- Extract, replace, convert elements of a list in Python
- Basics of list comprehensions
- Apply operation to all elements of the list
- Extract/remove elements that meet the conditions from the list
- Replace/convert elements that meet the conditions in the list
- Python: Replace Item in List (6 Different Ways)
- Replace an Item in a Python List at a Particular Index
- Replace a Particular Value in a List in Python Using a For Loop
- Replace a Particular Value in a List in Python Using a List Comprehension
- Change All Values in a List in Python Using a Function
- Replace Multiple Values in a Python List
- Replace Multiple Values with Multiple Values in a Python List
- Conclusion
- Additional Resources
Extract, replace, convert elements of a list in Python
In Python, list comprehensions allow you to create a new list by extracting, removing, replacing, or converting elements from an existing list based on specific conditions.
The sample code in this article uses the following list as an example.
l = list(range(-5, 6)) print(l) # [-5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] Refer to the following article for examples involving lists of strings.
You can also randomly sample elements from a list.
Basics of list comprehensions
In Python, you can create a list using list comprehensions. It is simpler than using the for loop.
[expression for variable_name in iterable if condition] expression is applied to the elements in iterable (list, tuple, etc.) that satisfy condition , creating a new list. The if condition can be omitted; if omitted, expression is applied to all elements.
See the following article for details on list comprehensions.
Apply operation to all elements of the list
If you write the desired operation in the expression part of list comprehensions, that operation is applied to all the elements of the list.
l_square = [i**2 for i in l] print(l_square) # [25, 16, 9, 4, 1, 0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25] l_str = [str(i) for i in l] print(l_str) # ['-5', '-4', '-3', '-2', '-1', '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5'] You can use this to convert a list of numbers to a list of strings. See the following article for details.
Extract/remove elements that meet the conditions from the list
If you just want to select elements by condition , you do not need to process them with expression , so you can write it as follows.
[variable_name for variable_name in original_list if condition] Only elements that satisfy the conditions (returning True for condition ) are extracted, creating a new list.
l_even = [i for i in l if i % 2 == 0] print(l_even) # [-4, -2, 0, 2, 4] l_minus = [i for i in l if i 0] print(l_minus) # [-5, -4, -3, -2, -1] If if condition is changed to if not condition , only elements that do not meet the condition (elements that return False for condition ) are extracted. This is equivalent to removing elements that meet the condition.
l_odd = [i for i in l if not i % 2 == 0] print(l_odd) # [-5, -3, -1, 1, 3, 5] l_plus = [i for i in l if not i 0] print(l_plus) # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] Of course, you can specify an equivalent condition without using not .
l_odd = [i for i in l if i % 2 != 0] print(l_odd) # [-5, -3, -1, 1, 3, 5] l_plus = [i for i in l if i >= 0] print(l_plus) # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] You can also connect multiple conditions with or or and . Negation not can also be used.
l_minus_or_even = [i for i in l if (i 0) or (i % 2 == 0)] print(l_minus_or_even) # [-5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 2, 4] l_minus_and_odd = [i for i in l if (i 0) and not (i % 2 == 0)] print(l_minus_and_odd) # [-5, -3, -1] Replace/convert elements that meet the conditions in the list
If you want to replace or convert elements that meet the condition without changing elements that do not meet the condition, use conditional expressions in the expression part of the list comprehensions.
In Python, conditional expressions can be written as follows:
X is value or expression for True , and Y is value or expression for False .
a = 80 x = 100 if a > 50 else 0 print(x) # 100 b = 30 y = 100 if b > 50 else 0 print(y) # 0 Use list comprehensions and conditional expressions:
[X if condition else Y for variable_name in original_list] The part enclosed in parentheses represents conditional expressions. However, parentheses are not necessary in the actual code.
[(X if condition else Y) for variable_name in original_list] If you write variable_name in X or Y , the value of the original element is used as it is, and if you write some expression, that expression is applied.
l_replace = [100 if i > 0 else i for i in l] print(l_replace) # [-5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100] l_replace2 = [100 if i > 0 else 0 for i in l] print(l_replace2) # [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100] l_convert = [i * 10 if i % 2 == 0 else i for i in l] print(l_convert) # [-5, -40, -3, -20, -1, 0, 1, 20, 3, 40, 5] l_convert2 = [i * 10 if i % 2 == 0 else i / 10 for i in l] print(l_convert2) # [-0.5, -40, -0.3, -20, -0.1, 0, 0.1, 20, 0.3, 40, 0.5] Python: Replace Item in List (6 Different Ways)
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use Python to replace an item or items in a list. You’l learn how to replace an item at a particular index, how to replace a particular value, how to replace multiple values, and how to replace multiple values with multiple values.
Being able to work with lists is an important skill for any Python developer, given how prevalent and understandable these Python data structures are.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have learned:
- How to use list assignment to replace an item in a Python list
- How to use for loops and while loops to replace an item in a Python list
- How to replace multiple items in a list
Replace an Item in a Python List at a Particular Index
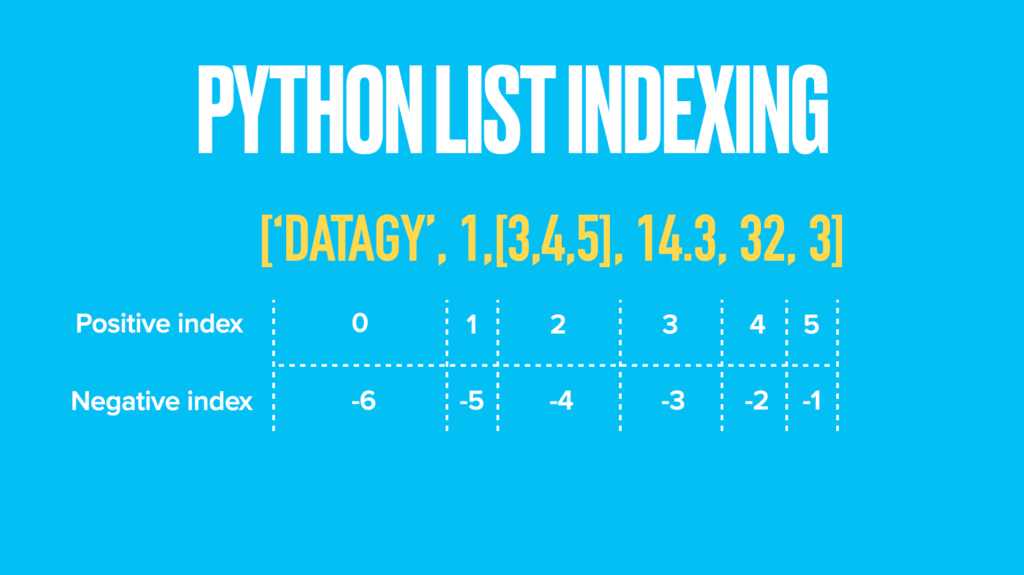
Python lists are ordered, meaning that we can access (and modify) items when we know their index position. Python list indices start at 0 and go all the way to the length of the list minus 1.
You can also access items from their negative index. The negative index begins at -1 for the last item and goes from there. To learn more about Python list indexing, check out my in-depth overview here.
If we want to replace a list item at a particular index, we can simply directly assign new values to those indices.
Let’s take a look at what that looks like:
# Replace an item at a particular index in a Python list a_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] # Mofidy first item a_list[0] = 10 print(a_list) # Returns: [10, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] # Modify last item a_list[-1] = 99 print(a_list) # Returns: [10, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 99]In the next section, you’ll learn how to replace a particular value in a Python list using a for loop.
Want to learn how to use the Python zip() function to iterate over two lists? This tutorial teaches you exactly what the zip() function does and shows you some creative ways to use the function.
Replace a Particular Value in a List in Python Using a For Loop
Python lists allow us to easily also modify particular values. One way that we can do this is by using a for loop.
One of the key attributes of Python lists is that they can contain duplicate values. Because of this, we can loop over each item in the list and check its value. If the value is one we want to replace, then we replace it.
Let’s see what this looks like. In our list, the word apple is misspelled. We want to replace the misspelled version with the corrected version.
# Replace a particular item in a Python list a_list = ['aple', 'orange', 'aple', 'banana', 'grape', 'aple'] for i in range(len(a_list)): if a_list[i] == 'aple': a_list[i] = 'apple' print(a_list) # Returns: ['apple', 'orange', 'apple', 'banana', 'grape', 'apple']Let’s take a look at what we’ve done here:
- We loop over each index in the list
- If the index position of the list is equal to the item we want to replace, we re-assign its value
In the next section, you’ll learn how to turn this for loop into a Python list comprehension.
Want to learn more about Python for-loops? Check out my in-depth tutorial that takes your from beginner to advanced for-loops user! Want to watch a video instead? Check out my YouTube tutorial here.
Replace a Particular Value in a List in Python Using a List Comprehension
One of the key attributes of Python list comprehensions is that we can often turn for loops into much shorter comprehensions. Let’s see how we can use a list comprehension in Python to replace an item in a list.
We’ll use the same example we used in the for loop, to help demonstrate how elegant a Python list comprehension can be:
# Replace a particular item in a Python list using a list comprehension a_list = ['aple', 'orange', 'aple', 'banana', 'grape', 'aple'] a_list = ['apple' if item == 'aple' else item for item in a_list] print(a_list) # Returns: ['apple', 'orange', 'apple', 'banana', 'grape', 'apple']We can see here that there are two main benefits of list comprehensions compared to for loops:
- We don’t need to initialize an empty list
- The comprehension reads in a relatively plain English
In the next section, you’ll learn how to change all values in a list using a formula.
Want to learn more about Python list comprehensions? Check out this in-depth tutorial that covers off everything you need to know, with hands-on examples. More of a visual learner, check out my YouTube tutorial here.
Change All Values in a List in Python Using a Function
Neither of the approaches above are immediately clear as to what they are doing. Because of this, developing a formula to do this is a helpful approach to help readers of your code understand what it is you’re doing.
Let’s take a look at how we can use the list comprehension approach and turn it into a formula:
# Replace a particular item in a Python list using a function a_list = ['aple', 'orange', 'aple', 'banana', 'grape', 'aple'] def replace_values(list_to_replace, item_to_replace, item_to_replace_with): return [item_to_replace_with if item == item_to_replace else item for item in list_to_replace] replaced_list = replace_values(a_list, 'aple', 'apple') print(replaced_list) # Returns: ['apple', 'orange', 'apple', 'banana', 'grape', 'apple']Here, we simply need to pass in the list, the item we want to replace, and the item we want to replace it with. The function name makes it easy to understand what we’re doing, guiding our readers to better understand our actions.
In the next section, you’ll learn how to replace multiple values in a Python list.
Replace Multiple Values in a Python List
There may be many times when you want to replace not just a single item, but multiple items. This can be done quite simply using the for loop method shown earlier.
Let’s take a look at an example where we want to replace all known typos in a list with the word typo .
# Replace multiple items in a Python list with the same value a_list = ['aple', 'ornge', 'aple', 'banana', 'grape', 'aple'] for i in range(len(a_list)): if a_list[i] in ['aple', 'ornge']: a_list[i] = 'typo' print(a_list) # Returns: ['typo', 'typo', 'typo', 'banana', 'grape', 'typo']Similar to the for loop method shown earlier, we check whether or not an item is a typo or not and replace its value.
In the next section, you’ll learn how to replace multiple values in a Python list with different values.
Replace Multiple Values with Multiple Values in a Python List
The approach above is helpful if we want to replace multiple values with the same value. There may be times where you want to replace multiple values with different values.
Looking again at our example, we may want to replace all instances of our typos with their corrected spelling. We can again use a for loop to illustrate how to do this.
Instead of using a single if statement, we’ll nest in some elif statements that check for a value’s value before replacing.
# Replace multiple items in a Python list with the different values a_list = ['aple', 'ornge', 'aple', 'banana', 'grape', 'aple'] for i in range(len(a_list)): if a_list[i] == 'aple': a_list[i] = 'apple' elif a_list[i] == 'ornge': a_list[i] = 'orange' print(a_list) # Returns: ['apple', 'orange', 'apple', 'banana', 'grape', 'apple']Need to check if a key exists in a Python dictionary? Check out this tutorial, which teaches you five different ways of seeing if a key exists in a Python dictionary, including how to return a default value.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to use Python to replace items in a list. You learned how to use Python to replace an item at a particular index, how to replace a particular value, how to modify all values in a list, and how to replace multiple values in a list.
To learn more about Python list indexing, check out the official documentation here.
Additional Resources
To learn more about related topics, check out the tutorials below: