- 3 Ways to Upload Large Files in PHP (Settings, Chunking, Resumable)
- TABLE OF CONTENTS
- LARGE UPLOADS IN PHP
- METHOD 1) TWEAK PHP SETTINGS
- 1A) UPDATE PHP.INI
- 1B) UPDATING THE HTACCESS FILE
- 1C) UPLOAD!
- 1D) INI SET?
- METHOD 2) CHUNK UPLOAD
- 2A) HTML & JAVASCRIPT
- 2B) SERVER-SIDE UPLOAD HANDLER
- METHOD 3) RESUMABLE UPLOAD
- 3A) HTML & JAVASCRIPT
- 3B) DOWNLOAD FLOW PHP SERVER
- 3C) FLOW PHP UPLOAD HANDLER
- DOWNLOAD & NOTES
- SUPPORT
- EXAMPLE CODE DOWNLOAD
- EXTRA BITS & LINKS
- FILE TYPE RESTRICTIONS
- LINKS & REFERENCES
- YOUTUBE TUTORIAL
- THE END
- Upload Multiple Files In PHP
3 Ways to Upload Large Files in PHP (Settings, Chunking, Resumable)
Welcome to a tutorial on how to upload large files in PHP. Once upon a time in the Stone Age of the Internet, uploads were manageable without large files. But these days, we have to deal with all kinds of oversized files, and the “traditional” upload mechanism just can’t handle it.
To deal with large uploads in PHP, there are a few possible alternatives:
- Change the upload_max_filesize limit in php.ini.
- Split and upload the file in smaller chunks, and assemble them when the upload is complete.
- Implement resumable uploads.
But just how does each of these methods work? Read on for the examples!
TABLE OF CONTENTS
LARGE UPLOADS IN PHP
All right, let us now get into the examples and possible ways of handling large uploads in PHP.
METHOD 1) TWEAK PHP SETTINGS
1A) UPDATE PHP.INI
upload_max_filesize = 150M post_max_size = 150M max_input_time = 300 max_execution_time = 300 - upload_max_filesize – The maximum allowed upload file size.
- post_max_size – The maximum allowed POST data size.
- max_input_time – Maximum allowed input time.
- max_execution_time – Maximum allowed time the scripts are allowed to run.
But of course, I will not recommend changing the php.ini file directly. This will affect the entire server and all your other websites as well.
1B) UPDATING THE HTACCESS FILE
php_value upload_max_filesize 150M php_value post_max_size 150M php_value max_input_time 300 php_value max_execution_time 300If you don’t have access to php.ini , or just want to apply the settings for a single site – It is also possible to change the settings by creating a .htaccess file. IIS and NGINX users, you will need to do some of your own research.
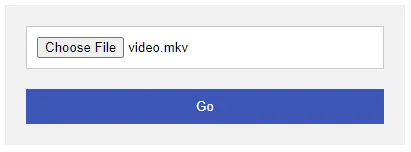
1C) UPLOAD!
Well, this is just a regular upload form. For those who may have missed out on basic file upload.
1D) INI SET?
For you guys who are thinking of using ini_set() to change the upload size – Take note that according to the official core php.ini directives, upload_max_filesize is only changeable in PHP_INI_PERDIR . Meaning, it can only be tweaked in the php.ini or .htaccess file; ini_set(«upload_max_filesize», «150M») will not work.
METHOD 2) CHUNK UPLOAD
2A) HTML & JAVASCRIPT
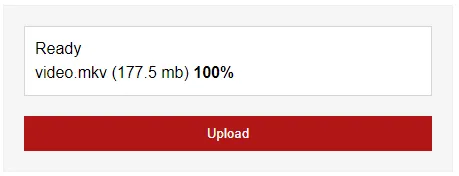
This second method is called “chunking” – Splitting a large file and uploading them in smaller chunks. While it may sound difficult, there is thankfully an open-source library called Plupload that we can use. This is pretty much a modified version of the “default Plupload” demo script.
- There are only 2 HTML elements here.
- Upload file list and progress.
- Click to pick files for upload.
- Captain Obvious. Load Plupload from the CDN.
- Initiate Plupload on page load. Not going to explain line by line, but this basically starts the upload immediately after choosing a file.
That is the gist of it, read the official documentation (links in the extra section below) if you need more customizations.
2B) SERVER-SIDE UPLOAD HANDLER
exit(json_encode(["ok"=>$ok, "info"=>$info])); > // (B) INVALID UPLOAD if (empty($_FILES) || $_FILES["file"]["error"]) < verbose(0, "Failed to move uploaded file."); >// (C) UPLOAD DESTINATION - CHANGE FOLDER IF REQUIRED! $filePath = __DIR__ . DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR . "uploads"; if (!file_exists($filePath)) < if (!mkdir($filePath, 0777, true)) < verbose(0, "Failed to create $filePath"); >> $fileName = isset($_REQUEST["name"]) ? $_REQUEST["name"] : $_FILES["file"]["name"]; $filePath = $filePath . DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR . $fileName; // (D) DEAL WITH CHUNKS $chunk = isset($_REQUEST["chunk"]) ? intval($_REQUEST["chunk"]) : 0; $chunks = isset($_REQUEST["chunks"]) ? intval($_REQUEST["chunks"]) : 0; $out = @fopen(".part", $chunk == 0 ? "wb" : "ab"); if ($out) < $in = @fopen($_FILES["file"]["tmp_name"], "rb"); if ($in) < while ($buff = fread($in, 4096)) < fwrite($out, $buff); >> else < verbose(0, "Failed to open input stream"); >@fclose($in); @fclose($out); @unlink($_FILES["file"]["tmp_name"]); > else < verbose(0, "Failed to open output stream"); >// (E) CHECK IF FILE HAS BEEN UPLOADED if (!$chunks || $chunk == $chunks - 1) < rename(".part", $filePath); > verbose(1, "Upload OK"); Once again, this is pretty much a modified version of the demo upload handler. Not going to explain line-by-line, but how this works essentially:
- Create an empty .part file on the first chunk.
- Append chunks into the .part file as they are being uploaded.
- When all the chunks are assembled, rename the .part file back to what it’s supposed to be.
Done! You now have a system that is capable of handling large file uploads.
METHOD 3) RESUMABLE UPLOAD
3A) HTML & JAVASCRIPT
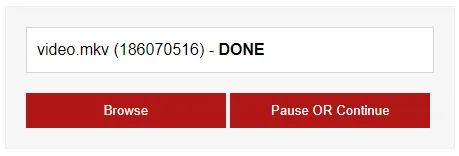
You should be familiar with this last method – Resumable uploads. Yep, not going to reinvent the wheel. Using FlowJS here to drive the resumable upload.
- The HTML only has 3 elements.
- Upload file list.
- Upload button.
- Pause/resume button.
- Load the FlowJS library.
- Initiate FlowJS, not going to run through line-by-line again. But just like Plupload, this starts uploading once a file is selected. Read their documentation if you want the full list of settings and events. Links below.
3B) DOWNLOAD FLOW PHP SERVER
- Download and install Composer if you have not done so.
- Open the command line, navigate to your project folder.
- Run composer require flowjs/flow-php-server .
That’s all. Composer will fetch the latest version into the vendor/ folder.
3C) FLOW PHP UPLOAD HANDLER
setTempDir(__DIR__ . DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR . "temp"); $request = new \Flow\Request(); // (B) HANDLE UPLOAD $uploadFolder = __DIR__ . DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR . "uploads" . DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR; $uploadFileName = uniqid() . "_" . $request->getFileName(); $uploadPath = $uploadFolder . $uploadFileName; if (\Flow\Basic::save($uploadPath, $config, $request)) < // File saved successfully >else < // Not final chunk or invalid request. Continue to upload. >Just a small modified version of the official demo once again. Probably shouldn’t use this as-it-is, but a good start nonetheless.
DOWNLOAD & NOTES
Here is the download link to the example code, so you don’t have to copy-paste everything.
SUPPORT
600+ free tutorials & projects on Code Boxx and still growing. I insist on not turning Code Boxx into a «paid scripts and courses» business, so every little bit of support helps.
EXAMPLE CODE DOWNLOAD
Click here for the source code on GitHub gist, just click on “download zip” or do a git clone. I have released it under the MIT license, so feel free to build on top of it or use it in your own project.
EXTRA BITS & LINKS
That’s it for all the upload methods, and here is a section of small extras and links that may be useful to you.
FILE TYPE RESTRICTIONS
All the above examples now accept all kinds of files and extensions. If you want to restrict the file types, I will highly recommend doing a simple server-side check instead.
LINKS & REFERENCES
- File upload directives in php.ini
- Official documentation for Plupload
- Flow JS
- FlowJS – GitHub
- Flow PHP Server – GitHub
- CDNJS
- Official Website
- GitHub
- CDNJS
YOUTUBE TUTORIAL
THE END
Thank you for reading, and we have come to the end of this short tutorial. I hope that it has helped to solve your big upload woes. If you have stuff you like to add to this guide, please feel free to comment below. Good luck and happy coding!
