- 2 Ways to Read a Text File in Java? BufferredReader and Scanner Examples
- How to read a text file in Java? Examples
- Example 1 — Reading File using Scanner in Java
- Example 2 — Reading Text File using BufferedReader in Java
- Java Program to read a file line by line in Java
- File Handling in Java
- Java
- Streams in Java
- 1. Input Stream:
- Creating an InputStream
- Methods of InputStream
- 2. Output Stream:
- Creating an OutputStream
- Methods of OutputStream
- 1. Byte Stream:
- 2. Character Stream:
- Java File Class Methods
- File operations in Java
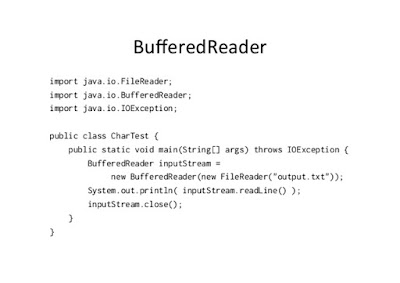
2 Ways to Read a Text File in Java? BufferredReader and Scanner Examples
You can read a text file in Java by using either Files, BufferedReader or Scanner class. Both classes provide convenient methods to read a text file line by line e.g. Scanner provides nextLine() method and BufferedReader provides readLine() method. If you are reading a binary file, you can use FileInputStream . By the way, when you are reading text data, you also need to provide character encoding, if you don’t then the platform’s default character encoding is used. In Java IO, streams like InputStream are used to read bytes, and Readers like FileReader are used to read character data.
BufferedReader is the traditional way to read data because it reads file buffer by buffer instead of character by character, so it’s more efficient if you are reading large files. BufferedReader is also there from JDK 1 itself while Scanner was added to Java 5.
The Scanner has more features than BufferedReader, when it comes to file reading, for example, you can specify any delimiter instead of the new line, which is not possible with BufferedReader. Java 7 added a new File API, which makes reading/writing from the file even easier.
It’s also possible to read the entire file in one line in Java 7, but given most of the projects are still running on Java 6, it’s good to know about these two ways to read a text file in Java. For Java beginners, I also suggest referring to a good book like Cay S. Horstmann, Core Java Volume 1 and 2 to learn the basics of Java programming.
How to read a text file in Java? Examples
You can read a text file in the Java program by using BufferedReader and Scanner and we will discuss steps to read a file in this article. First, we will see how to use the Scanner class to read a file line by line in Java, and then we will learn how to use BufferedReader class to do the same.
Example 1 — Reading File using Scanner in Java
Scanner class is defined in java.util package, so the first step is to import this class into your Java program. Once you imported this class, you can create an object of Scanner by passing a FileInputStream to it, pointing to the file you want to read.
Now you are all set to read a text file line by line in Java. The scanner provides a method called hasNextLine() which returns true if the file has one more line to read.
This check is platform-independent so it will work in both Windows and UNIX even though the line separator is different in these two operating systems e.g. line separator is \n in Windows and \r\n in UNIX.
You can read data from the file by calling nextLine() method, this will return the next line and advance the file pointer to the next line. This method returns a String object representing a line in the file. You can use a while() loop as shown in our first example, to read all lines from files one by one.
You can also see Core Java Volume 2 — Advanced Features by Cay S. Horstmann to learn more about how to use Scanner to read a file in Java.
Example 2 — Reading Text File using BufferedReader in Java
BufferedReader provides another way to read files line by line in Java. It follows a decorator pattern and adds buffering capability to an existing reader. You can create an object of InputStreamReader by passing FileInputStream , pointing to the text file you want to read.
Optionally, you can also provide character encoding to the InputStreamReader, if you don’t then it will use the platform’s default character encoding. InputStreamReader actually acts as a bridge between streams and reader classes.
Once you have an object of BufferedReader, you can call the readLine() method to read the next line from the file. This method returns a String object containing data from a file, if there is no more line to read then this method return null . By using this properly, you can write a while loop to read a file line by line in Java, as shown in our second example.
Though I have not closed the buffered reader here, you should do it on your real production code, as suggested earlier on the right way to close streams in Java. It’s better to call the close() method on the finally block. If you are on Java 7, consider using try-with-resource statement to automatically close resources once you are done with it. You can also use the Files class to read whole file in one line.
Java Program to read a file line by line in Java
Here is our complete Java program to read a file in Java. This program contains two examples, the first example shows how to read a text file using the Scanner class and the second example shows how to read a file using BufferedReader class.
Both classes are defined in java.util package so you need to import them before using them. If you are coding in Eclipse then don’t worry, Eclipse will take care of it. In order to run this program from the command line, create a Java source file with the name FileReaderDemo.java and write this program there.
Once you are done with it, you can follow the steps given on how to run Helloworld in Java to run this program from the command line. If you are using Eclipse IDE, then just select a Java project and copy-paste this code there, Eclipse will take care rest of it. To run a program in Eclipse, just right-click and select «Run as Java Program».
