- One Hot Encoding in Machine Learning
- One Hot Encoding
- The disadvantages of using one hot encoding include:
- One Hot Encoding Examples
- One-Hot Encoding Using Python
- Creating Dataframe
- One-Hot Encoding in Scikit-Learn with OneHotEncoder
- What is One-Hot Encoding?
- Why is One-Hot Encoding Important to Machine Learning?
- How to Use Sklearn’s OneHotEncoder
- How to Use ColumnTransformer with OneHotEncoder
- How to One-Hot Encode Multiple Columns with Scikit-Learn
- Conclusion
- Additional Resources
One Hot Encoding in Machine Learning
Most real-life datasets we encounter during our data science project development have columns of mixed data type. These datasets consist of both categorical as well as numerical columns. However, various Machine Learning models do not work with categorical data and to fit this data into the machine learning model it needs to be converted into numerical data. For example, suppose a dataset has a Gender column with categorical elements like Male and Female. These labels have no specific order of preference and also since the data is string labels, machine learning models misinterpreted that there is some sort of hierarchy in them.
One approach to solve this problem can be label encoding where we will assign a numerical value to these labels for example Male and Female mapped to 0 and 1. But this can add bias in our model as it will start giving higher preference to the Female parameter as 1>0 but ideally, both labels are equally important in the dataset. To deal with this issue we will use the One Hot Encoding technique.
One Hot Encoding
One hot encoding is a technique that we use to represent categorical variables as numerical values in a machine learning model.
The advantages of using one hot encoding include:
- It allows the use of categorical variables in models that require numerical input.
- It can improve model performance by providing more information to the model about the categorical variable.
- It can help to avoid the problem of ordinality, which can occur when a categorical variable has a natural ordering (e.g. “small”, “medium”, “large”).
The disadvantages of using one hot encoding include:
- It can lead to increased dimensionality, as a separate column is created for each category in the variable. This can make the model more complex and slow to train.
- It can lead to sparse data, as most observations will have a value of 0 in most of the one-hot encoded columns.
- It can lead to overfitting, especially if there are many categories in the variable and the sample size is relatively small.
- One-hot-encoding is a powerful technique to treat categorical data, but it can lead to increased dimensionality, sparsity, and overfitting. It is important to use it cautiously and consider other methods such as ordinal encoding or binary encoding.
One Hot Encoding Examples
In One Hot Encoding, the categorical parameters will prepare separate columns for both Male and Female labels. So, wherever there is a Male, the value will be 1 in the Male column and 0 in the Female column, and vice-versa. Let’s understand with an example: Consider the data where fruits, their corresponding categorical values, and prices are given.
| Fruit | Categorical value of fruit | Price |
|---|---|---|
| apple | 1 | 5 |
| mango | 2 | 10 |
| apple | 1 | 15 |
| orange | 3 | 20 |
The output after applying one-hot encoding on the data is given as follows,
| apple | mango | orange | price |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 10 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 20 |
One-Hot Encoding Using Python
Creating Dataframe
Creating a dataframe to implement one hot encoding from CSV file.
One-Hot Encoding in Scikit-Learn with OneHotEncoder
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the OneHotEncoder class in Scikit-Learn to one hot encode your categorical data in sklearn. One-hot encoding is a process by which categorical data (such as nominal data) are converted into numerical features of a dataset. This is often a required preprocessing step since machine learning models require numerical data.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have learned:
- What one-hot encoding is and why it’s important in machine learning
- How to use sklearn’s OneHotEncoder class to one-hot encode categorical data
- How to one-hot encode multiple columns
- How to use the ColumnTransformer class to manage multiple transformations
Are you looking to one-hot encode data in Pandas? You can also use the pd.get_dummies() function for this!
What is One-Hot Encoding?
