- How to Round Numbers in Python?
- Round Numbers in Python using Built-in round() Function
- python3
- Round Numbers in Python using Truncation concept
- python3
- Round Numbers in Python using Math.ceil() and Math.floor() functions
- python3
- Round Numbers in Python using math.ceil
- python3
- Round Numbers in Python using math.floor
- python3
- Round Numbers in Python using Rounding Bias concept.
How to Round Numbers in Python?
Rounding a number means making the number simpler by keeping its value intact but closer to the next number. Below are the following points that will cover in this article using Python:
- using Built-in round() Function
- using Truncation concept
- using Math.ceil() and Math.floor() functions
- using math.ceil
- using math.floor
- using Rounding Bias concept
- Rounding Half Away From Zero in Python
Input: 3.5 Output: 4 Explanation: Nearest whole number. Input: 3.74 Output: 3.7 Explanation: Rounded to one decimal place.
Round Numbers in Python using Built-in round() Function
In Python, there is a built-in round() function that rounds off a number to the given number of digits. The function round() accepts two numeric arguments, n, and n digits, and then returns the number n after rounding it to n digits. If the number of digits is not provided for rounding off, the function rounds off the given number n to the nearest integer.
python3
Round Numbers in Python using Truncation concept
In this function, each digit after a given position is replaced with 0. python truncate() function can be used with positive as well as negative numbers. The truncation function can be implemented in the following way:
- Multiplying the number by 10^p (10 raised to the pth power) to shift the decimal point p places to the right.
- Taking the integer part of that new number using int().
- Shifting the decimal place p places back to the left by dividing by 10^p.
python3
Round Numbers in Python using Math.ceil() and Math.floor() functions
Math.ceil(): This function returns the nearest integer that is greater than or equal to a given number.
Math.floor(): This function returns the nearest integer less than or equal to a given number.
python3
Round Numbers in Python using math.ceil
In Rounding Up a number is rounded up to a specified number of digits. The rounding up function can be implemented in the following way:
- First, the decimal point in n is shifted to the correct number of places to the right by multiplying n by 10 ** decimals.
- The new value is rounded up to the nearest integer using math.ceil()
- Finally, the decimal point is shifted back to the left by dividing by 10 ** decimals.
python3
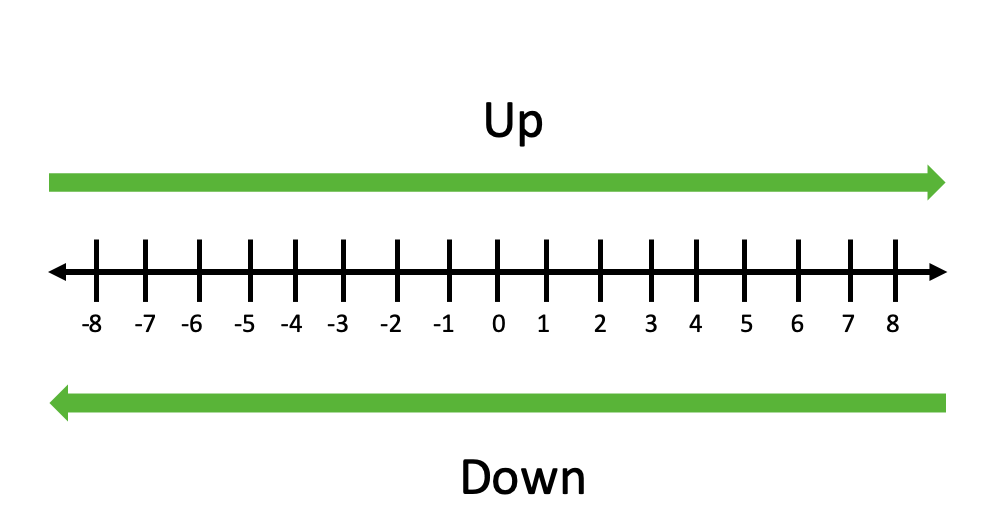
We can follow the diagram below to understand round up and round down. Round up to the right and down to the left.
Rounding up always rounds a number to the right on the number line and rounding down always rounds a number to the left on the number line.
Round Numbers in Python using math.floor
In Rounding Down a number is rounded down to a specified number of digits. The rounding down function can be implemented in the following way:
- First, the decimal point in n is shifted to the correct number of places to the right by multiplying n by 10 ** decimals.
- The new value is rounded up to the nearest integer using math.floor().
- Finally, the decimal point is shifted back to the left by dividing by 10 ** decimals.
python3
Round Numbers in Python using Rounding Bias concept.
The concept of symmetry introduces the notion of rounding bias, which describes how rounding affects numeric data in a dataset.
The rounding up strategy has a round towards positive infinity bias, as the value is always rounded up in the direction of positive infinity. Similarly, the rounding down strategy has a round towards negative infinity bias. The truncation strategy has a round towards negative infinity bias on positive values and a round towards positive infinity for negative values. Rounding functions with this behavior are said to have a round towards zero bias, in general.
a) Rounding Half Up concept in Python
The rounding half-up rounds every number to the nearest number with the specified precision and breaks ties by rounding up.
The rounding half-up strategy is implemented by shifting the decimal point to the right by the desired number of places. In this case, we will have to determine whether the digit after the shifted decimal point is less than or greater than equal to 5.
We can add 0.5 to the value which is shifted and then round it down with the math.floor() function.
Implementation of round_half_up() function: