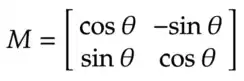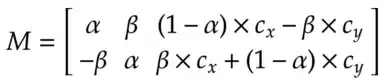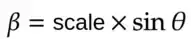- Python Pillow – Rotate Image 45, 90, 180, 270 degrees
- Syntax of PIL Image.rotate()
- Examples
- 1: Rotate given image by 45 degrees
- 2. Rotate image and adjust the output size
- 3. Rotate image by 90 degrees
- 4. Rotate image by 180 degrees
- Summary
- Как повернуть изображение используя Pillow
- Угол вращения картинки в Pillow
- Поворачиваем изображение полностью
- Фильтры NEAREST, BILINEAR и BICUBIC в Pillow
- Меняем центр изображения при её поворачивании
- How to Rotate Images with OpenCV and Python
- Rotate Images with OpenCV
- Summary
- Recent Posts
Python Pillow – Rotate Image 45, 90, 180, 270 degrees
To rotate an image by an angle with Python Pillow, you can use rotate() method on the Image object. rotate() method rotates the image in counter clockwise direction.
In this tutorial, we shall learn how to rotate an image, using PIL Python library, with the help of example programs.
Syntax of PIL Image.rotate()
The syntax of rotate() method is as shown in the following code block.
Image.rotate(angle, resample=0, expand=0, center=None, translate=None, fillcolor=None)- angle – In degrees counter clockwise.
- resample – An optional resampling filter. This can be one of PIL.Image.NEAREST (use nearest neighbour), PIL.Image.BILINEAR (linear interpolation in a 2×2 environment), or PIL.Image.BICUBIC (cubic spline interpolation in a 4×4 environment). If omitted, or if the image has mode “1” or “P”, it is set PIL.Image.NEAREST. See Filters.
- expand – Optional expansion flag. If true, expands the output image to make it large enough to hold the entire rotated image. If false or omitted, make the output image the same size as the input image. Note that the expand flag assumes rotation around the center and no translation.
- center – Optional center of rotation (a 2-tuple). Origin is the upper left corner. Default is the center of the image.
- translate – An optional post-rotate translation (a 2-tuple).
- fillcolor – An optional color for area outside the rotated image.
Examples
1: Rotate given image by 45 degrees
In the following example, we will rotate the image by 45 degrees in counter clockwise direction.
Python Program
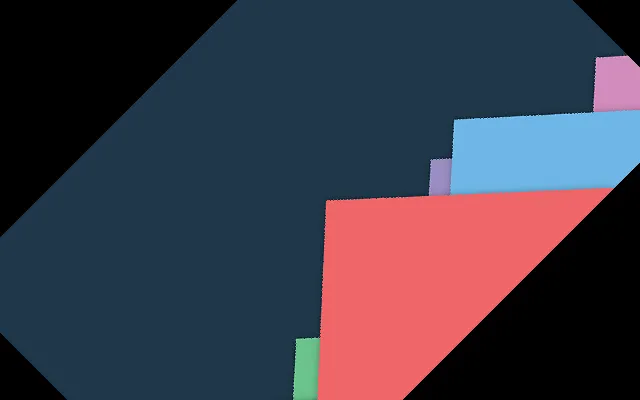
from PIL import Image #read the image im = Image.open("sample-image.png") #rotate image angle = 45 out = im.rotate(angle) out.save('rotate-output.png')Input Image – sample-image.png
Output Image – rotate-image.png
The size of the original image is preserved. You can make the size of the output image adjust to the rotation.
2. Rotate image and adjust the output size
In the following example, we will adjust the size of output image to the rotation, by using the parameter expand=True.
from PIL import Image #read the image im = Image.open("sample-image.png") #rotate image angle = 45 out = im.rotate(angle, expand=True) out.save('rotate-output.png')
3. Rotate image by 90 degrees
You can rotate an image by 90 degrees in counter clockwise direction by providing the angle=90. We also give expand=True, so that the rotated image adjusts to the size of output.
from PIL import Image #read the image im = Image.open("sample-image.png") #rotate image by 90 degrees angle = 90 out = im.rotate(angle, expand=True) out.save('rotate-output.png')4. Rotate image by 180 degrees
In this Python Pillow example, we will rotate the image by 180 degrees.
from PIL import Image #read the image im = Image.open("sample-image.png") #rotate image by 180 degrees angle = 180 out = im.rotate(angle, expand=True) out.save('rotate-output.png')
Summary
Concluding this tutorial of Python Examples, we learned how to rotate an image using Python PIL library.
Как повернуть изображение используя Pillow
Метод rotate() из модуля Image применяется для поворачивания изображения в зависимости от указанных градусов.
Загружаем и сохраняем картинку: guido-van-rossum.jpg
Данный код выведет наше изображение.
Угол вращения картинки в Pillow
В методе rotate() указываем угол вращения изображения в градусах в качестве первого аргумента. Направление вращения будет против часовой стрелки.
Есть вопросы по Python?
На нашем форуме вы можете задать любой вопрос и получить ответ от всего нашего сообщества!
Telegram Чат & Канал
Вступите в наш дружный чат по Python и начните общение с единомышленниками! Станьте частью большого сообщества!
Одно из самых больших сообществ по Python в социальной сети ВК. Видео уроки и книги для вас!
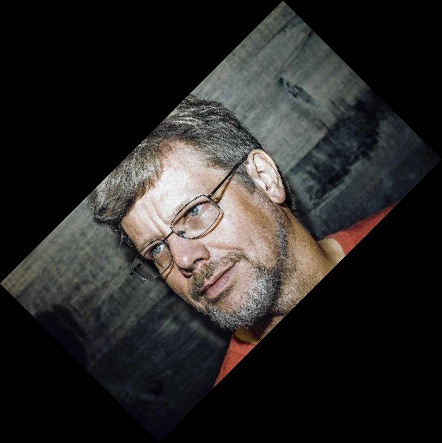
Поворачиваем изображение на 90 градусов:
Полученный результат с повернутой картинкой на 90 градусов против часовой стрелки:
Поворачиваем изображение на 45 градусов через PIL в Python:
Поворачиваем изображение полностью
Как видно на картинках в примерах выше, по умолчанию размер готового изображения равен размеру изначального изображения, а части повернутого изображения которые попали за пределами изначального размера отсекаются. Если мы поставим параметр expand на True , то повернутое изображение удовлетворит наши требования.
Теперь изображение выглядит так как мы ожидали. Она повернулась полностью, без черных границ по сторонам.
Поворачиваем изображение на 45 градусов.
Фильтры NEAREST, BILINEAR и BICUBIC в Pillow
Параметр resample можно использовать для указания определенного фильтра, который будет использоваться при поворачивании изображения.
С помощью фильтра Image.BICUBIC детали изображения станут более четким, чем в случае использования фильтра по умолчанию Image.NEAREST .
| Image.NEAREST | Image.BILINEAR | Image.BICUBIC |
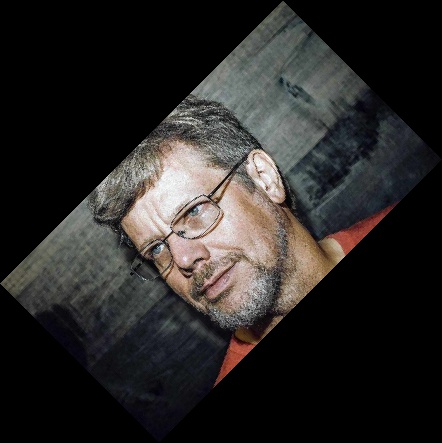 |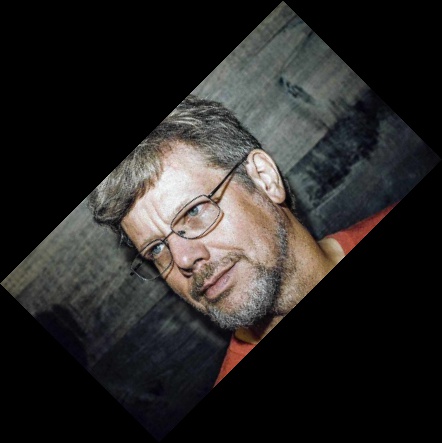  |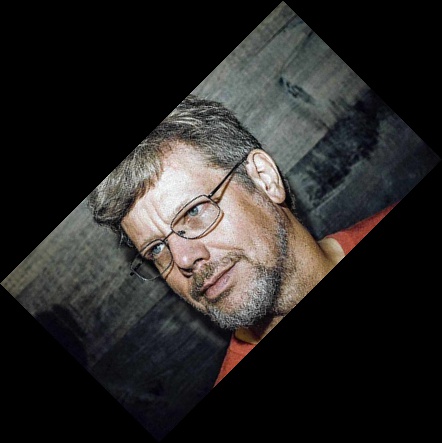  |
Небольшие различия есть, но у данной картинки они не очень видны. Но, например фильтр Image.BILINEAR сделал картинку более гладкой.
Меняем центр изображения при её поворачивании
Вы можете уточнить позицию центра изображения с помощью параметра center в методе rotate() .
How to Rotate Images with OpenCV and Python
In this tutorial, we will see how to rotate images with OpenCV using some built-in functions.
The first one is cv2.getRotationMatrix2D which, as its name suggests, will give us the transformation matrix that we will use to rotate the image. The second function is cv2.warpAffine, this function applies the rotation by using the transformation matrix.
This article is part 5 of the tutorial series on computer vision and image processing with OpenCV:
- How to Read, Write, and Save Images with OpenCV and Python
- How to Read and Write Videos with OpenCV and Python
- How to Resize Images with OpenCV and Python
- How to Crop Images with OpenCV and Python
- How to Rotate Images with OpenCV and Python (this article)
- How to Annotate Images with OpenCV and Python (coming soon)
- Bitwise Operations and Image Masking with OpenCV and Python
- Image Filtering and Blurring with OpenCV and Python
- Image Thresholding with OpenCV and Python
- Morphological Operations with OpenCV and Python
- Edge and Contour Detection with OpenCV and Python
Rotate Images with OpenCV
The image below will be used throughout this tutorial:
We can rotate an image by an angle θ by defining a transformation matrix M, which is defined as follows:
Using this matrix, we can rotate an image by an angle θ around the center of the image. However, OpenCV provides the ability to define any arbitrary rotation center and a scale factor to resize the image.
In this case, the transformation matrix become:
and Cx and Cy are the coordinates around which the image is rotated.
If you are wondering how we are going to create this matrix and calculate the rotation, don’t worry, the cv2.getRotationMatrix2D function creates the above transformation matrix for us and the cv2.warpAffine function uses the transformation matrix to apply the rotation to the image.
The cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, scale) function takes 3 arguments:
- center: the center of rotation of the source image.
- angle: the rotation angle in degrees. providing positive values will rotate the image counter-clockwise.
- scale: an isotropic scale factor to resize the image.
The cv2.warpAffine(src, M, dsize, dst, flags, borderMode, borderValue) function takes 3 required arguments and 4 optional arguments:
- src: (required) the input mage.
- M: (required) the transformation matrix.
- dsize: (required) size of the output image.
- dst: (optional) the output image with size dsize.
- flags: (optional) combination of interpolation methods.
- borderMode: (optional) the pixel extrapolation method.
- borderValue: (optional) the value used in case of a constant border.
Let’s now write some code to see a concrete example of how to do image rotation with OpenCV:
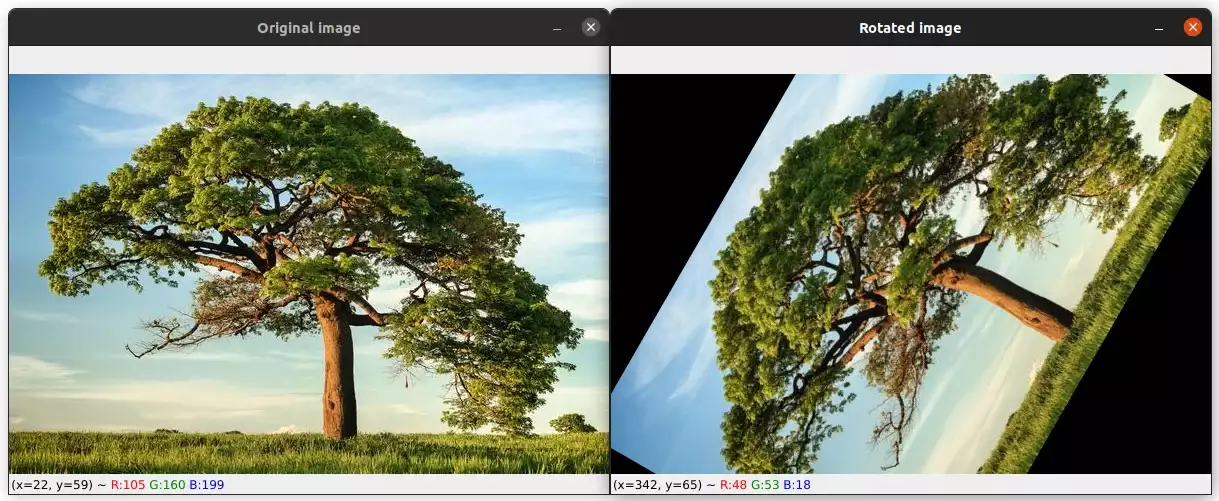
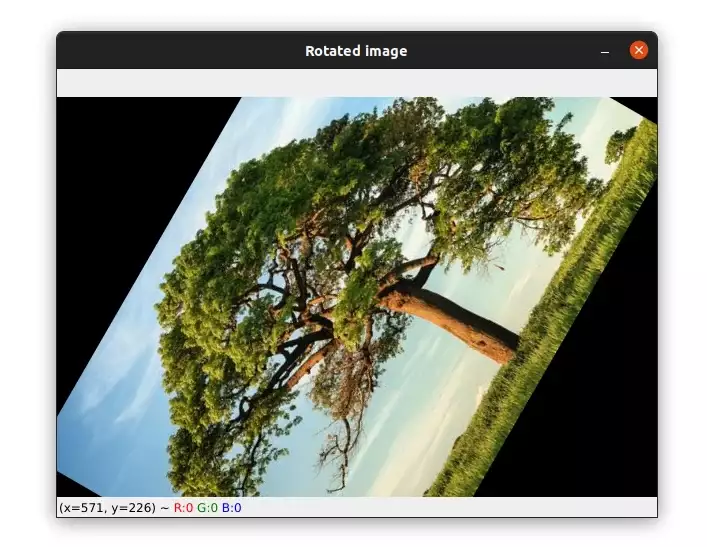
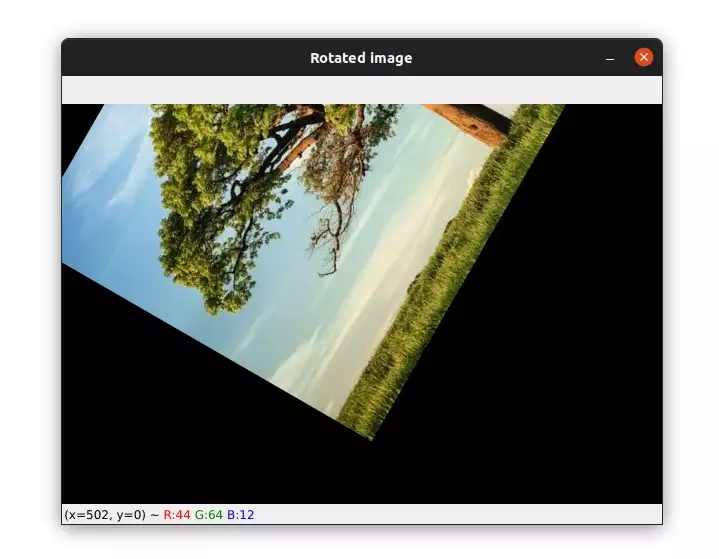
import cv2 image = cv2.imread("image2.jpg") height, width = image.shape[:2] # get the center of the image center_x, center_y = (width/2, height/2) # rotate the image by 60 degrees counter-clockwise around the center of the image M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((center_x, center_y), 60, 1.0) rotated_image = cv2.warpAffine(image, M, (width, height)) cv2.imshow("Rotated image", rotated_image) cv2.waitKey(0)We start by reading the image and getting its width and height.