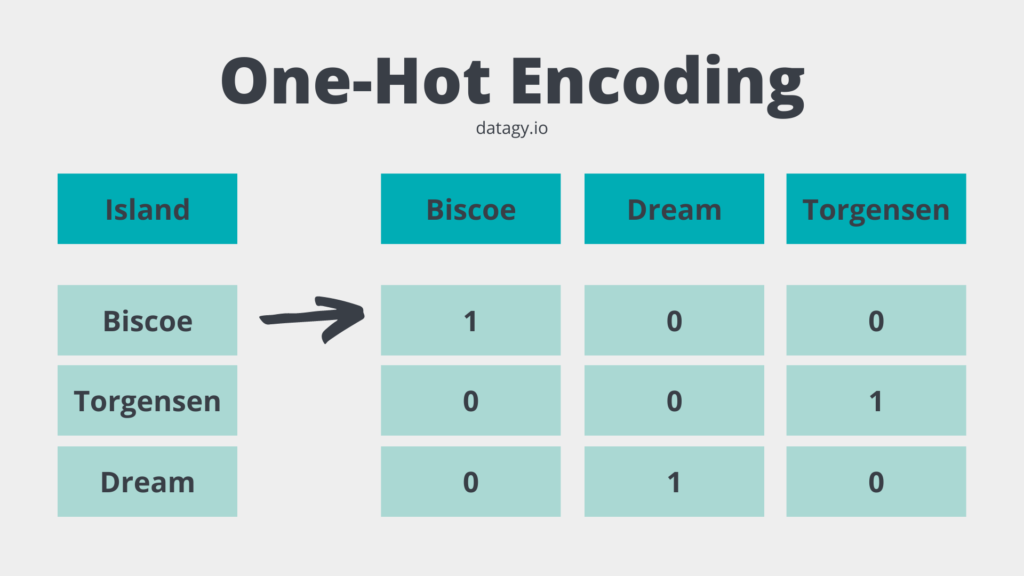
One-hot encoding is the process by which categorical data are converted into numerical data for use in machine learning. Categorical features are turned into binary features that are “one-hot” encoded, meaning that if a feature is represented by that column, it receives a 1 . Otherwise, it receives a 0 .
This is perhaps better explained by an image:
You may be wondering why we didn’t simply turn the values in the column to, say, . This would presume a larger difference between Biscoe and Dream than between Biscoe and Torgensen.
While this difference may exist, it isn’t specified in the data and shouldn’t be imagined.
However, if your data is ordinal, meaning that the order matters, then this approach may be appropriate. For example, when comparing shirt sizes, the difference between a Small and a Large is, in fact, bigger than between a Medium and a Large.
Why is One-Hot Encoding Important to Machine Learning?
Now that you understand the basic mechanics of one-hot encoding, you may be wondering how this all relates to machine learning. Because machine learning algorithms assume (and require) your data to be numeric, categorical data must be pre-processed in order for it to be accepted.
Following the example of the Island above – if we were to ask any classification or regression model to be built using the categorical data, an error would be raised. This is because machine learning algorithms cannot work with non-numerical data.
How to Use Sklearn’s OneHotEncoder
Sklearn comes with a one-hot encoding tool built-in: the OneHotEncoder class. The OneHotEncoder class takes an array of data and can be used to one-hot encode the data.
Let’s take a look at the different parameters the class takes:
# Understanding the OneHotEncoder Class in Sklearn from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder OneHotEncoder( categories='auto', # Categories per feature drop=None, # Whether to drop one of the features sparse=True, # Will return sparse matrix if set True dtype=, # Desired data type of the output handle_unknown='error' # Whether to raise an error ) Let’s see how we can create a one-hot encoded array using a categorical data column. For this, we’ll use the penguins dataset provided in the Seaborn library. We can load this using the load_dataset() function:
# One-hot encoding a single column from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder from seaborn import load_dataset df = load_dataset('penguins') ohe = OneHotEncoder() transformed = ohe.fit_transform(df[['island']]) print(transformed.toarray()) # Returns: # [[0. 0. 1.] # [0. 0. 1.] # [0. 0. 1.] # . # [1. 0. 0.] # [1. 0. 0.] # [1. 0. 0.]]Let’s break down what we did here:
- We loaded the dataset into a Pandas DataFrame, df
- We initialized a OneHotEncoder object and assigned it to ohe
- We fitted and transformed our data using the .fit_transform() method
- We returned the array version of the transformed data using the .toarray() method
We can see that each of the resulting three columns are binary values. There are three columns in the array, because there are three unique values in the Island column. The columns are returned alphabetically.
We can access the column labels using the .categories_ attribute of the encoder:
# Getting one hot encoded categories print(ohe.categories_) # Returns: # [array(['Biscoe', 'Dream', 'Torgersen'], dtype=object)]If we wanted to build these columns back into the DataFrame, we could add them as separate columns:
df[ohe.categories_[0]] = transformed.toarray() print(df.head()) # Returns: # species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_mm body_mass_g sex Biscoe Dream Torgersen # 0 Adelie Torgersen 39.1 18.7 181.0 3750.0 Male 0.0 0.0 1.0 # 1 Adelie Torgersen 39.5 17.4 186.0 3800.0 Female 0.0 0.0 1.0 # 2 Adelie Torgersen 40.3 18.0 195.0 3250.0 Female 0.0 0.0 1.0 # 3 Adelie Torgersen NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN 0.0 0.0 1.0 # 4 Adelie Torgersen 36.7 19.3 193.0 3450.0 Female 0.0 0.0 1.0In the next section, you’ll learn how to use the ColumnTransformer class to streamline the way in which you can one-hot encode data.
How to Use ColumnTransformer with OneHotEncoder
The process outlined above demonstrates how to one-hot encode a single column. It’s not the most intuitive approach, however. Sklearn comes with a helper function, make_column_transformer() which aids in the transformations of columns. The function generates ColumnTransformer objects for you and handles the transformations.
This allows us to simply pass in a list of transformations we want to do and the columns to which we want to apply them. It also handles the process of adding the data back into the original dataset. Let’s see how this works:
# Using make_column_transformer to One-Hot Encode from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder from sklearn.compose import make_column_transformer from seaborn import load_dataset import pandas as pd df = load_dataset('penguins') transformer = make_column_transformer( (OneHotEncoder(), ['island']), remainder='passthrough') transformed = transformer.fit_transform(df) transformed_df = pd.DataFrame( transformed, columns=transformer.get_feature_names() )Let’s see what we did here:
- We imported the make_column_transformer() function
- The function took a tuple containing the transformer we want to apply and the column to which to apply to. In this case, we wanted to use the OneHotEncoder() transformer and apply it to the ‘island’ column.
- We used the remainder=’passthrough’ parameter to specify that all other columns should be left untouched.
- We then applied the .fit_transform() method to our DataFrame.
- Finally, we reconstructed the DataFrame
In the next section, you’ll learn how to use the make_column_transformer() function to one-hot encode multiple columns with sklearn.
How to One-Hot Encode Multiple Columns with Scikit-Learn
The make_column_transformer() function makes it easy to one-hot encode multiple columns. In the argument where we specify which columns we want to apply transformations to, we can simply provide a list of additional columns.
Let’s reduce our DataFrame a bit to see what this result will look like:
# One-hot encoding multiple columns from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder from sklearn.compose import make_column_transformer from seaborn import load_dataset import pandas as pd df = load_dataset('penguins') df = df[['island', 'sex', 'body_mass_g']] df = df.dropna() transformer = make_column_transformer( (OneHotEncoder(), ['island', 'sex']), remainder='passthrough') transformed = transformer.fit_transform(df) transformed_df = pd.DataFrame(transformed, columns=transformer.get_feature_names()) print(transformed_df.head()) # Returns: # onehotencoder__island_Biscoe onehotencoder__island_Dream . onehotencoder__sex_Male remainder__body_mass_g # 0 0.0 0.0 . 1.0 3750.0 # 1 0.0 0.0 . 0.0 3800.0 # 2 0.0 0.0 . 0.0 3250.0 # 3 0.0 0.0 . 0.0 3450.0 # 4 0.0 0.0 . 1.0 3650.0Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to one-hot encode data using Scikit-Learn’s OneHotEncoder class. You learned what one-hot encoding is and why it matters in machine learning. You then learned how to use the OneHotEncoder class in sklearn to one-hot encode data. Finally, you learned how to use the make_column_transformer helper function for the ColumnTransformer class to one-hot encode multiple columns.
Additional Resources
To learn more about related topics, check out the tutorials below: