CLASSPATH in Java
Package in Java is a mechanism to encapsulate a group of classes, sub-packages, and interfaces. Packages are used for:
- Preventing naming conflicts. For example, there can be two classes with the name Employee in two packages, college.staff.cse.Employee and college.staff.ee.Employee
- Making searching/locating and usage of classes, interfaces, enumerations, and annotations easier
- Providing controlled access: protected and default have package level access control. A protected member is accessible by classes in the same package and its subclasses. A default member (without any access specifier) is accessible by classes in the same package only.
Packages can be considered as data encapsulation (or data-hiding). Here we will be discussing the responsibility of the CLASSPATH environment variable while programming in Java as we move forward we for sure short need usage of importing statements.
Illustration:
What does this import mean? It makes the Menu class available in the package org.company to our current class. Such that when we call the below command as follows:
Java
I/O classes are imported from java.io package
This package provides for system input and output through data streams, serialization, and the file system. Unless otherwise noted, passing a null argument to a constructor or method in any class or interface in this package will cause a NullPointerException to be thrown. All the classes listed here are imported or if we want to import a specific one then do use it as stated below.
The JVM knows where to find the class Menu. Now, how will the JVM know this location?
It is impractical for it to go through every folder on your system and search for it. Thus, using the CLASSPATH variable we provide it the place where we want it to look. We put directories and jars in the CLASSPATH variable.
Let’s say the above package resides in the directory dir. The complete path of the Menu class file would be dir/org/company/Menu. We’ll specify only the directory dir in our classpath variable, as the rest information regarding the path is provided by the import statements. Similar for jar, if you create a jar and mention its path in the variable, the VM will look inside the jar file and find the class.
One should know how to set a classpath if not done after configuring JDK in respecting operating systems in order to see it or to it and play with multiple IDE, versions game altogether. One must have an absolutely clear understanding of it.
This article is contributed by ekta1994. If you like GeeksforGeeks and would like to contribute, you can also write an article using write.geeksforgeeks.org or mail your article to review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks main page and help other Geeks. Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.
Java Classpath
Learn how to set classpath in Java either as an environment variable and pass as the command-line argument. During runtime of any Java application, the CLASSPATH is a parameter that tells the JVM where to look for classes and packages.
- The default value of the classpath is “ . ” (dot) , meaning that only the current directory is searched for dependencies.
- Specifying either the CLASSPATH environment variable or the -cp command line switch overrides this value.
- The order in which you specify multiple classpath entries is important. The Java interpreter will look for classes in the directories in the order they appear in the classpath variable.
Java Classpath separators are OS specific.
Windows – ; [Semicolon]Linux/Unix – : [Colon]
1. Setting CLASSPATH as Environment Variable
When you have set the location of jar files that are always required during the application runtime, then it’s probably best to add them in the machine’s environment variable ‘CLASSPATH’ .
During application runtime, application class loader will always scan the jar files and classes at specified paths in this variable.
To set CLASSPATH environment variable, find the location of user environment variables in your machine and add all paths where Jar files are stored. Use the separator between different two folders, jar files or classes.
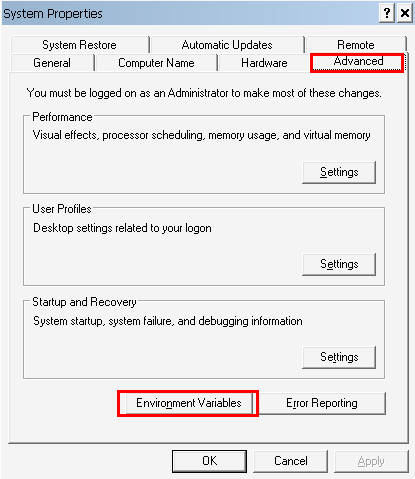
You can find the user environment variables window by –
- From the desktop, right-click the Computer icon.
- Choose Properties from the context menu.
- Click the Advanced system settings link.
- Click Environment Variables. In the section System Variables, find the CLASSPATH environment variable and select it. Click Edit. If the CLASSPATH environment variable does not exist, click New .
- Add all folders separated with a separator. Click OK. Close all remaining windows by clicking OK.
If you are creating CLASSPATH for the first time, you need to specify the name for the variable name in Windows 10. Use ‘.’ (dot) to denote the current directory.
2. Setting CLASSPATH from Command Line
Use -classpath argument to set classpath from command prompt/console. Use the following command to set the classpath for different requirements.
Let’s say we have a folder named dependency where JAR files and other classes are placed.
2.1. Add a Single Jar in CLASSPATH
Below syntax examples will add single jar file in classpath.
//WINDOWS $ set CLASSPATH=.;C:\dependency\framework.jar //Linux/Unix $ export CLASSPATH=.:/dependency/framework.jar2.2. Add Multiple Jars in CLASSPATH
Below syntax examples will add more than one jar file in classpath. To do so, simply use the delimiter for your operating system (either ; or : ) as a separator between the locations specified for the CLASSPATH.
To add all JAR files present in a directory, use wildcard character ( ‘*’ ).
//WINDOWS $ set CLASSPATH=C:\dependency\framework.jar;C:\location\otherFramework.jar $ set CLASSPATH=C:\dependency\framework.jar;C:\location\*.jar //Linux/Unix $ export CLASSPATH=/dependency/framework.jar:/location/otherFramework.jar $ export CLASSPATH=/dependency/framework.jar:/location/*.jar2.3. Add Multiple Classes in CLASSPATH
Many times, you may need to add individual classes in classpath as well. To do so, simply add the folder where classfile is present. e.g. let’s say there are five .class files are present in location folder which you want to include in classpath.
//WINDOWS $ set CLASSPATH=C:\dependency\*;C:\location //Linux/Unix $ export CLASSPATH=/dependency/*:/locationAs a best practice, always organize all JAR files and application classes inside one root folder. This may be the workspace for the application.
Please note that subdirectories contained within the CLASSPATH would not be loaded. In order to load files that are contained within subdirectories, those directories and/or files must be explicitly listed in the CLASSPATH.
If your CLASSPATH environment variable was set to a value that is not correct, then you can unset CLASSPATH by specifying an empty value to it.
3. Executing Programs with ‘-classpath’ or ‘-cp’ Option
Apart from setting the classpath to the environment variable, you can pass an additional classpath to Java runtime while launching the application using –classpath option or –cp option.
Use the . (dot) to include the current path in the classpath where the .class file has been generated.
$ javac –classpath C:\dependency\framework.jar MyApp.Java $ java –classpath .;C:\dependency\framework.jar MyApp4. Print Current CLASSPATH Value
Anytime you wish to verify all path entries in CLASSPATH variable, you can verify using the echo command.
//Windows c:/> echo %CLASSPATH% //Linux/Unix $ echo $CLASSPATH
If CLASSPATH is not set you will get a CLASSPATH: Undefined variable error (Solaris or Linux) console or simply %CLASSPATH% printed in the windows command prompt.