- How to Upload Files in Python?
- Method 1: Using the Python’s os Module:
- Python code [upload_script.py]:
- Method 2: Using the Requests library:
- Method 3: Using Filestack API:
- Uploading Multiple Files in Python:
- Как загружать файлы с помощью библиотеки запросов Python
- Загрузка одного файла с помощью библиотеки запросов Python
- Загрузка нескольких файлов с помощью Python библиотеки requests
- Заключение
- Источник:
How to Upload Files in Python?
File uploading is an essential utility every developer should know. Various software applications require uploading files to do certain operations. Several desktops and web applications demand uploading files from the client or the users in the form of a regular file (e.g., an audio file, an image file, text file, etc.) Most uploading of files refers to applications that use the internet.
Python supports different libraries that simplify data transfer over HTTP. There are three different packages that developers can use to upload a file in a python program.
Uploading Files through a Python program:
There are various ways of uploading files through a python program. Some might require the support of HTML script and buttons while others can directly upload files through the program itself.
Method 1: Using the Python’s os Module:
In this method, we have to use the HTML code to set specific actions. HTML caters to a variety of attributes for different HTML elements. We have to use the along with the action attribute to set the Python program for execution. Also, the enctype attribute with «multi-part/form-data» value will help the HTML form to upload a file. Lastly, we need the input tag with the filename attribute to upload the file we want.
Here is our HTML code:
Uploading file by executing a Python script Lastly, we need the input tag with the filename attribute to upload the file we want. The os module in Python allows the Python program to interact with the system. As our file resides as a part of our operating system, we need to use the os module in our Python program.
Python code [upload_script.py]:
import os fi = form['filename'] if fi.filename: # This code will strip the leading absolute path from your file-name fil = os.path.basename(fi.filename) # open for reading & writing the file into the server open(fn, 'wb').write(fi.file.read())Explanation:
Here, we have first imported the OS module so that we can deal with the operating system related operations. Next, we have to create an identifier that will hold the filename for uploading. Now, using the if condition, we have to check whether the file name exists or not.
If yes, we will use the os.path.basename() to extract the filename by striping the leading absolute path from the file. We will then use another identifier to store that path. Now, we can open the file for reading and writing it into the server.
Method 2: Using the Requests library:
The requests module contains many predefined methods that allow developers to send HTTP requests using Python. The HTTP request delivers a response object containing response data such as encoding, content, status, etc. Using this, you do not need to manually append query strings for the URLs or any other form-encoding for the PUT & POST data. Since it is not a built-in library, we have to install it using the pip.
Now, you can create the Python file and import the requests into your program.
import requests dfile = open("datafile.txt", "rb") url = "http://httpbin.org/post" test_res = requests.post(url, files = ) if test_res.ok: print(" File uploaded successfully ! ") print(test_res.text) else: print(" Please Upload again ! ")Explanation:
This technique uses the requests library and for using it, we have to import it in our Python program. Then, we will open our file (datafile.txt) in read binary mode. Next, define a string identifier that stores the URL. Then, we have to call the post() method and pass the URL and the opened file (as a Python dictionary).
Now, we will check whether test_res (test result) is Ok or not. If It is OK, then we will print a success message along with the resultant text. Otherwise, we will prompt the user to upload it again.
Method 3: Using Filestack API:
We can also use the Python SDK and call the filestack API (Application Programming Interface) to upload files through the Python program. To obtain this SDK, you need to install it using the PIP command.
pip install filestack-pythonOnce you have installed the filestack SDK, you have to begin it with your Python program. Then you have to create an instance of the Client using the Filestack API key. This Client will perform the heavy operations for you in this program.
from filestack import Client c = Client("API's Key") filelnk = c.upload(filepath = '/path/of/file.png') print(filelnk.url)Make sure you replace the «API’s Key» with the actual API key you generate before writing the program.
Explanation:
Filestack API requires importing in our Python Program. Once we import the Client module from the filestack, we will provide the API key (the one we will receive at the time of registration). Store it in a separate variable. Next, connect to the file link that you want to upload and set the file path as athe argument value in the upload() method. Finally, display the filelnk file.
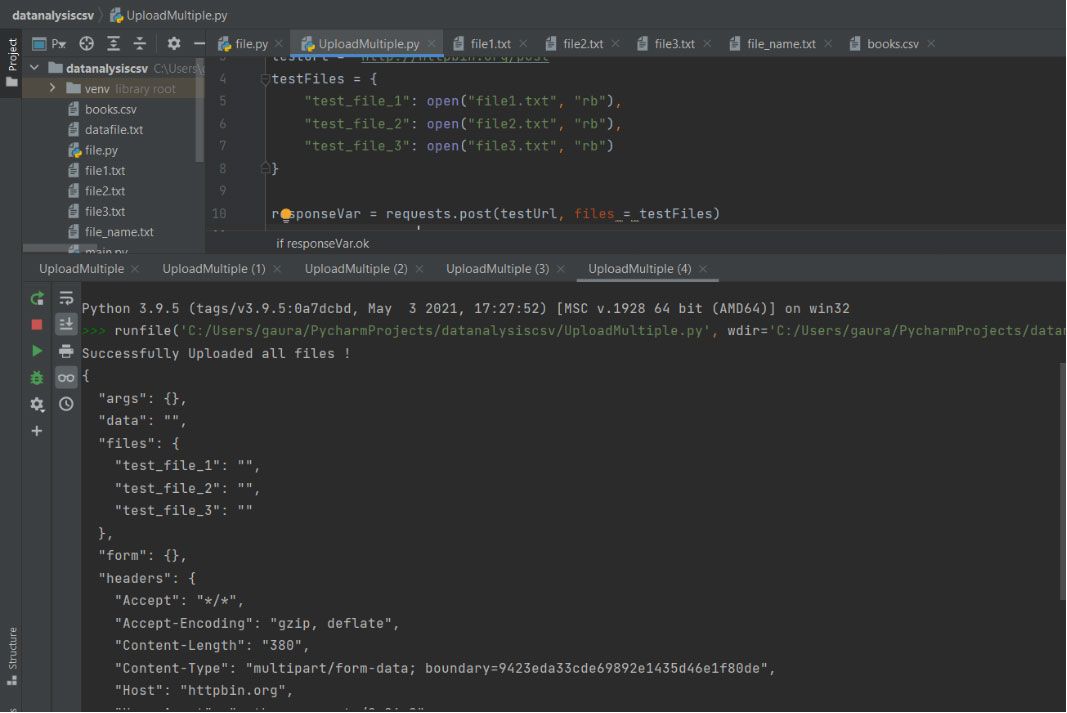
Uploading Multiple Files in Python:
Now, since you have got a basic understanding of how to deal with uploading a single file in Python, let us now move to a new topic – uploading multiple files in Python. Here, we will use the Python script to fetch the file from your system. In this section, you will use the requests library.
import requests testUrl = "http://httpbin.org/post" testFiles = < "test_file_1": open("file1.txt", "rb"), "test_file_2": open("file2.txt", "rb"), "test_file_3": open("file3.txt", "rb") >responseVar = requests.post(testUrl, files = testFiles) if responseVar.ok: print("Successfully Uploaded all files !") print(responseVar.text) else: print("Upload failed !")Explanation:
Here, we will first import the requests module. Then, we will use the testUrl variable to put the post HTTP request. Then we will create a dictionary by the name testFiles that will have three key-value pairs where the keys will be the file-id and values are the file names.
Then we will execute the post request method that will have two parameters, the testUrl and the files that will hold multiple filenames and store the entire return value in the responseVar. Then, we will check whether the responseVar is executing smoothly or not.
If yes, then a success message will be displayed using the print() along with the responseVar.text(). Otherwise, it will return an error or failure message using the print(). In this technique, you simply have to name the files in the dictionary value to upload them all at once.
Among all these methods, API calls (third method) take the maximum time and hence the least efficient. The first technique is explicitly used in web application development and the second technique is used in desktop or stand-alone application development. The OS module is faster as compared to the requests library because it uses frequent system calls and is closer to machine. But for file uploading purpose, the request module is easy to use.
- Learn Python Programming
- Null Object in Python
- TypeError: ‘int’ object is not subscriptable
- Python Comment
- Python Continue Statement
- Armstrong Number in Python
- Python Uppercase
- Python String find
- Python String Concatenation
- Python Enumerate
- Python input()
- Python eval
- Install Opencv Python PIP Windows
- Python String Title() Method
- Id() function in Python
- Area of Circle in Python
- Bubble Sort in Python
- Remove Punctuation Python
- Python Infinity
- Python Return Outside Function
Как загружать файлы с помощью библиотеки запросов Python
Python поддерживается многими библиотеками, которые упрощают передачу данных по HTTP. Библиотека requests является одним из наиболее популярных пакетов Python, и широко используется в веб — парсинге. Он также популярен для взаимодействия с серверами! Библиотека позволяет легко загружать данные в популярном формате, таком как JSON, но также упрощает загрузку файлов.
В этом руководстве мы рассмотрим, как загружать файлы с помощью библиотеки Python requests . Статья начнется с описания библиотеки и сигнатуры функции post() . Далее мы расскажем, как загрузить один файл с помощью пакета requests . И последнее, но не менее важное: мы загружаем несколько файлов за один запрос.
Загрузка одного файла с помощью библиотеки запросов Python
В этом руководстве рассказывается, как отправлять файлы, нас не волнует, как они создаются. Чтобы продолжить, создайте три файла с именами my_file.txt , my_file_2.txt и my_file_3.txt .
Первое, что нам нужно сделать, это установить нашу библиотеку request в нашу рабочую область. Хотя в этом нет необходимости, рекомендуется устанавливать библиотеки в виртуальной среде:
Активируйте виртуальную среду, чтобы мы больше не влияли на глобальную установку Python:
Теперь давайте установим библиотеку requests с помощью pip :
Создайте новый файл с именем single_uploader.py , в котором будет храниться наш код. В этом файле давайте начнем с импорта библиотеки requests :
Теперь мы готовы загрузить файл! При загрузке файла нам нужно открыть файл и выполнить потоковую передачу содержимого. В конце концов, мы не можем загрузить файл, к которому у нас нет доступа. Сделаем это с помощью функции open() .
Функция open() принимает два параметра: путь к файлу и режим. Путь к файлу может быть абсолютным или относительным путем к тому месту, где выполняется сценарий. Если вы загружаете файл в тот же каталог, вы можете просто использовать имя файла.
Второй аргумент, режим, будет принимать значение «read binary», которое представлено rb . Этот аргумент сообщает компьютеру, что мы хотим открыть файл в режиме чтения, и мы хотим использовать данные файла в двоичном формате:
test_file = open("my_file.txt", "rb") Примечание: важно читать файл в двоичном режиме. Библиотека requests обычно определяет заголовок Content-Length , который представляет собой значение в байтах. Если файл не читается в байтовом режиме, библиотека может получить неверное значение для Content-Length , что приведет к ошибкам при отправке файла.
В этом руководстве мы будем делать запросы к бесплатному сервису httpbin. Этот API позволяет разработчикам тестировать свои HTTP-запросы. Давайте создадим переменную, которая хранит URL-адрес, по которому мы будем размещать наши файлы:
test_url = "http://httpbin.org/post" Теперь у нас есть все, чтобы сделать запрос. Мы будем использовать метод post() библиотеки requests для загрузки файла. Чтобы это работало, нам нужны два аргумента: URL-адрес сервера и свойство files . Также сохраним ответ в переменной, напишем следующий код:
test_response = requests.post(test_url, files = ) Свойство files принимает словарь. Ключ — это имя поля формы, которое принимает файл. Значение — это байты открытого файла, который вы хотите загрузить.
Обычно, чтобы проверить, был ли ваш метод post() успешным, мы проверяем HTTP код статуса ответа. Мы можем использовать свойство ok объекта ответа test_url . Если он True , мы распечатаем ответ HTTP-сервера, в этом случае он отобразит запрос:
if test_response.ok: print("Upload completed successfully!") print(test_response.text) else: print("Something went wrong!") Давай попробуем! В терминале выполните свой скрипт с помощью команды python :
Ваш результат будет примерно таким:
Upload completed successfully! < "args": <>, "data": "", "files": < "form_field_name": "This is my file\nI like my file\n" >, "form": <>, "headers": < "Accept": "*/*", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Content-Length": "189", "Content-Type": "multipart/form-data; boundary=53bb41eb09d784cedc62d521121269f8", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "python-requests/2.25.0", "X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-5fc3c190-5dea2c7633a02bcf5e654c2b" >, "json": null, "origin": "102.5.105.200", "url": "http://httpbin.org/post" > В качестве проверки работоспособности вы можете убедиться, что значение form_field_name соответствует тому, что находится в вашем файле.
Загрузка нескольких файлов с помощью Python библиотеки requests
Загрузка нескольких файлов с помощью requests очень похожа на загрузку одного файла, с основным отличием в том, что мы используем списки. Создайте новый файл с именем multi_uploader.py и следующий код внутри:
import requests test_url = "http://httpbin.org/post" Теперь создайте переменную словарь под названием test_files с несколькими именами и файлами:
Как и раньше, ключи — это имена полей формы, а значения — файлы в байтах.
Мы также можем создавать переменные наших файлов в виде списка кортежей. Каждый кортеж содержит имя поля формы, принимающего файл, за которым следует содержимое файла в байтах:
test_files = [("test_file_1", open("my_file.txt", "rb")), ("test_file_2", open("my_file_2.txt", "rb")), ("test_file_3", open("my_file_3.txt", "rb"))] Любой вариант работает, поэтому выберите тот, который вам больше нравится!
Когда список файлов будет готов, вы можете отправить запрос и проверить его ответ, как и раньше:
test_response = requests.post(test_url, files = test_files) if test_response.ok: print("Upload completed successfully!") print(test_response.text) else: print("Something went wrong!") Выполните этот скрипт с помощью команды:
Upload completed successfully! < "args": <>, "data": "", "files": < "test_file_1": "This is my file\nI like my file\n", "test_file_2": "All your base are belong to us\n", "test_file_3": "It's-a me, Mario!\n" >, "form": <>, "headers": < "Accept": "*/*", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Content-Length": "470", "Content-Type": "multipart/form-data; boundary=4111c551fb8c61fd14af07bd5df5bb76", "Host": "httpbin.org", "User-Agent": "python-requests/2.25.0", "X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-5fc3c744-30404a8b186cf91c7d239034" >, "json": null, "origin": "102.5.105.200", "url": "http://httpbin.org/post" > Заключение
В этой статье мы узнали, как загружать файлы в Python с помощью библиотеки requests . Если это один файл или несколько файлов, требуется лишь несколько настроек метода post() . Мы также проверили наш ответ, чтобы убедиться, что загрузка прошла успешно.