- Python json loads bytes
- # Table of Contents
- # Convert Bytes to Dictionary in Python
- # Convert Bytes to Dictionary using json.loads()
- # Replacing the single quotes with double quotes before using json.loads()
- # Converting a Dictionary to Bytes
- # Additional Resources
- [python] Python — Convert a bytes array into JSON format
- The answer is
Python json loads bytes
Last updated: Feb 22, 2023
Reading time · 3 min
# Table of Contents
# Convert Bytes to Dictionary in Python
To convert a bytes object to a dictionary:
- Use the bytes.decode() method to convert the bytes to a string.
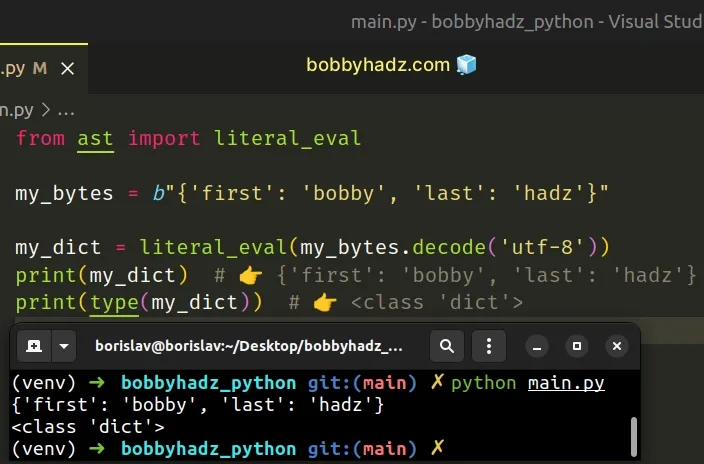
- Use the ast.literal_eval() method to convert the string to a dictionary.
- The literal_eval() method safely evaluates a string that contains a Python literal.
Copied!from ast import literal_eval my_bytes = b"" my_dict = literal_eval(my_bytes.decode('utf-8')) print(my_dict) # 👉️ print(type(my_dict)) # 👉️
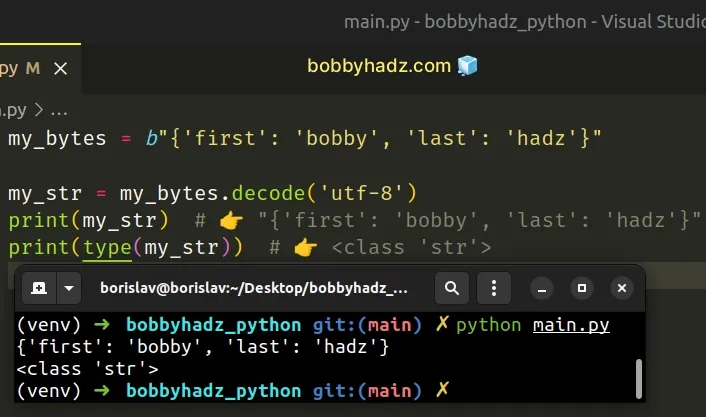
We used the bytes.decode() method to convert the bytes object to a string.
Copied!my_bytes = b"" my_str = my_bytes.decode('utf-8') print(my_str) # 👉️ "" print(type(my_str)) # 👉️
The bytes.decode method returns a string decoded from the given bytes. The default encoding is utf-8 .
The last step is to pass the string to the ast.literal_eval() method.
The ast.literal_eval method allows us to safely evaluate a string that contains a Python literal.
Copied!from ast import literal_eval my_bytes = b"" my_dict = literal_eval(my_bytes.decode('utf-8')) print(my_dict) # 👉️ print(type(my_dict)) # 👉️
The string may consist of strings, bytes, numbers, tuples, lists, dictionaries, sets, booleans and None.
If the properties in your bytes object are wrapped in double quotes, you can also use the json.loads() method.
# Convert Bytes to Dictionary using json.loads()
This is a two-step process:
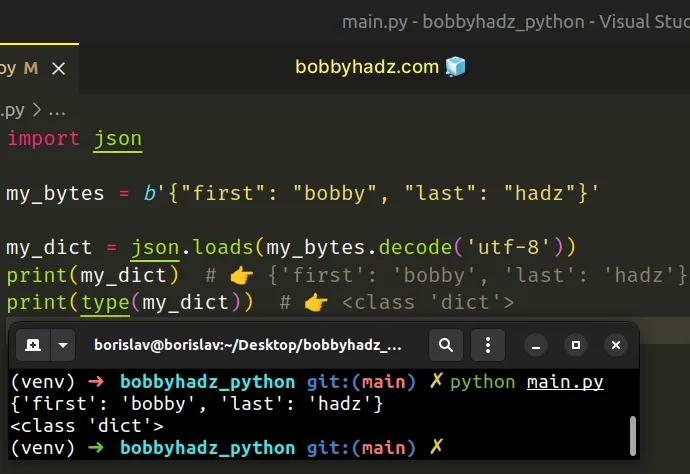
- Use the bytes.decode() method to convert the bytes to a string.
- Use the json.loads() method to parse the string into a dictionary.
Copied!import json my_bytes = b'' my_dict = json.loads(my_bytes.decode('utf-8')) print(my_dict) # 👉️ print(type(my_dict)) # 👉️
The json.loads method parses a JSON string into a native Python object.
Copied!import json json_str = r'' my_dict = json.loads(json_str) print(type(my_dict)) # 👉️
However, the method only accepts valid JSON strings.
If the properties in your bytes object are not wrapped in double quotes, use the ast.literal_eval() method.
# Replacing the single quotes with double quotes before using json.loads()
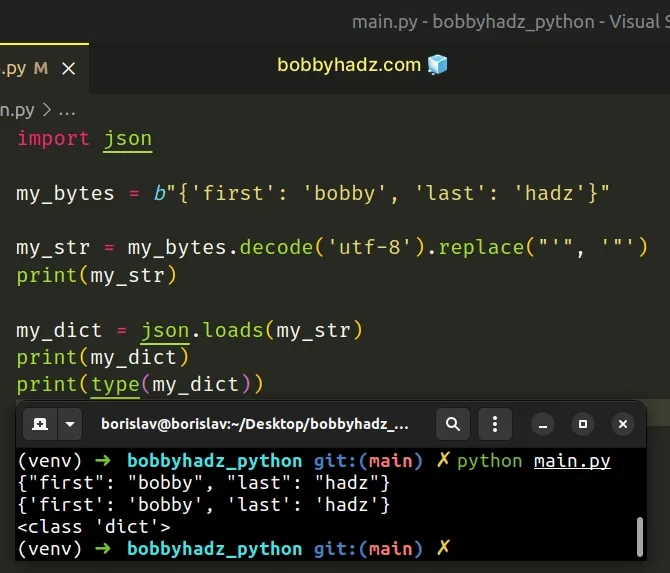
An alternative approach would be to replace the single quotes in the string with double quotes.
Copied!import json my_bytes = b"" my_str = my_bytes.decode('utf-8').replace("'", '"') print(my_str) my_dict = json.loads(my_str) print(my_dict) # 👉️ print(type(my_dict)) # 👉️
We used the str.replace() method to replace all single quotes in the string with double quotes.
However, this could go wrong if some of the values also contain single quotes.
The ast.literal_eval() method safely evaluates the string, so it should be your preferred approach.
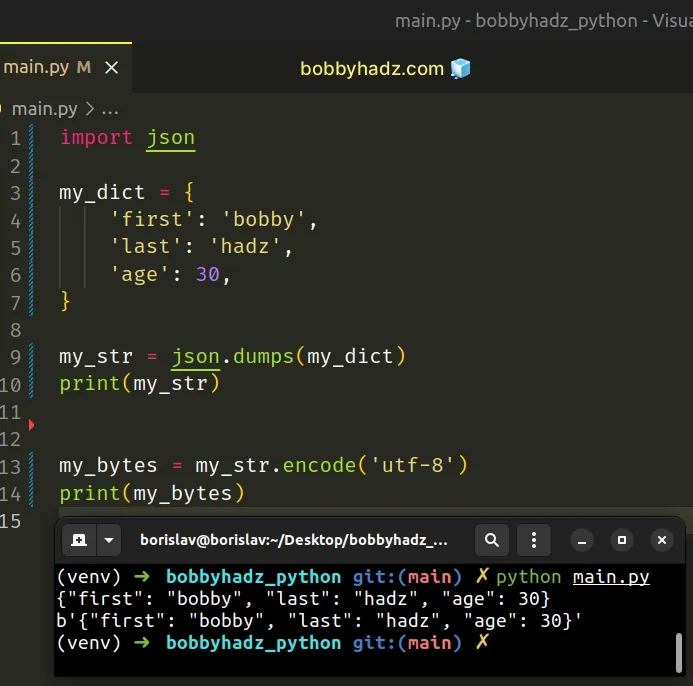
# Converting a Dictionary to Bytes
If you need to convert a dictionary to bytes:
- Use the json.dumps() method to convert the dictionary to a JSON string.
- Use the str.encode() method to convert the string to bytes.
Copied!import json my_dict = 'first': 'bobby', 'last': 'hadz', 'age': 30, > my_str = json.dumps(my_dict) print(my_str) # 👉️ '' my_bytes = my_str.encode('utf-8') print(my_bytes) # 👉️ b''
The json.dumps method converts a Python object to a JSON formatted string.
Once we have a string, we can use the str.encode() method to convert it to bytes.
The str.encode method returns an encoded version of the string as a bytes object. The default encoding is utf-8 .
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
I wrote a book in which I share everything I know about how to become a better, more efficient programmer.
[python] Python — Convert a bytes array into JSON format
I want to convert a bytes array to JSON format. This is the source I have:
And this is the desired outcome I want to have:
First, I converted the bytes to string:
my_new_string_value = my_bytes_value.decode("utf-8") but when I try to loads to JSON:
my_json = json.loads(my_new_string_value) json.decoder.JSONDecodeError: Expecting value: line 1 column 174 (char 173) This question is related to python json
The answer is
Your bytes object is almost JSON, but it’s using single quotes instead of double quotes, and it needs to be a string. So one way to fix it is to decode the bytes to str and replace the quotes. Another option is to use ast.literal_eval ; see below for details. If you want to print the result or save it to a file as valid JSON you can load the JSON to a Python list and then dump it out. Eg,
import json my_bytes_value = b'[]' # Decode UTF-8 bytes to Unicode, and convert single quotes # to double quotes to make it valid JSON my_json = my_bytes_value.decode('utf8').replace("'", '"') print(my_json) print('- ' * 20) # Load the JSON to a Python list & dump it back out as formatted JSON data = json.loads(my_json) s = json.dumps(data, indent=4, sort_keys=True) print(s) As Antti Haapala mentions in the comments, we can use ast.literal_eval to convert my_bytes_value to a Python list, once we’ve decoded it to a string.
from ast import literal_eval import json my_bytes_value = b'[]' data = literal_eval(my_bytes_value.decode('utf8')) print(data) print('- ' * 20) s = json.dumps(data, indent=4, sort_keys=True) print(s) Generally, this problem arises because someone has saved data by printing its Python repr instead of using the json module to create proper JSON data. If it’s possible, it’s better to fix that problem so that proper JSON data is created in the first place.
import json json.loads(my_bytes_value)