- Python Add to Dictionary
- How to Add to Dictionary in Python
- 1. By Using update() Method
- 2. By Using _setitem_() Method
- 3. By Using Subscript Notation
- 4. By Using ” ** ” Operator
- Adding Keys to Nested Python Dictionary
- Addition of Multiple Key-Value Pairs to Python Dictionary
- Addition of a Dictionary to Another Dictionary
- Conclusion
- References
- Python: How to Add Items to Dictionary
- How to Add an Item to a Dictionary in Python
- Method 1: Using The Assignment Operator
- Method 2: Using update()
- Method 3: Using __setitem__
- Method 4: Using The ** Operator
- Method 5: Checking If A Key Exists
- Method 6: Using A For Loop
- Method 7: Using zip
- How to Update a Python Dictionary
- Python: Add Key:Value Pair to Dictionary
- Add an Item to a Python Dictionary
- Update an Item in a Python Dictionary
- Append Multiple Items to a Python Dictionary with a For Loop
- Add Multiple Items to a Python Dictionary with Zip
- Conclusion
- Additional Resources
Python Add to Dictionary
Python Dictionary basically contains elements in the form of key-value pairs.
It is an unordered collection of items.
Creation of Dictionary:
cities = print(cities) #type(cities)
How to Add to Dictionary in Python
- By using update() method
- By using _setitem_() method
- By using subscript notation
- By using “*” operator
1. By Using update() Method
The update() method enables the user to add multiple key-value pairs to the dict.
info = print("Current Dict is: ", info) info.update() print("Updated Information is: ", info) Current Dict is: Updated Information is:
2. By Using _setitem_() Method
Python Dictionary’s _setitem_() method is used to add a key-value pair to the dict.
info = info.__setitem__('Address', 'Pune') print(info) 3. By Using Subscript Notation
The subscript notation helps add a new key-value pair to the dict. If the key doesn’t exist, a new key is created with the mentioned value assigned to it.
info = info['Address'] = 'Pune' print(info)
4. By Using ” ** ” Operator
The ” ** ” operator basically adds key-value pairs to the new dict and merges it with the old dict.
info = #old dict #adding item to the new dict(result) and merging with old dict(info) result = <**info, **<'Address': 'Pune'>> print(result)
Adding Keys to Nested Python Dictionary
info = > print("The Input dictionary: " + str(info)) info['TEST']['Address'] = 'Pune' print("Dictionary after adding key to nested dict: " + str(info)) The Input dictionary: > Dictionary after adding key to nested dict: >Addition of Multiple Key-Value Pairs to Python Dictionary
info = > info.update([ ('Address', 'Pune') , ('zip_code',411027 )]) print(info) , 'Address': 'Pune', 'zip_code': 411027>Addition of a Dictionary to Another Dictionary
info = > info1 = < 'SET' : > #Adding elements of info1 to info info.update(info1) print(info)
Conclusion
Thus, in this article, we have understood and implemented the possible ways to add key-value pairs to Python Dictionary.
References
Python: How to Add Items to Dictionary
Dictionaries are Python’s built-in data types for storing key-value pairs. The dictionary elements are changeable and don’t allow duplicates. In Python 3.7 and higher, dictionary items are ordered. Lower versions of Python treat dictionary elements as unordered.
Depending on the desired result and given data, there are various ways to add items to a dictionary.
This guide shows how to add items to a Python dictionary through examples.
- Python version 3.7 or higher.
- A text editor or IDE to write code.
- A method to run the code, such as a terminal or IDE.
How to Add an Item to a Dictionary in Python
To test out different methods of adding items to a dictionary, create a dictionary with two items. Use the following code:
The methods below show how to add one or multiple items to a Python dictionary.
Note: Adding an item with an existing key replaces the dictionary item with a new value. Make sure to provide unique keys to avoid overwriting data.
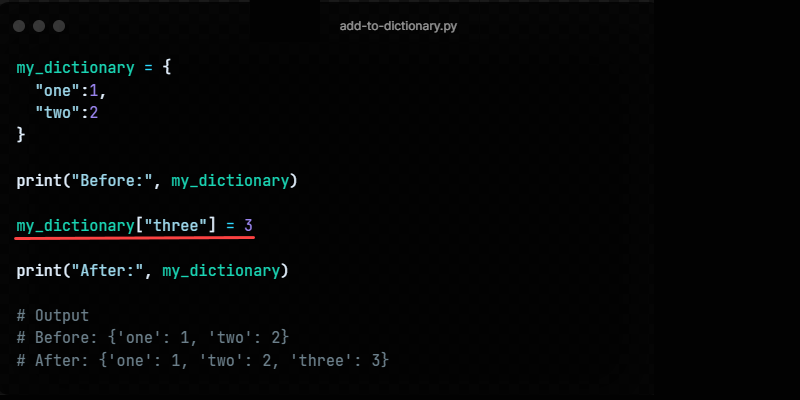
Method 1: Using The Assignment Operator
The assignment operator sets a value to a key using the following syntax:
dictionary_namePython dict set item = valueThe assignment operator adds a new key-value pair if the key does not exist.
The following code demonstrates how to add an item to a Python dictionary using the assignment operator:
my_dictionary = < "one": 1, "two": 2 >print("Before:", my_dictionary) my_dictionary["tree"] = 3 print("After:", my_dictionary)The code outputs the dictionary contents before and after adding a new item.
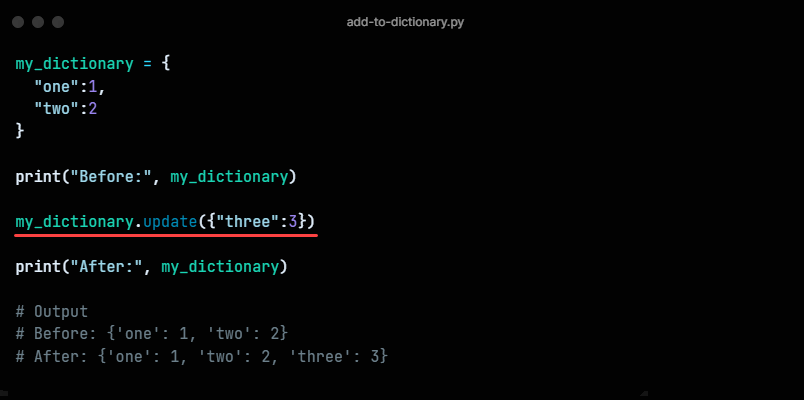
Method 2: Using update()
The update() method updates an existing dictionary with a new dictionary item:
The method accepts one or multiple key-value pairs, which is convenient for adding more than one element.
The example code looks like the following:
my_dictionary = < "one": 1, "two": 2 >print("Before:", my_dictionary) my_dictionary.update() print("After:", my_dictionary)Use this method to add multiple new items or append a dictionary to an existing one.
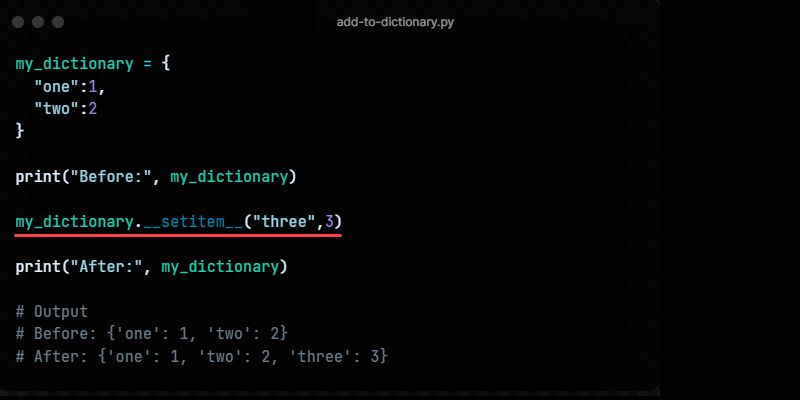
Method 3: Using __setitem__
The __setitem__ method is another way to append a new dictionary item:
dictionary_name.__setitem__(key,value)my_dictionary = < "one": 1, "two": 2 >print("Before:", my_dictionary) my_dictionary.__setitem__("three", 3) print("After:", my_dictionary)The method sets the item key as «three» with the value 3 .