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.Scanner; /** * Java program to read File in Java. It demonstrate two ways by simple example, * one uses java.util.Scanner class and other by using java.io.BufferedReader * class. * * @author http://java67.blogspot.com * */ public class FileReaderDemo< public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException < final String FILE_NAME = "C://temp//GDP.txt"; // 1st way to read File in Java - Using Scanner Scanner scnr = new Scanner(new FileInputStream(FILE_NAME)); while (scnr.hasNextLine()) < System.out.println(scnr.nextLine()); > scnr.close(); // 2nd way to read File in Java - Using BufferedReader BufferedReader buffReader = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(FILE_NAME))); String line = buffReader.readLine(); while (line != null) < System.out.println(line); line = buffReader.readLine(); > > >Output: United States 18,390.900 China 15,923.626 India 5,750.467 Japan 5,021.990 Germany 3,440.437 Russia 2,827.978 Brazil 2,656.858 United Kingdom 2,562.320 France 2,416.128 Mexico 2,040.222That's all about how to read a text file in Java using BufferedReader and Scanner. Use Scanner if you are running on Java 5 or Java 6, or use BufferedReader if you are running on Java 1.4. You can use the Files class to read text files from Java 7 onward.
- How to read XLS and XLSX files in Java using Apache POI? (example)
- How to create a file and directory in Java? (solution)
- How to read XML files in Java using JDOM Parser? (solution)
- How do you use the Scanner class in Java? (example)
- How to use BufferedReader class in Java? (demo)
- How do I read InputStream as String in Java? (solution)
- How to read JSON Files in Java? (solution)
- How do I read input from the console in Java? (example)
File Handling in Java
In Java, with the help of File Class, we can work with files. This File Class is inside the java.io package. The File class can be used by creating an object of the class and then specifying the name of the file.
Why File Handling is Required?
- File Handling is an integral part of any programming language as file handling enables us to store the output of any particular program in a file and allows us to perform certain operations on it.
- In simple words, file handling means reading and writing data to a file.
Java
In Java, the concept Stream is used in order to perform I/O operations on a file. So at first, let us get acquainted with a concept known as Stream in Java.
Streams in Java
- In Java, a sequence of data is known as a stream.
- This concept is used to perform I/O operations on a file.
- There are two types of streams :
1. Input Stream:
The Java InputStream class is the superclass of all input streams. The input stream is used to read data from numerous input devices like the keyboard, network, etc. InputStream is an abstract class, and because of this, it is not useful by itself. However, its subclasses are used to read data.
There are several subclasses of the InputStream class, which are as follows:
- AudioInputStream
- ByteArrayInputStream
- FileInputStream
- FilterInputStream
- StringBufferInputStream
- ObjectInputStream
Creating an InputStream
// Creating an InputStream InputStream obj = new FileInputStream();
Here, an input stream is created using FileInputStream.
Note: We can create an input stream from other subclasses as well as InputStream.
Methods of InputStream
| S No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | read() | Reads one byte of data from the input stream. |
| 2 | read(byte[] array)() | Reads byte from the stream and stores that byte in the specified array. |
| 3 | mark() | It marks the position in the input stream until the data has been read. |
| 4 | available() | Returns the number of bytes available in the input stream. |
| 5 | markSupported() | It checks if the mark() method and the reset() method is supported in the stream. |
| 6 | reset() | Returns the control to the point where the mark was set inside the stream. |
| 7 | skips() | Skips and removes a particular number of bytes from the input stream. |
| 8 | close() | Closes the input stream. |
2. Output Stream:
The output stream is used to write data to numerous output devices like the monitor, file, etc. OutputStream is an abstract superclass that represents an output stream. OutputStream is an abstract class and because of this, it is not useful by itself. However, its subclasses are used to write data.
There are several subclasses of the OutputStream class which are as follows:
- ByteArrayOutputStream
- FileOutputStream
- StringBufferOutputStream
- ObjectOutputStream
- DataOutputStream
- PrintStream
Creating an OutputStream
// Creating an OutputStream OutputStream obj = new FileOutputStream();
Here, an output stream is created using FileOutputStream.
Note: We can create an output stream from other subclasses as well as OutputStream.
Methods of OutputStream
| S. No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | write() | Writes the specified byte to the output stream. |
| 2. | write(byte[] array) | Writes the bytes which are inside a specific array to the output stream. |
| 3. | close() | Closes the output stream. |
| 4. | flush() | Forces to write all the data present in an output stream to the destination. |
Based on the data type, there are two types of streams :
1. Byte Stream:
This stream is used to read or write byte data. The byte stream is again subdivided into two types which are as follows:
- Byte Input Stream: Used to read byte data from different devices.
- Byte Output Stream: Used to write byte data to different devices.
2. Character Stream:
This stream is used to read or write character data. Character stream is again subdivided into 2 types which are as follows:
- Character Input Stream: Used to read character data from different devices.
- Character Output Stream: Used to write character data to different devices.
Owing to the fact that you know what a stream is, let’s polish up File Handling in Java by further understanding the various methods that are useful for performing operations on the files like creating, reading, and writing files.
Java File Class Methods
The following table depicts several File Class methods:
| Method Name | Description | Return Type |
|---|---|---|
| canRead() | It tests whether the file is readable or not. | Boolean |
| canWrite() | It tests whether the file is writable or not. | Boolean |
| createNewFile() | It creates an empty file. | Boolean |
| delete() | It deletes a file. | Boolean |
| exists() | It tests whether the file exists or not. | Boolean |
| length() | Returns the size of the file in bytes. | Long |
| getName() | Returns the name of the file. | String |
| list() | Returns an array of the files in the directory. | String[] |
| mkdir() | Creates a new directory. | Boolean |
| getAbsolutePath() | Returns the absolute pathname of the file. | String |
Let us now get acquainted with the various file operations in Java.
File operations in Java
The following are the several operations that can be performed on a file in Java :
Now let us study each of the above operations in detail.
1. Create a File
- In order to create a file in Java, you can use the createNewFile() method.
- If the file is successfully created, it will return a Boolean value true and false if the file already exists.
Following is a demonstration of how to create a file in Java :