- Строки. Функции и методы строк
- Базовые операции
- Таблица «Функции и методы строк»
- # Sum a List of Strings using try/except
- # Sum a List of Strings using str.join()
- # Convert all values to strings before calling join()
- # Concatenate to a string in a for loop in Python
- # Sum the digits in a string in Python
- # Additional Resources
- Как просуммировать элементы строк в питоне?
Строки. Функции и методы строк
Итак, о работе со строками мы немного поговорили, теперь поговорим о функциях и методах строк.
Я постарался собрать здесь все строковые методы и функции, но если я что-то забыл — поправляйте.
Базовые операции
При вызове методов необходимо помнить, что строки в Python относятся к категории неизменяемых последовательностей, то есть все функции и методы могут лишь создавать новую строку.
: Поэтому все строковые методы возвращают новую строку, которую потом следует присвоить переменной. Таблица «Функции и методы строк»
| Функция или метод | Назначение |
|---|---|
| S = ‘str’; S = «str»; S = »’str»’; S = «»»str»»» | Литералы строк |
| S = «s\np\ta\nbbb» | Экранированные последовательности |
| S = r»C:\temp\new» | Неформатированные строки (подавляют экранирование) |
| S = b»byte» | Строка байтов |
| S1 + S2 | Конкатенация (сложение строк) |
| S1 * 3 | Повторение строки |
| S[i] | Обращение по индексу |
| S[i:j:step] | Извлечение среза |
| len(S) | Длина строки |
| S.find(str, [start],[end]) | Поиск подстроки в строке. Возвращает номер первого вхождения или -1 |
| S.rfind(str, [start],[end]) | Поиск подстроки в строке. Возвращает номер последнего вхождения или -1 |
| S.index(str, [start],[end]) | Поиск подстроки в строке. Возвращает номер первого вхождения или вызывает ValueError |
| S.rindex(str, [start],[end]) | Поиск подстроки в строке. Возвращает номер последнего вхождения или вызывает ValueError |
| S.replace(шаблон, замена[, maxcount]) | Замена шаблона на замену. maxcount ограничивает количество замен |
| S.split(символ) | Разбиение строки по разделителю |
| S.isdigit() | Состоит ли строка из цифр |
| S.isalpha() | Состоит ли строка из букв |
| S.isalnum() | Состоит ли строка из цифр или букв |
| S.islower() | Состоит ли строка из символов в нижнем регистре |
| S.isupper() | Состоит ли строка из символов в верхнем регистре |
| S.isspace() | Состоит ли строка из неотображаемых символов (пробел, символ перевода страницы (‘\f’), «новая строка» (‘\n’), «перевод каретки» (‘\r’), «горизонтальная табуляция» (‘\t’) и «вертикальная табуляция» (‘\v’)) |
| S.istitle() | Начинаются ли слова в строке с заглавной буквы |
| S.upper() | Преобразование строки к верхнему регистру |
| S.lower() | Преобразование строки к нижнему регистру |
| S.startswith(str) | Начинается ли строка S с шаблона str |
| S.endswith(str) | Заканчивается ли строка S шаблоном str |
| S.join(список) | Сборка строки из списка с разделителем S |
| ord(символ) | Символ в его код ASCII |
| chr(число) | Код ASCII в символ |
| S.capitalize() | Переводит первый символ строки в верхний регистр, а все остальные в нижний |
| S.center(width, [fill]) | Возвращает отцентрованную строку, по краям которой стоит символ fill (пробел по умолчанию) |
| S.count(str, [start],[end]) | Возвращает количество непересекающихся вхождений подстроки в диапазоне [начало, конец] (0 и длина строки по умолчанию) |
| S.expandtabs([tabsize]) | Возвращает копию строки, в которой все символы табуляции заменяются одним или несколькими пробелами, в зависимости от текущего столбца. Если TabSize не указан, размер табуляции полагается равным 8 пробелам |
| S.lstrip([chars]) | Удаление пробельных символов в начале строки |
| S.rstrip([chars]) | Удаление пробельных символов в конце строки |
| S.strip([chars]) | Удаление пробельных символов в начале и в конце строки |
| S.partition(шаблон) | Возвращает кортеж, содержащий часть перед первым шаблоном, сам шаблон, и часть после шаблона. Если шаблон не найден, возвращается кортеж, содержащий саму строку, а затем две пустых строки |
| S.rpartition(sep) | Возвращает кортеж, содержащий часть перед последним шаблоном, сам шаблон, и часть после шаблона. Если шаблон не найден, возвращается кортеж, содержащий две пустых строки, а затем саму строку |
| S.swapcase() | Переводит символы нижнего регистра в верхний, а верхнего – в нижний |
| S.title() | Первую букву каждого слова переводит в верхний регистр, а все остальные в нижний |
| S.zfill(width) | Делает длину строки не меньшей width, по необходимости заполняя первые символы нулями |
| S.ljust(width, fillchar=» «) | Делает длину строки не меньшей width, по необходимости заполняя последние символы символом fillchar |
| S.rjust(width, fillchar=» «) | Делает длину строки не меньшей width, по необходимости заполняя первые символы символом fillchar |
| S.format(*args, **kwargs) | Форматирование строки |
Для вставки кода на Python в комментарий заключайте его в теги
Сложить элементы строки python
Last updated: Feb 19, 2023
Reading time · 5 min
# Table of Contents
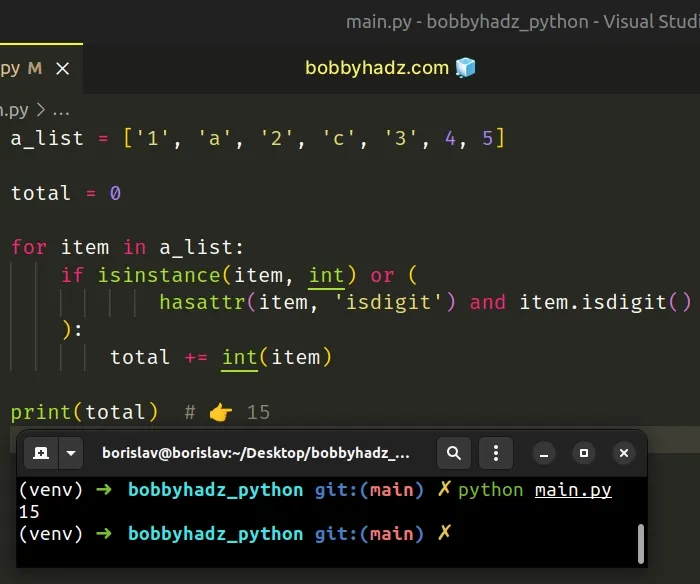
# Sum a List of Strings in Python
To sum a list of strings:
- Use a for loop to iterate over the list.
- Check if each value is a valid number.
- Convert the valid numbers to integers or floats and sum them.
Copied!a_list = ['1', 'a', '2', 'c', '3', 4, 5] total = 0 for item in a_list: if isinstance(item, int) or ( hasattr(item, 'isdigit') and item.isdigit() ): total += int(item) print(total) # 👉️ 15
We used a for loop to iterate over the list of strings.
On each iteration, we check if the current item is an integer or an integer wrapped in a string.
If the condition is met, we add the value to the total variable.
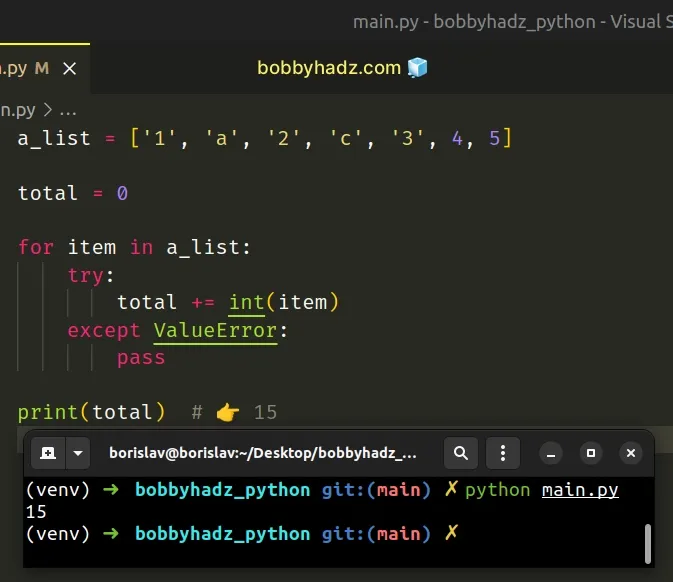
# Sum a List of Strings using try/except
You can also use a try/except statement to sum a list of strings.
Copied!a_list = ['1', 'a', '2', 'c', '3', 4, 5] total = 0 for item in a_list: try: total += int(item) except ValueError: pass print(total) # 👉️ 15
On each iteration, we try to convert the current item to an integer.
If a ValueError exception is raised, the except block runs.
Otherwise, the number gets added to the total .
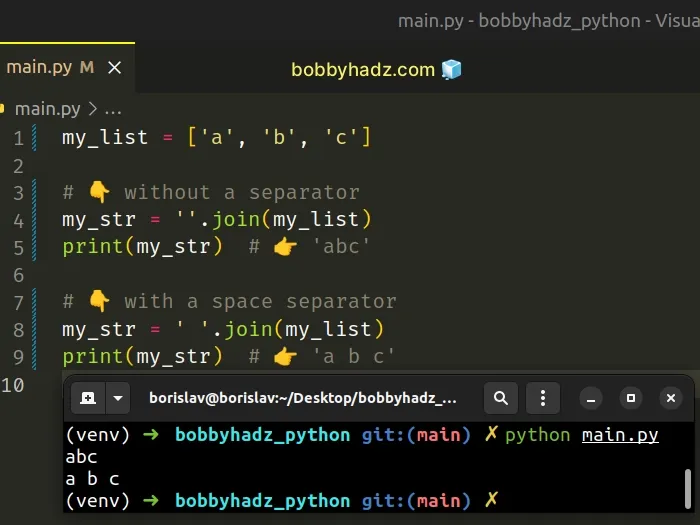
# Sum a List of Strings using str.join()
This is a three-step process:
- Call the str.join() method on an empty string.
- Pass the iterable (e.g. a list of strings) to the join() method.
- The result will be a string containing the items of the iterable.
Copied!my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] # 👇️ without a separator my_str = ''.join(my_list) print(my_str) # 👉️ 'abc' # 👇️ with a space separator my_str = ' '.join(my_list) print(my_str) # 👉️ 'a b c'
The str.join method takes an iterable as an argument and returns a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the iterable.
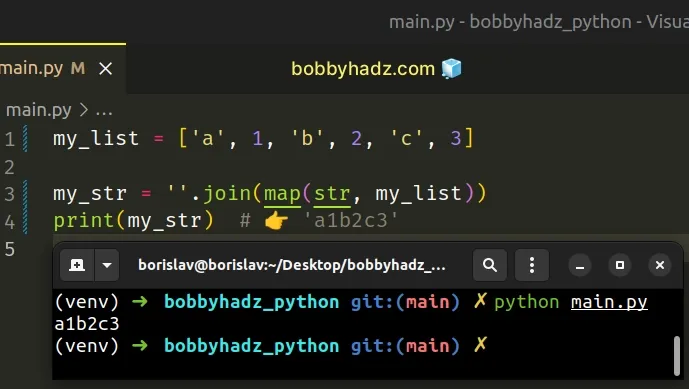
# Convert all values to strings before calling join()
If your list contains numbers or other types, convert all of the values to string before calling join() .
Copied!my_list = ['a', 1, 'b', 2, 'c', 3] my_str = ''.join(map(str, my_list)) print(my_str) # 👉️ 'a1b2c3'
The map() function takes a function and an iterable as arguments and calls the function with each item of the iterable.
We used the function to convert each item in the list to a string, before passing the items to the str.join() method.
The string the join() method is called on is used as the separator between elements.
Copied!my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] my_str = '-'.join(my_list) print(my_str) # 👉️ 'a-b-c'
If you need to join the list of strings with spaces, call the method on a string that contains a space.
Copied!my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] # 👇️ with a space separator my_str = ' '.join(my_list) print(my_str) # 👉️ 'a b c'
If you don't need a separator and just want to join the iterable's elements into a string, call the join() method on an empty string.
Copied!my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c'] my_str = ''.join(my_list) print(my_str) # 👉️ 'abc'
Alternatively, you can concatenate to a string in a for loop.
# Concatenate to a string in a for loop in Python
This is a three-step process:
- Declare a variable and initialize it to an empty string.
- Use a for loop to iterate over the sequence.
- Reassign the variable to its current value plus the current item.
Copied!my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com'] my_str = '' for item in my_list: my_str += item print(my_str) # 👉️ 'bobbyhadzcom'
The first step is to declare a new variable and initialize it to an empty string.
On each iteration in the for loop, we reassign the variable to its current value plus the value of the current list item.
The following code sample achieves the same result.
Copied!my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com'] my_str = '' for item in my_list: my_str = my_str + item print(my_str) # 👉️ 'bobbyhadzcom'
# Sum the digits in a string in Python
If you need to sum the digits in a string:
- Use a generator expression to iterate over the string.
- On each iteration, convert each character to an integer if it is a digit.
- Use the sum() function to get the sum of the digits.
Copied!my_str = '1ab2c3' # ✅ sum digits in a string that might contain non-digits total = sum(int(char) for char in my_str if char.isdigit()) print(total) # 👉️ 6 # ----------------------------------------------------------- # ✅ sum digits in a string that contains only digits my_str = '246' total = sum(int(d) for d in my_str) print(total) # 👉️ 12
We used a generator expression to iterate over the string.
Generator expressions are used to perform some operation for every element or select a subset of elements that meet a condition.
On each iteration, we check if the character is a digit.
The str.isdigit method returns True if all characters in the string are digits and there is at least 1 character, otherwise False is returned.
We convert all digits to integers and use the sum() function to get the total.
Copied!my_str = '1ab2c3' total = sum(int(char) for char in my_str if char.isdigit()) print(total) # 👉️ 6
The sum function takes an iterable, sums its items from left to right and returns the total.
The sum function takes the following 2 arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| iterable | the iterable whose items to sum |
| start | sums the start value and the items of the iterable. sum defaults to 0 (optional) |
If your string is guaranteed to only contain digits, you don't have to use the str.isdigit() method.
Copied!my_str = '246' total = sum(int(d) for d in my_str) print(total) # 👉️ 12
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
I wrote a book in which I share everything I know about how to become a better, more efficient programmer.
Как просуммировать элементы строк в питоне?
[-0.0, -0.0, -0.0, -0.0, -0.0, -0.0, -0.0, -0.0, -0.0][0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 15.626869483055735, 0.0]
[0.0, 19.305019168249604, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 22.424106744929986, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 24.802126691039216, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 25.41793956879349]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 32.17848566247153, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[34.33750876274861, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 38.54533200463435, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 40.605066388577725, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
вот у меня строки, как мне просуммировать их элементы , типо вывести сумму всех первых, вторых и третьих, всего 9 элементов
>>> sum([x[0] for x in arrays]) 34.33750876274861 >>> sum([x[1] for x in arrays]) 19.305019168249604 >>> sum([x[2] for x in arrays]) 32.17848566247153 >>> sum([x[3] for x in arrays]) 22.424106744929986 . import json data = ''' [-0.0, -0.0, -0.0, -0.0, -0.0, -0.0, -0.0, -0.0, -0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 15.626869483055735, 0.0] [0.0, 19.305019168249604, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 22.424106744929986, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 24.802126691039216, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 25.41793956879349] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 32.17848566247153, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [34.33750876274861, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 38.54533200463435, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 40.605066388577725, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] ''' arrays = [json.loads(x) for x in data.split('\n') if x]