Upload Multiple Files In PHP
I wonder whether someone may be able to help me please. Using some excellent online tutorials I’ve put together the code below which allows a user to upload image files to a server folder and the filename and other details to a mySQL database. PHP Script
$ratio2) < $thumb_w=$new_w; $thumb_h=$old_y/$ratio1; >else < $thumb_h=$new_h; $thumb_w=$old_x/$ratio2; >// we create a new image with the new dimmensions $dst_img=ImageCreateTrueColor($thumb_w,$thumb_h); // resize the big image to the new created one imagecopyresampled($dst_img,$src_img,0,0,0,0,$thumb_w,$thumb_h,$old_x,$old_y); // output the created image to the file. Now we will have the thumbnail into the file named by $filename if(!strcmp("png",$ext)) imagepng($dst_img,$filename); else imagejpeg($dst_img,$filename); //destroys source and destination images. imagedestroy($dst_img); imagedestroy($src_img); > // This function reads the extension of the file. // It is used to determine if the file is an image by checking the extension. function getExtension($str) < $i = strrpos($str,"."); if (!$i) < return ""; >$l = strlen($str) - $i; $ext = substr($str,$i+1,$l); return $ext; > $title = ($_POST['title']); if ($title == '') // if title is not set $title = '(No Title Provided)';// use (empty title) string //reads the name of the file the user submitted for uploading $image=$_FILES['image']['name']; if ($image) < // get the original name of the file from the clients machine $filename = stripslashes($_FILES['image']['name']); // get the extension of the file in a lower case format $extension = getExtension($filename); $extension = strtolower($extension); // if it is not a known extension, we will suppose it is an error, print an error message //and will not upload the file, otherwise we continue if (($extension != "jpg") && ($extension != "jpeg") && ($extension != "png")) < echo 'Error! - The image that you attempted to upload is not in the correct format. The file format must be one of the following: "jpg", "jpeg" or "png" . Please try again.'; $errors=1; > else < // get the size of the image in bytes // $_FILES[\'image\'][\'tmp_name\'] is the temporary filename of the file in which the uploaded file was stored on the server $size=getimagesize($_FILES['image']['tmp_name']); $sizekb=filesize($_FILES['image']['tmp_name']); //compare the size with the maxim size we defined and print error if bigger if ($sizekb >1150000) < echo 'Error! - The file that you are attempting to upload is greater than the prescribed 1MB limit. Please try again.'; $errors=1; > //we will give an unique name, for example the time in unix time format $image_name=time().'.'.$title.'.'.$extension; //the new name will be containing the full path where will be stored (images folder) $newname="images/".$image_name; $copied = copy($_FILES['image']['tmp_name'], $newname); if (!$copied) < //echo 'Error! Your file has not been loaded'; //$errors=1; > else < // the new thumbnail image will be placed in images/thumbs/ folder $thumb_name='images/thumbs/'.$image_name; // call the function that will create the thumbnail. The function will get as parameters //the image name, the thumbnail name and the width and height desired for the thumbnail $thumb=make_thumb($newname,$thumb_name,WIDTH,HEIGHT); >>> //If no errors registred, print the success message and show the thumbnail image created if(isset($_POST['Submit']) && !$errors) < //echo '
Success! - Your image has been uploaded'; //echo ''; > require("mapmyfindsdbinfo.php"); // Gets data from form $userid = $_POST["userid"]; $locationid = $_POST["locationid"]; $findosgb36lat = $_POST["findosgb36lat"]; $findosgb36lon = $_POST["findosgb36lon"]; $dateoftrip = $_POST["dateoftrip"]; $findcategory = $_POST["findcategory"]; $findname = $_POST["findname"]; $finddescription = $_POST["finddescription"]; $detectorid= $_POST["detectorname"]; $searchheadid = $_POST["searchheadname"]; if( empty($_POST["detectorsettings"]) ) < $detectorsettings = 'No details provided.'; >else < $detectorsettings = $_POST["detectorsettings"]; >if( empty($_POST["pasref"]) ) < $pasref = 'No PAS Ref. number provided.'; >else < $pasref = $_POST["pasref"]; >if( empty($_POST["additionalcomments"]) ) < $additionalcomments = 'No additional comments made.'; >else < $additionalcomments = $_POST["additionalcomments"]; >$makepublic = $_POST["makepublic"]; // Opens a connection to a MySQL server $conn = mysql_connect ("hostname", $username, $password); if (!$conn) < die('Not connected : ' . mysql_error()); >// Set the active MySQL database $db_selected = mysql_select_db($database, $conn); if (!$db_selected) < die ('Can\'t use db : ' . mysql_error()); >$sql = "INSERT INTO finds (userid, locationid, findosgb36lat, findosgb36lon, dateoftrip, findcategory, findname, finddescription, detectorid, searchheadid, detectorsettings, pasref, additionalcomments, makepublic) VALUES ('$userid', '$locationid', '$findosgb36lat', '$findosgb36lon', '$dateoftrip', '$findcategory', '$findname', '$finddescription', '$detectorid', '$searchheadid', '$detectorsettings', '$pasref', '$additionalcomments', '$makepublic')"; $result = mysql_query($sql, $conn); $findid = mysql_insert_id($conn); $sql = "INSERT INTO testimages (title, imagename, findid) VALUES ('$title', '$image_name', '$findid')"; $result = mysql_query($sql, $conn); if (!$result) < die('Invalid query: ' . mysql_error()); >?>
It all works well, but I’d now like to extend the functionality of allowing a user to upload more than 1 file at a time. I’ve done a fair bit of research to look at how to upload multiple files, but I’m fairly new to PHP and a little unsure as to which is the best way to progress this. I just wondered whether someone could perhaps have a look at what I’ve put together and offer some guidance on how I can change this to upload mutiple files upon the form submit. Many thanks