Next, we calculate the center of the image which will be used as the rotation point. Please note that we can use any other point for rotation as mentioned above.
Then we used the cv2.getRotationMatrix2D to define a rotation matrix M. We need to give it the center of rotation as the first argument. The second argument is the angle in degrees by which we want to rotate the image. In this case, the image will be rotated 60 degrees counter-clockwise.
The third argument is the scale factor. 1.0 means the output image will be the same size as the input image, 2.0 means the output image will be double the size of the input image.
Finally, we apply the rotation matrix M to our image using the cv2.warpAffine function. The function takes three arguments.
The first one is the input image. The second and third arguments are the rotation matrix M and the size of the output image respectively.
The image below shows the result of this rotation:
Let’s see another example of rotation using a scale of 0.5:
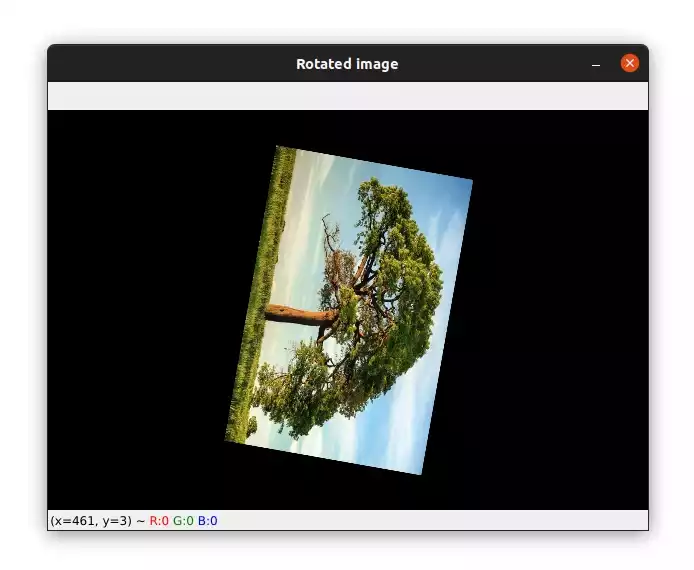
# rotate the image by 100 degrees clockwise around the center # of the image and divide the size of the image by half M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((center_x, center_y), -100, 0.5) rotated_image = cv2.warpAffine(image, M, (width, height))The image will be rotated 100 degrees clockwise around the center of rotation and the size of the output image will be half of the input image.
let’s see a final example in which we use a different center of rotation:
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((100, 100), 60, 1.0) rotated_image = cv2.warpAffine(image, M, (width, height))In this example, the image will be rotated around x=100 and y=100. Please note that the coordinate origin is located at the top-left corner.
Here is what the output image looks like:
Summary
To rotate an image with OpenCV, we first created a 2D rotation matrix using the cv2.getRotationMatrix2D function. We then applied an affine transformation using the cv2.warpAffine function to rotate the image.
If you want to learn more about computer vision and image processing then check out my course Computer Vision and Image Processing with OpenCV and Python.
If you need help, don’t hesitate to ask in the comment section.
Search
Recent Posts
Hi, I’m Yacine Rouizi — a self-taught developer passionate about machine learning, deep learning, and computer vision. My mission is to make these complex topics accessible to everyone through hands-on tutorials and clear explanations.

In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn everything you need to know to master YOLO. With detailed explanations, practical examples, and step-by-step tutorials, this book will help you build your understanding of YOLO from the ground up.
Discover how to train the YOLO model to accurately detect and recognize license plates in images and real-time videos.