- Java main() Method
- Java main() Method – public static void main(String[] args)
- Syntax of main() Method
- Java
- 1. Public
- Java
- 2. Static
- Java
- 3. Void
- Java
- 4. main
- Java
- 5. String[] args
- Java
- FAQs on Java main() Method
- Q1. Can the main method be int? If not, why?
- Java
- Java
- Explanation of the above programs:
- Q2. Can we execute a Java program without the main method?
- Q3. Can we declare the main() method without String[] args?
Java main() Method
Have you ever tried to reason why Java’s main() method is public , static and void ? Why its name is main ? What happens inside JVM when you invoke main() method? What is the purpose of main method? Let’s find out.
Since Java 21, we can create instance main() methods that do not require the public and static access modifiers, as well as, the method arguments are optional.
If we have not created the unnamed class, the discussion in this article still applies.
1. Java main() Method Syntax
Start with reminding the syntax of the main method in Java.
2. Why Java main Method is public?
This is a big question and perhaps most difficult to answer, too. I tried hard to find a good reason for this question in all the good learning material in my reach, but nothing proved enough.
So, my analysis says (like many others): the main method is public so that it can be accessible everywhere and to every object which may desire to use it for launching the application.
Here, I am not saying that JDK/JRE had this exact similar reason because java.exe or javaw.exe (for windows) can use Java Native Interface (JNI) to execute the invoke method for calling the main() method, so they can have invoked it, either way, irrespective of any access modifier.
A second way to answer this is another question, why not public? All methods and constructors in java have some access modifier. The main() method also needs one. There is no reason why it should not be public , and be any other modifier(default/protected/private).
Notice that if we do not make main() method public, there is no compilation error. You will runtime error because the matching main() method is not present. Remember that the whole syntax should match to execute main() method.
Error: Main method not found in class Main, please define the main method as: public static void main(String[] args)Another big question. To understand this, let suppose we do not have the main method as static . Now, to invoke any method you need an instance of it. Right?
Java can have overloaded constructors, we all know. Now, which one should be used, and from where the parameters for overloaded constructors will come. These are just more difficult questions, which helped Java designers to make up their minds and to have the main method as static .
Notice that if you do not make main() method static , there is no compilation error. You will runtime error.
Error: Main method is not static in class main, please define the main method as: public static void main(String[] args)Why should it not be void? Have you called this method from your code? NO. Then there is no use of returning any value to JVM, who actually invokes this method. It simply doesn’t need any returning value.
The only thing application would like to communicate to the invoking process is normal or abnormal termination. This is already possible using System.exit(int) . A non-zero value means abnormal termination otherwise everything was fine.
No rock-solid reason. Let us assume because it was already in use with C and C++ language. So, most developers were already comfortable with this name.
Otherwise, there is no other good reason.
6. What happens internally when you invoke main method?
The purpose of the main method in Java is to be a program execution start point.
When you run java.exe , then there are a couple of Java Native Interface (JNI) calls. These calls load the DLL that is really the JVM (that’s right – java.exe is NOT the JVM). JNI is the tool that we use when we have to bridge between the virtual machine world, and the world of C, C++, etc. The reverse is also true. It is not possible to actually get a JVM running without using JNI.
Basically, java.exe is a super simple C application that parses the command line, creates a new String array in the JVM to hold those arguments, parses out the class name that you specified as containing main() , uses JNI calls to find the main() method itself, then invokes the main() method, passing in the newly created string array as a parameter.
This is very, very much like what you do when you use the reflection from Java, it just uses confusingly named native function calls instead.
It would be perfectly legal for you to write your own version of java.exe (the source is distributed with the JDK), and have it do something entirely different.
7. main() method native code in java.c
Download and extract the source jar and check out ../launcher/java.c . It is something like this:
/* * Get the application's main class. */ if (jarfile != 0) < mainClassName = GetMainClassName(env, jarfile); . . mainClass = LoadClass(env, classname); if(mainClass == NULL) < /* exception occured */ . . /* Get the application's main method */ mainID = (*env)-&amp;amp;gt;GetStaticMethodID(env, mainClass, "main", "([Ljava/lang/String;)V"); . . /* Invoke main method. */ (*env)-&amp;amp;gt;CallStaticVoidMethod(env, mainClass, mainID, mainArgs);So, here you can see what happens when you invoke a java program with the main method.
Java’s main method is used by all developers and everybody knows the basic syntax to write it. Yet, very few completely understand the correct reasoning and the way it works.
In this post, we got a very basic understanding of the things behind the main method that is the primary starting point of an application.
Java main() Method – public static void main(String[] args)
In Java programs, the point from where the program starts its execution or simply the entry point of Java programs is the main() method. Hence, it is one of the most important methods of Java, and having a proper understanding of it is very important.
The Java compiler or JVM looks for the main method when it starts executing a Java program. The signature of the main method needs to be in a specific way for the JVM to recognize that method as its entry point. If we change the signature of the method, the program compiles but does not execute.
The execution of the Java program, the java.exe is called. The Java.exe in turn makes Java Native Interface or JNI calls, and they load the JVM. The java.exe parses the command line, generates a new String array, and invokes the main() method. A daemon thread is attached to the main method, and this thread gets destroyed only when the Java program stops execution.
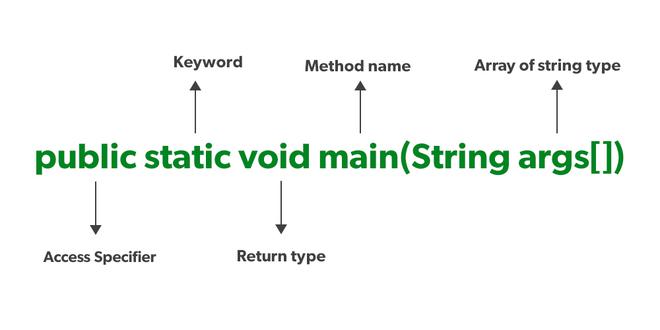
Syntax of main() Method
The most common in defining the main() method is shown in the below example.
Java
Every word in the public static void main statement has got a meaning in the JVM that is described below:
1. Public
It is an Access modifier, which specifies from where and who can access the method. Making the main() method public makes it globally available. It is made public so that JVM can invoke it from outside the class as it is not present in the current class.
Java
Error: Main method not found in class, please define the main method as: public static void main(String[] args) or a JavaFX application class must extend javafx.application.Application
2. Static
It is a keyword that is when associated with a method, making it a class-related method. The main() method is static so that JVM can invoke it without instantiating the class. This also saves the unnecessary wastage of memory which would have been used by the object declared only for calling the main() method by the JVM.
Java
Error: Main method is not static in class test, please define the main method as: public static void main(String[] args)
3. Void
It is a keyword and is used to specify that a method doesn’t return anything. As the main() method doesn’t return anything, its return type is void. As soon as the main() method terminates, the java program terminates too. Hence, it doesn’t make any sense to return from the main() method as JVM can’t do anything with the return value of it.
Java
Error: Main method not found in class, please define the main method as: public static void main(String[] args) or a JavaFX application class must extend javafx.application.Application
4. main
It is the name of the Java main method. It is the identifier that the JVM looks for as the starting point of the java program. It’s not a keyword.
Java
Error: Main method not found in class, please define the main method as: public static void main(String[] args) or a JavaFX application class must extend javafx.application.Application
5. String[] args
It stores Java command-line arguments and is an array of type java.lang.String class. Here, the name of the String array is args but it is not fixed and the user can use any name in place of it.
Java
Apart from the above-mentioned signature of main, you could use public static void main(String args[]) or public static void main(String… args) to call the main function in Java. The main method is called if its formal parameter matches that of an array of Strings.
FAQs on Java main() Method
Q1. Can the main method be int? If not, why?
Java
prg1.java:6: error: missing return statement > ^ 1 error
Java does not return int implicitly, even if we declare the return type of main as int. We will get a compile-time error
Java
Error: Main method must return a value of type void in class GeeksforGeeks, please define the main method as: public static void main(String[] args)
Now, even if we do return 0 or an integer explicitly ourselves, from int main. We get a run time error.
Explanation of the above programs:
The C and C++ programs which return int from main are processes of Operating System. The int value returned from main in C and C++ is exit code or exit status. The exit code of the C or C++ program illustrates, why the program was terminated. Exit code 0 means successful termination. However, the non-zero exit status indicates an error.
For Example exit code 1 depicts Miscellaneous errors, such as “divide by zero”.
The parent process of any child process keeps waiting for the exit status of the child. And after receiving the exit status of the child, cleans up the child process from the process table and free the resources allocated to it. This is why it becomes mandatory for C and C++ programs(which are processes of OS) to pass their exit status from the main explicitly or implicitly.
However, the Java program runs as a ‘main thread’ in JVM. The Java program is not even a process of Operating System directly. There is no direct interaction between the Java program and Operating System. There is no direct allocation of resources to the Java program directly, or the Java program does not occupy any place in the process table. Whom should it return an exit status to, then? This is why the main method of Java is designed not to return an int or exit status.
But JVM is a process of an operating system, and JVM can be terminated with a certain exit status. With help of java.lang.Runtime.exit(int status) or System.exit(int status).
Q2. Can we execute a Java program without the main method?
Yes, we can execute a Java program without a main method by using a static block.
A static block in Java is a group of statements that gets executed only once when the class is loaded into the memory by ClassLoader, It is also known as a static initialization block, and it goes into the stack memory.
Q3. Can we declare the main() method without String[] args?
Yes, we can declare the main() method without String[] args. Although it will generate an error message if we directly try to execute the main method inside the driver class as done in the below example.