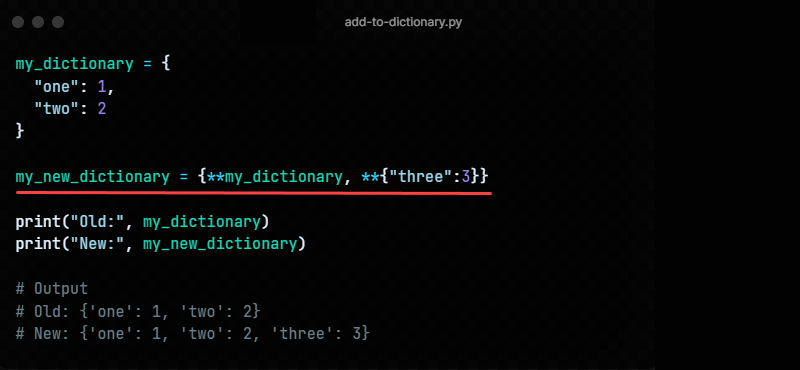
Method 4: Using The ** Operator
The ** operator helps merge an existing dictionary into a new dictionary and adds additional items. The syntax is:
For example, to copy an existing dictionary and append a new item to a new one, see the following code:
my_dictionary = < "one": 1, "two": 2 >my_new_dictionary = <**my_dictionary, **<"three":3>> print("Old:", my_dictionary) print("New:", my_new_dictionary)The new dictionary contains the added item, preserving the old dictionary values. Use this method to avoid changing existing dictionaries.
Method 5: Checking If A Key Exists
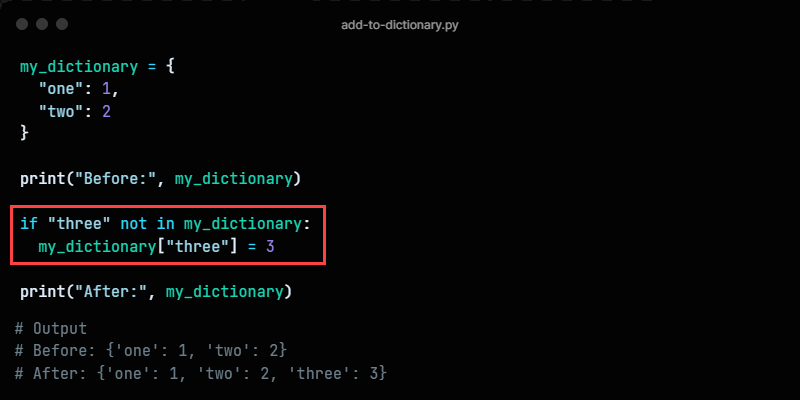
Use an if statement to check whether a key exists before adding a new item to a dictionary. The example syntax is:
if key not in dictionary_name: dictionary_namePython dict set item = valuemy_dictionary = < "one": 1, "two": 2 >print("Before:", my_dictionary) if "three" not in my_dictionary: my_dictionary["three"] = 3 print("After:", my_dictionary)The code checks whether a key with the provided name exists before adding the item to the dictionary. If the provided key exists, the existing key value does not update, and the dictionary stays unchanged.
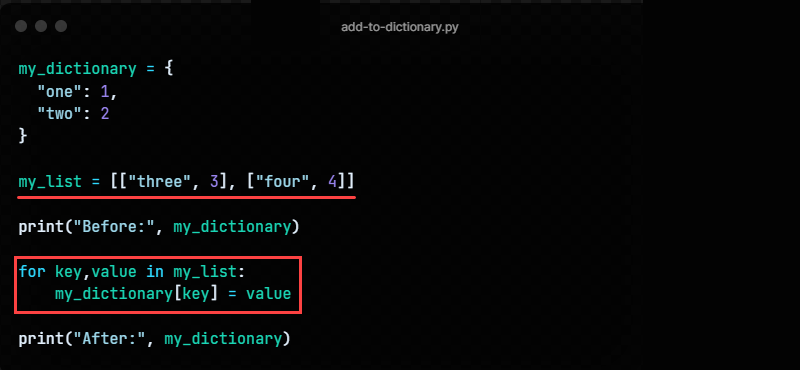
Method 6: Using A For Loop
Add key-value pairs to a nested list and loop through the list to add multiple items to a dictionary. For example:
my_dictionary = < "one": 1, "two": 2 >my_list = [["three", 3], ["four", 4]] print("Before:", my_dictionary) for key,value in my_list: my_dictionaryPython dict set item = value print("After:", my_dictionary)The for loop goes through the pairs inside the list and adds two new elements.
Note: For loop and a counter are also used as one of the methods to identify the length of a list. Learn more by visiting our guide How to Find the List Length in Python.
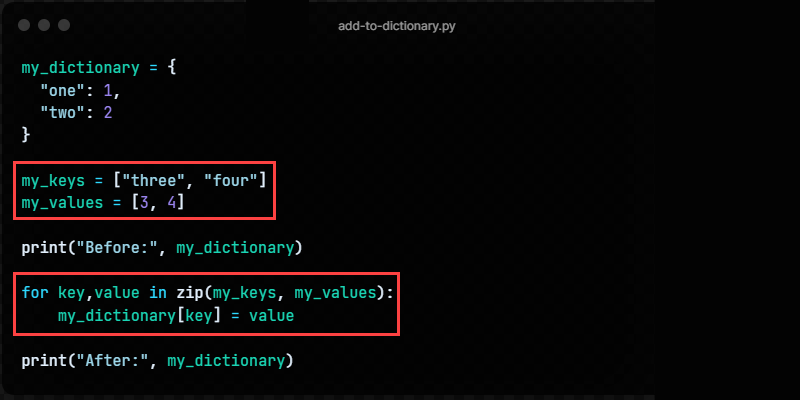
Method 7: Using zip
Use zip to create key-value pairs from two lists. The first list contains keys and the second contains the values.
my_dictionary = < "one": 1, "two": 2 >my_keys = ["three", "four"] my_values = [3, 4] print("Before:", my_dictionary) for key,value in zip(my_keys, my_values): my_dictionaryPython dict set item = value print("After:", my_dictionary)The zip function matches elements from two lists by index, creating key-value pairs.
How to Update a Python Dictionary
Update Python dictionary values using the same syntax as adding a new element. Provide the key name of an existing key, for example:
my_dictionary = < "one": 1, "two": 2 >print("Before:", my_dictionary) my_dictionary["one"] = 3 print("After:", my_dictionary)Since Python does not allow duplicate entries in a dictionary, the code updates the value for the provided key and overwrites the existing information.
After going through the examples in this tutorial, you know how to add items to a Python dictionary. All methods provide unique functionalities, so choose a way that best suits your program and situation.
For more Python tutorial refer to our article and find out how to pretty print a JSON file using Python.
Python: Add Key:Value Pair to Dictionary
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to add key:value pairs to Python dictionaries. You’ll learn how to do this by adding completely new items to a dictionary, adding values to existing keys, and dictionary items in a for loop, and using the zip() function to add items from multiple lists.
What are Python dictionaries? Python dictionaries are incredibly helpful data types, that represent a hash table, allowing data retrieval to be fast and efficient. They consist of key:value pairs, allowing you to search for a key and return its value. Python dictionaries are created using curly braces, <> . Their keys are required to be immutable and unique, while their values can be any data type (including other dictionaries) and do not have to be unique.
The Quick Answer: Use dictPython dict set item = [value] to Add Items to a Python Dictionary
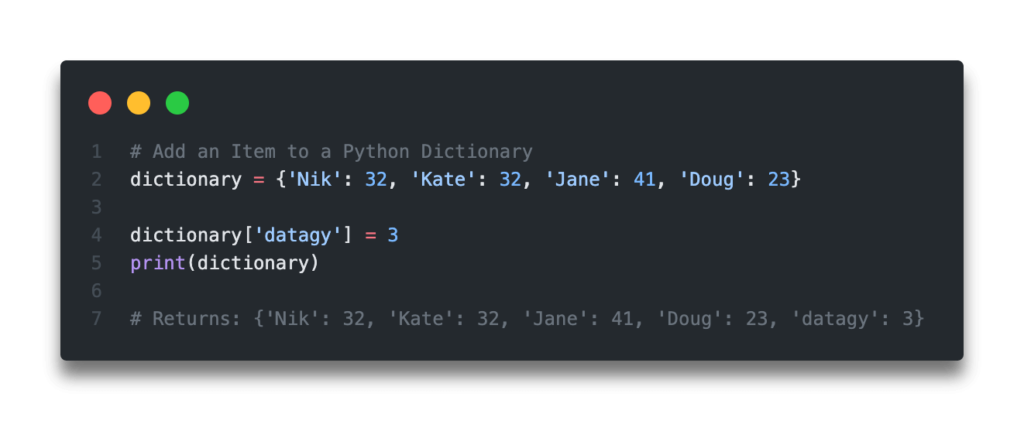
Add an Item to a Python Dictionary
The easiest way to add an item to a Python dictionary is simply to assign a value to a new key. Python dictionaries don’t have a method by which to append a new key:value pair. Because of this, direct assignment is the primary way of adding new items to a dictionary.
Let’s take a look at how we can add an item to a dictionary:
# Add an Item to a Python Dictionary dictionary = dictionary['Evan'] = 30 print(dictionary) # Returns:
We can see here that we were able to easily append a new key:value pair to a dictionary by directly assigning a value to a key that didn’t yet exist.
What can we set as dictionary keys? It’s important to note that we can add quite a few different items as Python dictionary keys. For example, we could make our keys strings, integers, tuples – any immutable item that doesn’t already exist. We can’t, however, use mutable items (such as lists) to our dictionary keys.
In the next section, you’ll learn how to use direct assignment to update an item in a Python dictionary.
Update an Item in a Python Dictionary
Python dictionaries require their keys to be unique. Because of this, when we try to add a key:value pair to a dictionary where the key already exists, Python updates the dictionary. This may not be immediately clear, especially since Python doesn’t throw an error.
Let’s see what this looks like, when we add a key:value pair to a dictionary where the key already exists:
# Update an Item in a Python Dictionary dictionary = dictionary['Nik'] = 30 print(dictionary) # Returns:
We can see that when we try to add an item to a dictionary when the item’s key already exists, that the dictionary simply updates. This is because Python dictionaries require the items to be unique, meaning that it can only exist once.
In the next section, you’ll learn how to use a for loop to add multiple items to a Python dictionary.
Append Multiple Items to a Python Dictionary with a For Loop
There may be times that you want to turn two lists into a Python dictionary. This can be helpful when you get data from different sources and want to combine lists into a dictionary data structure.
Let’s see how we can loop over two lists to create a dictionary:
# Loop Over Two Lists to Create a Dictionary keys = ['Nik', 'Kate', 'Jane'] values = [32, 31, 30] dictionary = <> for i in range(len(keys)): dictionaryPython dict set item] = values[i] print(dictionary) # Returns:
Here, we loop over each value from 0 through to the length of the list minus 1, to access the indices of our lists. We then access the i th index of each list and assign them to the keys and values of our lists.
There is actually a much simpler way to do this – using the Python zip function, which you’ll learn about in the next section.
Add Multiple Items to a Python Dictionary with Zip
The Python zip() function allows us to iterate over two iterables sequentially. This saves us having to use an awkward range() function to access the indices of items in the lists.
Let’s see what this looks like in Python:
# Loop Over Two Lists to Create a Dictionary using Zip keys = ['Nik', 'Kate', 'Jane'] values = [32, 31, 30] dictionary = <> for key, value in zip(keys, values): dictionaryPython dict set item = value print(dictionary) # Returns:
The benefit of this approach is that it is much more readable. Python indices can be a difficult thing for beginner Python developers to get used to. The zip function allows us to easily interpret what is going on with our code. We can use the zip function to name our iterable elements, to more easily combine two lists into a dictionary.
If you’re working with a dictionary that already exists, Python will simply update the value of the existing key. Because Python lists can contain duplicate values, it’s important to understand this behaviour. This can often lead to unexpected results since the program doesn’t actually throw an error.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to use Python to add items to a dictionary. You learned how to do this using direct assignment, which can be used to add new items or update existing items. You then also learned how to add multiple items to a dictionary using both for loops and the zip function.
To learn more about Python dictionaries, check out the official documentation here.
Additional Resources
To learn more about related topics, check out the articles below: