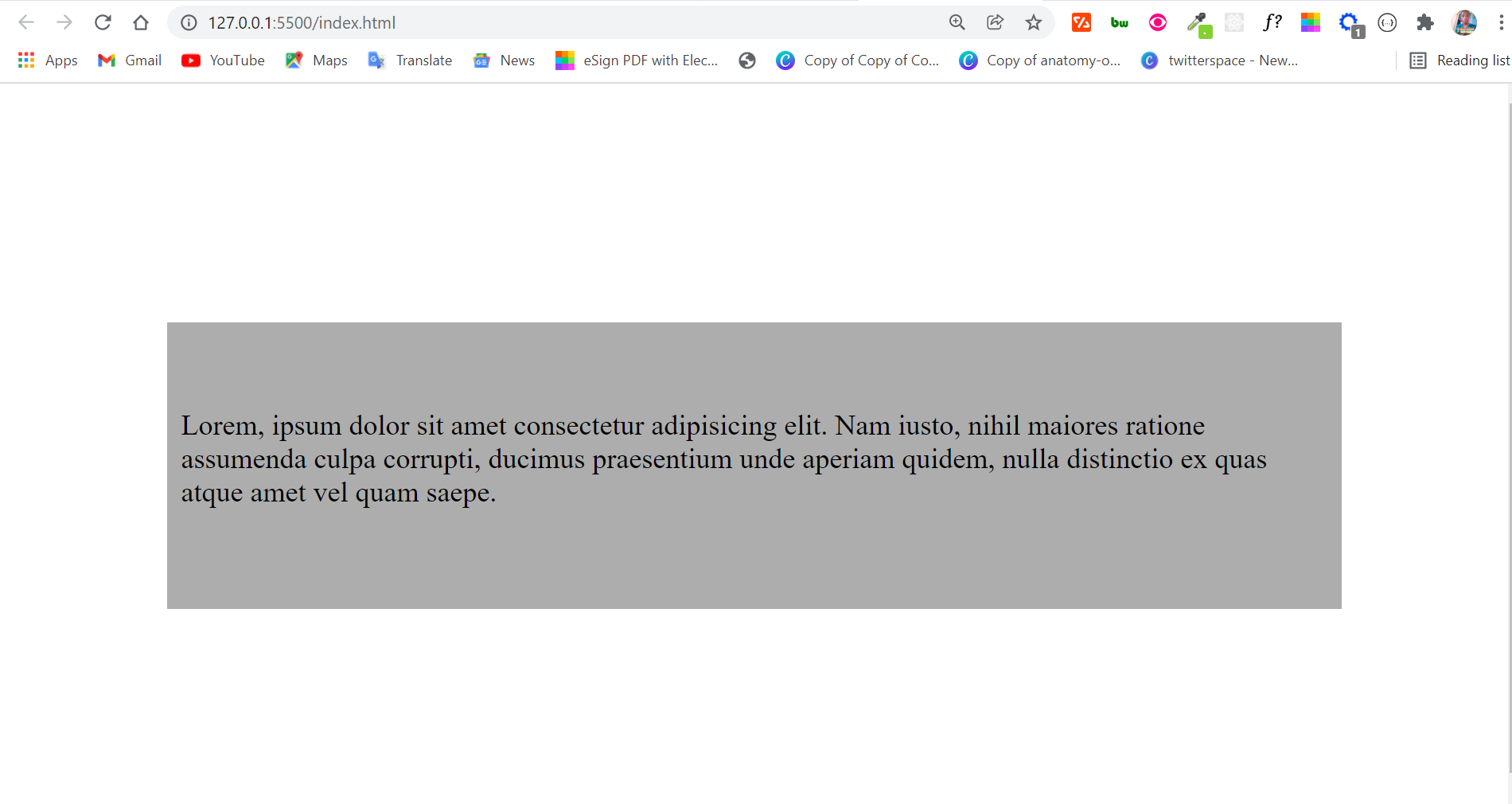
- text-align:center — Выравнивание каждой строки по центру элемента, например параграфа.
- text-align:left — Каждая строка вплотную прижимается к левой стороне элемента (это значение по умолчанию).
- text-align:right — Каждая строка прижимается к правой стороне.
- text-align:justify — Выравнивание сразу по левой и правой сторонам элемента. Объясню. Обычно у элемента, например параграфа, одна сторона текста всегда ровная, а другая — «рваная», так как длины строк получаются немного разными. А когда мы используем значение text-align:justify , то каждая строка равномерно распределяется по ширине. В случае необходимости между словами браузер добавляет дополнительные пробелы, а первое и последнее слово строки всегда прижаты к соответствующим сторонам, поэтому получается ровный с обеих сторон блок.
Пример выравнивания содержимого тегов
Заголовок по центру.
Текст параграфа прижимается вправо.
Параграф по центру.
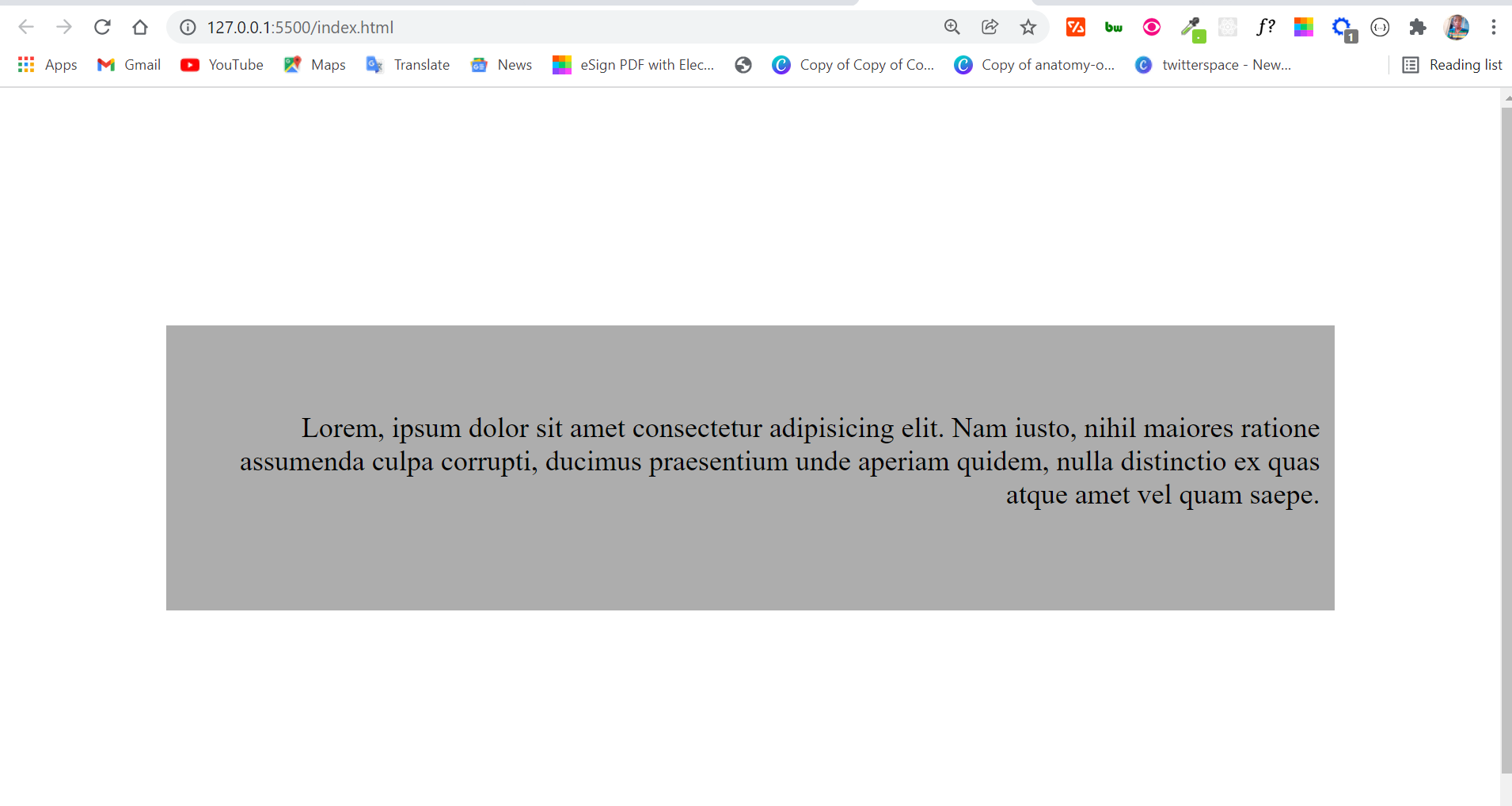
Заголовок по центру.
Текст параграфа прижимается вправо.
Вообще, горизонтальное выравнивание применяется только к блочным тегам и ячейкам таблицы (о них поговорим позже). Хотя, с другой стороны, даже если вы попытаетесь, то не сможете применить его к встроенным (inline). Почему? А помните мы недавно выяснили, что ширина встроенного элемента равна его содержимому? Соответственно получается, что этому самому содержимому просто некуда будет выравниваться и браузер элементарно проигнорирует ваши «художества». 🙂
- Создайте заголовок статьи, двух ее разделов и одного подраздела в первом разделе. И пусть заголовок статьи располагается по центру страницы.
- Установите для всей страницы шрифт Arial, а для всех заголовков — Times и пусть они будут написаны курсивом.
- Цвет текста заголовка статьи поставьте #FF6600, разделов #6600FF, а подраздела оставьте неизменным.
- Напишите под каждым заголовком по одному параграфу, причем текст каждого из них должен занимать не меньше трех строк при просмотре в браузере.
- Выровняйте второй параграф по центру, третий — по правой стороне, а четвертый по обоим.
- Введение
- Что такое HTML?
- Теги и синтаксис HTML
- Атрибуты HTML-тегов
- Общие и текст
- Структура HTML-документа
- Параграфы и заголовки
- Как изменить шрифт?
- Меняем цвет текста и фона
- Выравнивание содержимого
- Цитаты и обрыв строки
- Что такое спецсимволы HTML?
- Горизонтальные линии
- Группирование элементов
- Комментарии в HTML
- Ссылки
- Cсылки и их разновидности
- Меняем цвета ссылок
- Ссылки на электронную почту
- Якоря — создаем закладки
- Изображения
- Изображения
- Изображения для фонов
- Изображения — ссылки
- Таблицы
- Таблицы
- Границы, рамки и отступы HTML-таблиц
- Объединение ячеек таблицы
- Вложенные таблицы
- Списки
- Нумерованные и маркированные списки
- Метатеги
- Метатеги и их типы
Copyright © 2010-2015 seodon.ru Все права защищены.
С условиями использования материалов данного сайта вы можете ознакомиться на странице автора.
text-align
The text-align CSS property sets the horizontal alignment of the inline-level content inside a block element or table-cell box. This means it works like vertical-align but in the horizontal direction.
Try it
Syntax
/* Keyword values */ text-align: start; text-align: end; text-align: left; text-align: right; text-align: center; text-align: justify; text-align: justify-all; text-align: match-parent; /* Character-based alignment in a table column */ text-align: "."; text-align: "." center; /* Block alignment values (Non-standard syntax) */ text-align: -moz-center; text-align: -webkit-center; /* Global values */ text-align: inherit; text-align: initial; text-align: revert; text-align: revert-layer; text-align: unset;
The text-align property is specified in one of the following ways:
- Using the keyword values start , end , left , right , center , justify , justify-all , or match-parent .
- Using a value only, in which case the other value defaults to right .
- Using both a keyword value and a value.
Values
The same as left if direction is left-to-right and right if direction is right-to-left.
The same as right if direction is left-to-right and left if direction is right-to-left.
The inline contents are aligned to the left edge of the line box.
The inline contents are aligned to the right edge of the line box.
The inline contents are centered within the line box.
The inline contents are justified. Text should be spaced to line up its left and right edges to the left and right edges of the line box, except for the last line.
Same as justify , but also forces the last line to be justified.
Similar to inherit , but the values start and end are calculated according to the parent’s direction and are replaced by the appropriate left or right value.
When applied to a table cell, specifies the alignment character around which the cell’s contents will align.
Accessibility concerns
The inconsistent spacing between words created by justified text can be problematic for people with cognitive concerns such as Dyslexia.
Formal definition
| Initial value | start , or a nameless value that acts as left if direction is ltr , right if direction is rtl if start is not supported by the browser. |
|---|---|
| Applies to | block containers |
| Inherited | yes |
| Computed value | as specified, except for the match-parent value which is calculated against its parent’s direction value and results in a computed value of either left or right |
| Animation type | discrete |
Formal syntax
text-align =
start |
end |
left |
right |
center |
justify |
match-parent |
justify-all
Examples
Start alignment
HTML
p class="example"> Integer elementum massa at nulla placerat varius. Suspendisse in libero risus, in interdum massa. Vestibulum ac leo vitae metus faucibus gravida ac in neque. Nullam est eros, suscipit sed dictum quis, accumsan a ligula. p>
CSS
.example text-align: start; border: solid; > CSS Text Align – Centered, Justified, Right Aligned Text Style Example
Kolade Chris
We use the CSS text-align property to align content inside a block-level element.
Examples of block-level elements are paragraphs (
.
), divs (
), sections (
), articles (
), and so on.
This alignment affects the horizontal axis only. So the text-align property is different from the vertical-align property which we use to set the vertical alignment of an element.
Table of Contents
Basic Syntax
Here’s the basic syntax for the text-align property:
Now we’ll look at the different values it can take to help you position things on the page.
Values of the text-align Property
The text-align property accepts left , center , right , justify , and inherit as values.
We will take a look at these values one by one.
Before I dive into the values and what they look like in the browser, take a look at the below CSS. I set these styles for improved visibility, so you can see things better:
The left Value
The left value of the text-align property is the default. So, every content inside a block-level element is aligned to the left by default.
If you want the content inside a block-level element to align to the left, you don’t need to assign it a text-align value of left . If you do, you’re just duplicating what’s already the default.
The center Value
With the center value, spaces are created on the left and right, so, everything gets pushed to the center.
If you want to align the content inside a block-level element to the center, the center value is your best bet.
The right Value
Assigning a value of right to the text-align property pushes the content inside a block-level element to the right.
The justify Value
The justify value of the text-align property lines up the content on the left and right edges of the block-level element (the box). If the last line isn’t a full line, then it leaves it alone. It’s easier to see how this works in the image below:
The inherit Value
The inherit value of the text-align property behaves as the name implies. An element with its text-align value set to inherit inherits the text-align value of its direct parent.
In this case, our div inherits the text-align value of the body – which is left by default.
If the text-align value of the body is set to right , and that of the div is left to inherit, the text inside the div aligns to the right.
Conclusion
In this article, you learned about the CSS text-align property and its values.
The examples we looked at here to see how the values behave contained text only – so you might be wondering if the values work on images too. Well, yes they do.
Below is an image inside a div with text-align set to center: