- Generate a list of n numbers in Python
- Method #1: Using range() function
- Method #2: Using numpy arange() function
- Method #3: Using List Comprehension
- Python list create numbers
- # Table of Contents
- # Create a list of numbers from 1 to N in Python
- # Create a list of numbers from 1 to N using a list comprehension
- # Using a floating-point number for the step with numpy
- # Create a list of numbers from 1 to N using a list comprehension
- # Create a list of numbers from 1 to N using a for loop
- # Create a list of numbers from 1 to N using a while loop
- # Additional Resources
- How to create a list of numbers in python ?
- Create a list of integers
- Create a list of floats using arange
- Create a list of floats using linspace
- Create a list of random integers
- References
- Benjamin
Generate a list of n numbers in Python
Python is a versatile language that you can use to write programs to complete a variety of tasks. In this article, you’ll learn how to generate a list of numbers in Python. You’ll also learn how to modify the list to meet your needs.
numbers = list(range(5)) print(numbers)Method #1: Using range() function
Python’s range() function is a handy tool for generating a list of consecutive integers. The function takes two arguments: the first is the starting value, and the second is the stopping value.
range(START_NUMBER, END_NUMBER)START_NUMBER: The number from where you want to start your list. Default is 0.
END_NUMBER: The number where you want to end your list — 1.
For example, the following code will generate a list of numbers starting at 0 and stopping at 9:
num_list = list(range(10)) print('Generated numbers List', num_list)Generated numbers List [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]This code example generates a list of numbers from 0 to 9 using the range() function.
The list() function is then used to convert the range object into a list object.
Finally, the generated list is printed on the console.
Code example — Generate a list from 1 to 10
num_list = list(range(1, 11)) print('Generated numbers List', num_list)Generated numbers List [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] If you want to shuffle the list also then you can read the below article.
Method #2: Using numpy arange() function
Python’s NumPy library has a function called arange() which generates a list of numbers. This is useful for creating lists of numbers for various purposes, such as creating a list of numbers to use in a For loop.
import numpy as np np.arrage(start, end, increment)Parameters: start: The number from where you want to start the list. Default 0. end: Number on which you want to end the list. increment: The number that you want to add in each step.Code example: Generate a list from 1 to 10
import numpy as np num_list = list(np.arange(1, 11)) print(num_list) # [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]The numpy.arange() function creates a list of evenly spaced numbers over a specified interval. In this case, the function generates a list of numbers from 1 to 10.
Another example is to generate a number list using np.arrange() function. This time we will use the increment value in each step as 0.4.
import numpy as np num_list = list(np.arange(.5, 5, .5)) print(num_list) # [0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5]The code example above creates a list of numbers from 0.5 to 5 in steps of 0.5.
Method #3: Using List Comprehension
Python’s list comprehension is a handy tool for generating lists of numbers. To generate a list of n numbers, simply use the following syntax: [num for num in range(n)]. This will create a list of numbers starting at 0 and going up to (n-1).
start=1 end=10 result = [item for item in range(start, end+1)] print(result) # [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]The above code is an example of list comprehension in Python. A list comprehension is a concise way to create a list in Python.
It consists of square brackets containing an expression followed by a for clause, then zero or more for or if clauses. The expression can be anything, meaning you can put all kinds of objects in lists.
The result will be a new list resulting from evaluating the expression in the context of the for and if clauses that follow it.
In the above code, the expression is «item for item in range(start, end+1)«, meaning that each item in the list will be the numbers from start to end (inclusive).
Python list create numbers
Last updated: Feb 22, 2023
Reading time · 5 min
# Table of Contents
# Create a list of numbers from 1 to N in Python
To create a list of numbers from 1 to N:
- Use the range() class to create a range object from 1 to N.
- Use the list() class to convert the range object to a list.
- The new list will contain the numbers in the specified range.
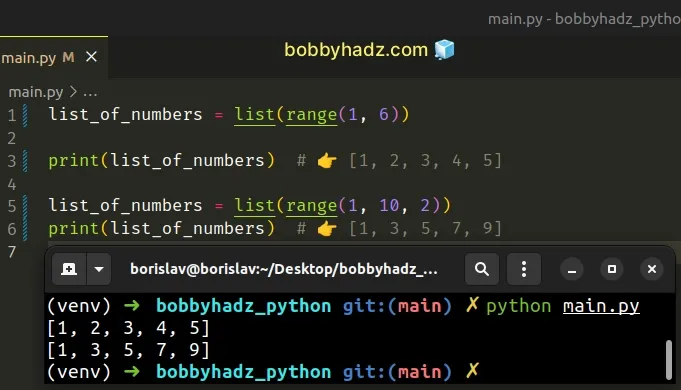
Copied!list_of_numbers = list(range(1, 6)) print(list_of_numbers) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] list_of_numbers = list(range(1, 10, 2)) print(list_of_numbers) # 👉️ [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
The range class is commonly used for looping a specific number of times in for loops and takes the following arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| start | An integer representing the start of the range (defaults to 0 ) |
| stop | Go up to, but not including the provided integer |
| step | Range will consist of every N numbers from start to stop (defaults to 1 ) |
If you only pass a single argument to the range() constructor, it is considered to be the value for the stop parameter.
Copied!list_of_numbers = list(range(5)) # 👇️ [0, 1, 2, 3, 4] print(list_of_numbers)
The example shows that if the start argument is omitted, it defaults to 0 and if the step argument is omitted, it defaults to 1 .
If values for the start and stop parameters are provided, the start value is inclusive, whereas the stop value is exclusive.
Copied!list_of_numbers = list(range(1, 5)) # 👇️ [1, 2, 3, 4] print(list_of_numbers)
If you need to specify a step, pass a third argument to the range() class.
Copied!list_of_numbers = list(range(1, 10, 2)) print(list_of_numbers) # 👉️ [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
The list contains every second number starting from 1 to 10 .
The step argument can only be set to an integer.
# Create a list of numbers from 1 to N using a list comprehension
You can also use a list comprehension to create a list of numbers from 1 to N.
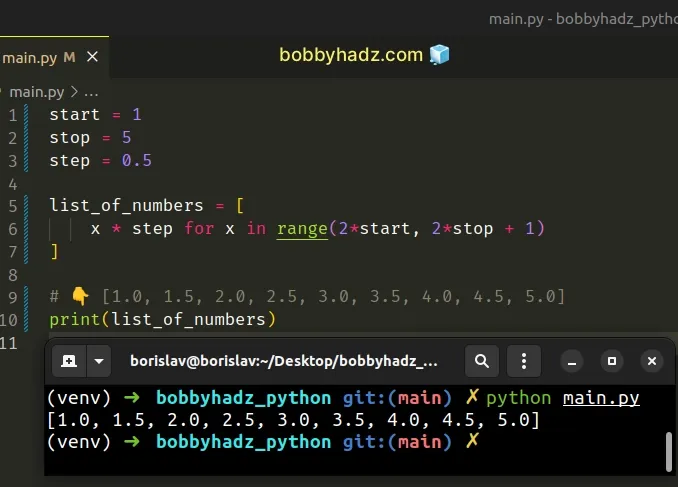
Copied!start = 1 stop = 5 step = 0.5 list_of_numbers = [ x * step for x in range(2*start, 2*stop + 1) ] # 👇️ [1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0] print(list_of_numbers)
List comprehensions are used to perform some operation for every element or select a subset of elements that meet a condition.
The list in the example starts at 1 and goes to 5 (inclusive) in increments of 0.5 .
You can update the start , stop and setup values.
This approach is useful when you have a step value that is not an integer because the range() class only supports integer values.
# Using a floating-point number for the step with numpy
If you need to use a floating-point number for the step , use the numpy.arange() method.
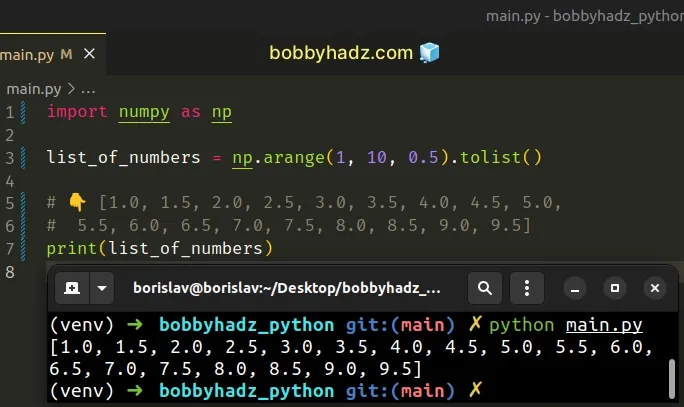
Copied!import numpy as np list_of_numbers = np.arange(1, 10, 0.5).tolist() # 👇️ [1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, # 5.5, 6.0, 6.5, 7.0, 7.5, 8.0, 8.5, 9.0, 9.5] print(list_of_numbers)
The numpy.arange method returns an array of evenly spaced values within the given interval.
We used the tolist method to convert the array to a list.
If you need to install the NumPy package, run the following command.
Copied!pip install numpy # 👇️ or pip3 pip3 install numpy
You can omit the step argument to get a list of values from 1 to N in increments of 1.
Copied!import numpy as np list_of_numbers = np.arange(1, 11).tolist() # 👇️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] print(list_of_numbers)
The numpy.arange() method is very similar to the range() class but allows for step values that are floating-point numbers.
# Create a list of numbers from 1 to N using a list comprehension
You can also use a list comprehension to create a list of numbers from 1 to N.
Copied!list_of_numbers = [number for number in range(1, 6)] print(list_of_numbers) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
List comprehensions are used to perform some operation for every element or select a subset of elements that meet a condition.
On each iteration, we return the current number.
The new list contains the numbers in the range object.
However, this isn’t necessary unless you need to perform some operation for every number in the range object.
# Create a list of numbers from 1 to N using a for loop
The same can be achieved using a simple for loop.
Copied!list_of_numbers = [] for number in range(1, 6): list_of_numbers.append(number) print(list_of_numbers) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
We used a for loop to iterate over the range object.
On each iteration, we use the list.append() method to append the current number to a list.
The list.append() method adds an item to the end of the list.
Copied!my_list = ['bobby', 'hadz'] my_list.append('com') print(my_list) # 👉️ ['bobby', 'hadz', 'com']
Using the list() class to convert the range object to a list should be sufficient unless you have to perform some operation for every number in the range object.
You can also define a reusable function that creates a list of numbers in a for loop.
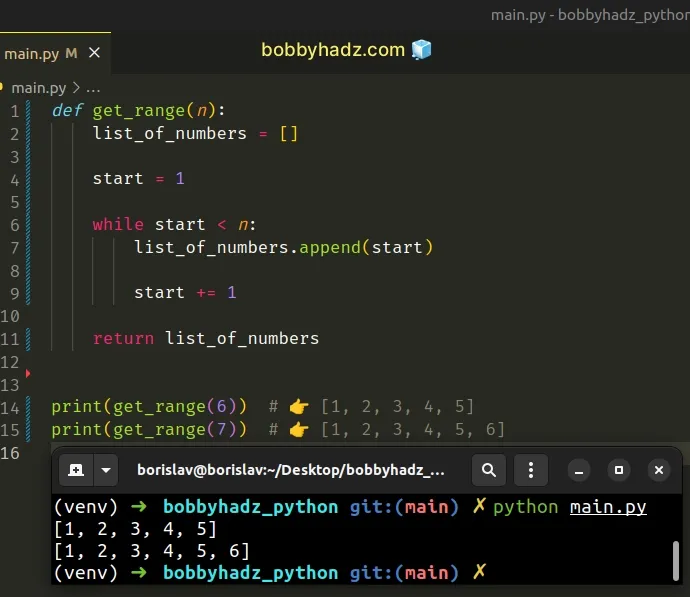
Copied!def get_range(n): list_of_numbers = [] for number in range(1, n + 1): list_of_numbers.append(number) return list_of_numbers print(get_range(6)) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] print(get_range(7)) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
The function takes n as a parameter and creates a list of numbers from 1 to n.
# Create a list of numbers from 1 to N using a while loop
You can also use a while loop to create a list of numbers from 1 to N.
Copied!def get_range(n): list_of_numbers = [] start = 1 while start n: list_of_numbers.append(start) start += 1 return list_of_numbers print(get_range(6)) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] print(get_range(7)) # 👉️ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
The get_range function takes n as a parameter and creates a list of numbers from 1 to n .
On each iteration, we append the current start value to the list and increment it.
Once the start value is equal to or greater than n , the condition is no longer met and the while loop exits.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
I wrote a book in which I share everything I know about how to become a better, more efficient programmer.
How to create a list of numbers in python ?
Examples of how to create a list of numbers in python using list comprehensions or built-in functions list():
Create a list of integers
To create a list of integers between 0 and N, a solution is to use the range(N) function:
>>> l = [i for i in range(10)]>>> l[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]>>> l = list(range(10))>>> l[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
To create a list of integers between N and M (with M>N), the function range() can still be used:
>>> l = [i for i in range(25,35)]>>> l[25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34]>>> l = list(range(25,35))>>> l[25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34]
Create a list of floats using arange
To create a list of floats between (N,M) with a given step, a solution is to use the numpy function called arange:
>>> import numpy as np>>> l = [i for i in np.arange(2,8,0.5)]>>> l[2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 5.5, 6.0, 6.5, 7.0, 7.5]>>> l = list(np.arange(2,8,0.5))>>> l[2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 5.5, 6.0, 6.5, 7.0, 7.5]
Create a list of floats using linspace
To create a list of floats between (N,M) with a given number of elementsa solution is to use the numpy function linspace:
>>> import numpy as np>>> l = [i for i in np.linspace(12,16,8)]>>> l[12.0, 12.571428571428571, 13.142857142857142, 13.714285714285714, 14.285714285714285, 14.857142857142858, 15.428571428571429, 16.0]>>> l = list(np.linspace(12,16,8))>>> l[12.0, 12.571428571428571, 13.142857142857142, 13.714285714285714, 14.285714285714285, 14.857142857142858, 15.428571428571429, 16.0]
Create a list of random integers
The python function randint can be used to generate a random integer in a chosen interval [a,b]:
>>> import random>>> random.randint(0,10)7>>> random.randint(0,10)0
A list of random numbers can be then created using python list comprehension approach:
>>> l = [random.randint(0,10) for i in range(5)]>>> l[4, 9, 8, 4, 5]
Another solution is to use randrange function (except that can specify a step if you need):
>>> l = [random.randrange(0,10) for i in range(5)]>>> l[1, 7, 4, 3, 1]>>> l = [random.randrange(0,10,2) for i in range(5)]>>> l[2, 4, 4, 6, 0]
A third solution is to create a list of random numbers with no repetition, is to use random.sample function
>>> l = random.sample(range(1,100), 10)>>> l[89, 56, 87, 51, 46, 25, 52, 44, 10, 32]
References
Benjamin
Greetings, I am Ben! I completed my PhD in Atmospheric Science from the University of Lille, France. Subsequently, for 12 years I was employed at NASA as a Research Scientist focusing on Earth remote sensing. Presently, I work with NOAA concentrating on satellite-based Active Fire detection. Python, Machine Learning and Open Science are special areas of interest to me.