- Java Guides
- YouTube Video
- 5. Prerequisites
- What we will build?
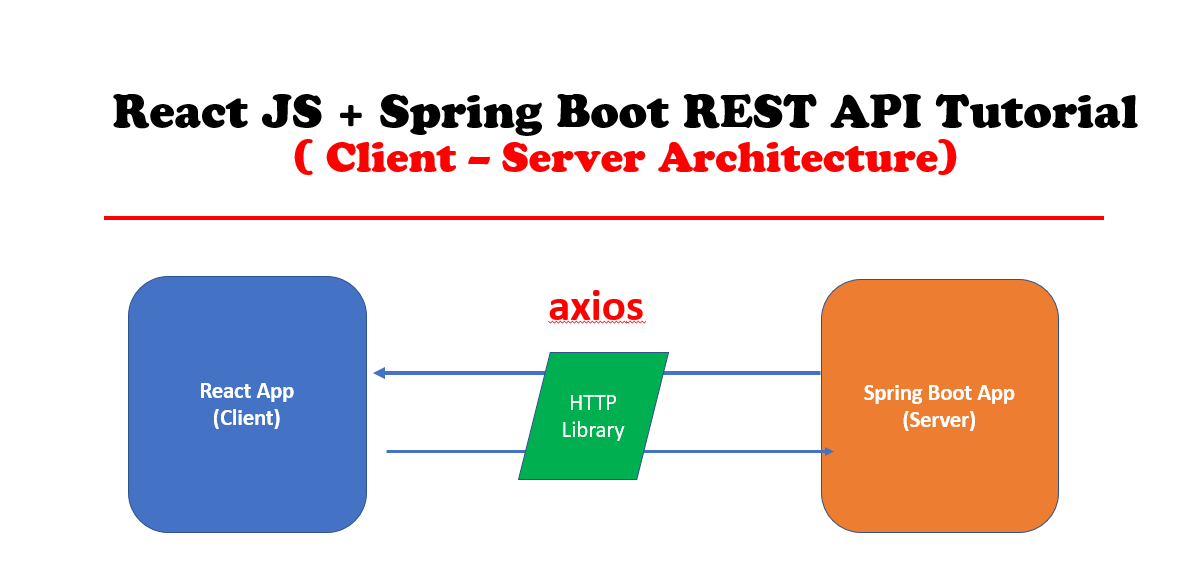
- Client-Server Architecture
- 1. Develop Spring Boot Backend Application
- 1. Create a Spring Boot Application
- 2. Add maven dependencies
- Create JPA Entity — User.java
- Create Spring Data JPA Repository — UserRepository.java
- Spring Controller with REST API — /api/users
- Run Spring Boot Application and Test Rest API
- Build React JS Frontend Application
- 1 — Create a React UI with Create React App
- Using npx
- Using npm
- Using Yarn
- 2 — Adding Bootstrap in React Using NPM
- src/index.js
- 3. React Service Component — REST API Call
- 4. Develop a React Component
- 5. App.js
- 6. Run React App
- Conclusion
Java Guides
In this tutorial, we will create a simple «single page application» using React as frontend and spring boot as backend.
If you want to use React Hooks in React App then check out React JS ( React Hooks) + Spring Boot Tutorial
As we know, React is a JavaScript-based library that does not have the ability to make HTTP requests; thus, we need to use third-party libraries to achieve this.
There are plenty of libraries available to make HTTP calls into React apps. A few of them are listed below.
- Axios
- Fetch
- Superagent
- React-axios
- Use-http
- React-request
YouTube Video
5. Prerequisites
- Basic familiarity with HTML & CSS
- Basic knowledge of JavaScript and programming
- Spring Boot Basics
- ReactJS basics
- Node.js and npm installed globally
What we will build?
Client-Server Architecture
1. Develop Spring Boot Backend Application
We will use Spring Data JPA to develop the repository layer and we use the H2 in-memory database to store the data.
1. Create a Spring Boot Application
There are many ways to create a Spring Boot application. You can refer to below articles to create a Spring Boot application.
2. Add maven dependencies
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion> parent> groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId> version>2.3.0.RELEASEversion> relativePath/> lookup parent from repository --> parent> groupId>net.javaguidesgroupId> artifactId>springboot-backendartifactId> version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion> name>springboot-backendname> description>Demo project for Spring Bootdescription> properties> java.version>1.8java.version> properties> dependencies> dependency> groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpaartifactId> dependency> dependency> groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> dependency> groupId>com.h2databasegroupId> artifactId>h2artifactId> scope>runtimescope> dependency> dependency> groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId> scope>testscope> exclusions> exclusion> groupId>org.junit.vintagegroupId> artifactId>junit-vintage-engineartifactId> exclusion> exclusions> dependency> dependencies> build> plugins> plugin> groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId> plugin> plugins> build> project>
Create JPA Entity — User.java
Create a new package called model inside net.javaguides.springboot package and then create the User class inside the model package with the following contents —
package net.javaguides.springboot.model; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.GenerationType; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Table; @Entity @Table(name = "users") public class User < @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private long id; @Column(name = "first_name") private String firstName; @Column(name = "last_name") private String lastName; private String email; public User() < >public User(String firstName, String lastName, String email) < super(); this.firstName = firstName; this.lastName = lastName; this.email = email; > public long getId() < return id; > public void setId(long id) < this.id = id; > public String getFirstName() < return firstName; > public void setFirstName(String firstName) < this.firstName = firstName; > public String getLastName() < return lastName; > public void setLastName(String lastName) < this.lastName = lastName; > public String getEmail() < return email; > public void setEmail(String email) < this.email = email; > >
Create Spring Data JPA Repository — UserRepository.java
Create a new package called repository inside net.javaguides.springboot package and then create the following interface inside the repository package —
package net.javaguides.springboot.repository; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import net.javaguides.springboot.model.User; @Repository public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepositoryUser, Long>
Spring Controller with REST API — /api/users
package net.javaguides.springboot.controller; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import net.javaguides.springboot.model.User; import net.javaguides.springboot.repository.UserRepository; @CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:3000") @RestController @RequestMapping("api/") public class UserController < @Autowired private UserRepository userRepository; @GetMapping("users") public List < User > getUsers() < return this.userRepository.findAll(); > >
@CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:3000")Run Spring Boot Application and Test Rest API
package net.javaguides.springboot; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import net.javaguides.springboot.model.User; import net.javaguides.springboot.repository.UserRepository; @SpringBootApplication public class SpringbootBackendApplication implements CommandLineRunner < public static void main(String[] args) < SpringApplication.run(SpringbootBackendApplication.class, args); > @Autowired private UserRepository userRepository; @Override public void run(String. args) throws Exception < this.userRepository.save(new User("Ramesh", "Fadatare", "ramesh@gmail.com")); this.userRepository.save(new User("Tom", "Cruise", "tom@gmail.com")); this.userRepository.save(new User("Tony", "Stark", "tony@gmail.com")); > >
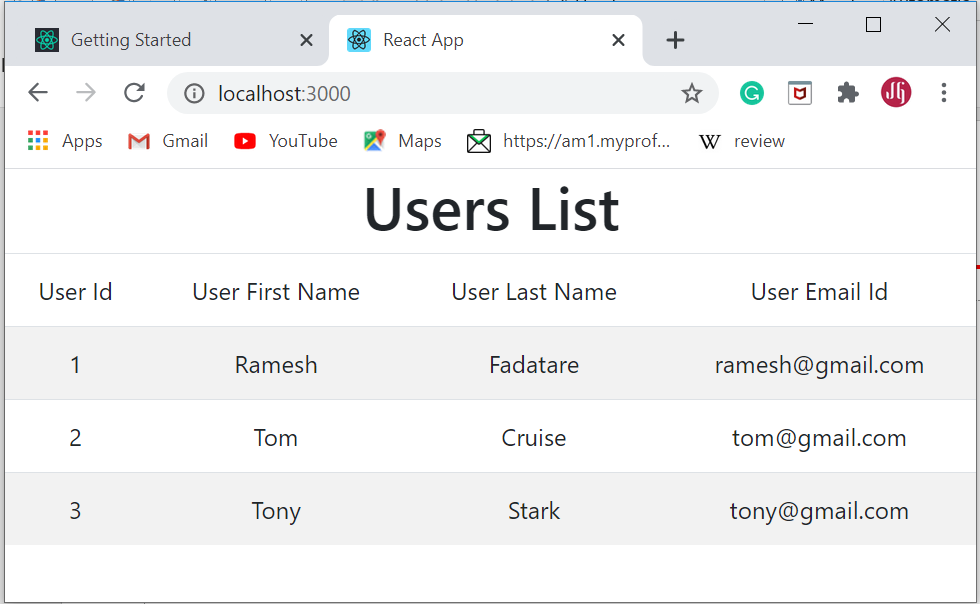
["id":1,"firstName":"Ramesh","lastName":"Fadatare","email":"ramesh@gmail.com">,"id":2,"firstName":"Tom","lastName":"Cruise","email":"tom@gmail.com">,"id":3,"firstName":"Tony","lastName":"Stark","email":"tony@gmail.com">]
Build React JS Frontend Application
1 — Create a React UI with Create React App
The Create React App CLI tool is an officially supported way to create single-page React applications. It offers a modern build setup with no configuration.
Using npx
npx create-react-app react-frontendUsing npm
npm init react-app react-frontend Using Yarn
yarn create react-app react-frontend Running any of these commands will create a directory called react-frontend inside the current folder. Inside that directory, it will generate the initial project structure and install the transitive dependencies:
react-frontend ├── README.md ├── node_modules ├── package.json ├── .gitignore ├── public │ ├── favicon.ico │ ├── index.html │ ├── logo192.png │ ├── logo512.png │ ├── manifest.json │ └── robots.txt └── src ├── App.css ├── App.js ├── App.test.js ├── index.css ├── index.js ├── logo.svg └── serviceWorker.js package.json — The package.json file contains all the required dependencies for our React JS project. Most importantly, you can check the current version of React that you are using. It has all the scripts to start, build, and eject our React app.
public folder — The public folder contains index.html . As react is used to build a single page application, we have this single HTML file to render all our components. Basically, it’s an HTML template. It has a div element with id as root and all our components are rendered in this div with index.html as a single page for the complete react app.
src folder— In this folder, we have all the global javascript and CSS files. All the different components that we will be building, sit here.
node_modules — All the packages installed by NPM or Yarn will reside inside the node_modules folder.
App.js — The App.js file contains the definition of our App component which actually gets rendered in the browser and this is the root component.
2 — Adding Bootstrap in React Using NPM
$ npm install bootstrap --save import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css';
src/index.js
import React from 'react'; import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'; import './index.css'; import App from './App'; import * as serviceWorker from './serviceWorker'; import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css'; ReactDOM.render( React.StrictMode> App /> /React.StrictMode>, document.getElementById('root') ); // If you want your app to work offline and load faster, you can change // unregister() to register() below. Note this comes with some pitfalls. // Learn more about service workers: https://bit.ly/CRA-PWA serviceWorker.unregister();
3. React Service Component — REST API Call
import axios from 'axios' const USERS_REST_API_URL = 'http://localhost:8080/api/users'; class UserService getUsers() return axios.get(USERS_REST_API_URL); > > export default new UserService();
export default new UserService();
4. Develop a React Component
Components are the building blocks of our whole react app. They are like functions that accept inputs in terms of props, state, and outputs a UI that is rendered in the browser. They are reusable and composable.
React components can be either a function component or a class component. In this example, we are going to use the class component.
import React from 'react'; import UserService from '../services/UserService'; class UserComponent extends React.Component constructor(props) super(props) this.state = users:[] > > componentDidMount() UserService.getUsers().then((response) => this.setState( users: response.data>) >); > render () return ( div> h1 className = "text-center"> Users List/h1> table className = "table table-striped"> thead> tr> td> User Id/td> td> User First Name/td> td> User Last Name/td> td> User Email Id/td> /tr> /thead> tbody> this.state.users.map( user => tr key = user.id>> td> user.id>/td> td> user.firstName>/td> td> user.lastName>/td> td> user.email>/td> /tr> ) > /tbody> /table> /div> ) > > export default UserComponent
constructor() — The constructor () is invoked before the component is mounted. In the constructor, we have declared our state variables and bind the different methods so that they are accessible from the state inside of the render() method.
componentDidMount() — The componentDidMount() is called as soon as the component is mounted and ready.
render() — The render() method is the most used lifecycle method. The render() method actually outputs HTML to the DOM.
this.state.users.map( user => tr key = user.id>> td> user.id>/td> td> user.firstName>/td> td> user.lastName>/td> td> user.email>/td> /tr> ) > 5. App.js
In the previous step, we have created UserComponent so let’s go ahead add UserComponent to the App component:
import React from 'react'; import logo from './logo.svg'; import './App.css'; import UserComponent from './components/UserComponent'; function App() return ( div className="App"> UserComponent /> /div> ); > export default App;
6. Run React App
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have created a simple «single page application» using React as frontend and spring boot as backend. We have also seen how to integrate React frontend application with spring boot backend using Axios HTTP library.
If you want to use React Hooks in React App then check out React JS ( React Hooks) + Spring Boot Tutorial