- Что делает return в Python?
- Пример
- Вывод
- Пример оператора return Python
- Каждая функция что-то возвращает
- Что произойдет, если в операторе ничего нет?
- Может иметь несколько операторов
- Функция может возвращать несколько типов значений
- Возврат нескольких значений в одном операторе
- С блоком finally
- Оператор return в Python: возврат значений из функции
- Возврат нескольких значений
- Функция, возвращающая другую функцию
- Python return statement
- Python Function without return statement
- Python Return Statement Example
- Python return statement with expression
- Python return boolean
- Python return string
- Python return tuple
- Python function returning another function
- Python function returning outer function
- Python return multiple values
- Summary
Что делает return в Python?
Функция print() записывает, то есть «печатает», строку или число на консоли. Оператор return не выводит значение, которое возвращается при вызове функции. Это, однако, приводит к немедленному завершению или завершению функции, даже если это не последний оператор функции.
Во многих других языках функция, которая не возвращает значение, называется процедурой.
В данном коде значение, возвращаемое (то есть 2) при вызове функции foo(), используется в функции bar(). Эти возвращаемые значения печатаются на консоли только тогда, когда используются операторы печати, как показано ниже.
Пример
def foo(): print("Hello from within foo") return 2 def bar(): return 10*foo() print foo() print bar() Вывод
Hello from within foo 2 Hello from within foo 20
Мы видим, что когда foo() вызывается из bar(), 2 не записывается в консоль. Вместо этого он используется для вычисления значения, возвращаемого из bar().
Пример оператора return Python
Давайте посмотрим на простой пример сложения двух чисел и возврата суммы вызывающему абоненту.
def add(x, y): total = x + y return total
Мы можем оптимизировать функцию, указав выражение в операторе возврата.
Каждая функция что-то возвращает
Давайте посмотрим, что возвращается, когда функция не имеет оператора возврата.
>>> def foo(): . pass . >>> >>> print(foo()) None >>>
Что произойдет, если в операторе ничего нет?
Когда оператор return не имеет значения, функция возвращает None.
>>> def return_none(): . return . >>> print(return_none()) None >>>
Может иметь несколько операторов
def type_of_int(i): if i % 2 == 0: return 'even' else: return 'odd'
Функция может возвращать несколько типов значений
В отличие от других языков программирования, функции Python не ограничиваются возвратом значений одного типа. Если вы посмотрите на определение функции, в нем нет никакой информации о том, что она может вернуть.
Давайте посмотрим на пример, в котором функция возвращает несколько типов значений.
def get_demo_data(object_type): if 'str' == object_type: return 'test' elif 'tuple' == object_type: return (1, 2, 3) elif 'list' == object_type: return [1, 2, 3] elif 'dict' == object_type: return else: return None
Возврат нескольких значений в одном операторе
Мы можем вернуть несколько значений из одного оператора возврата. Эти значения разделяются запятой и возвращаются вызывающей программе в виде кортежа.
def return_multiple_values(): return 1, 2, 3 print(return_multiple_values()) print(type(return_multiple_values()))
С блоком finally
Как работает оператор return внутри блока try-except? Сначала выполняется код блока finally перед возвратом значения вызывающей стороне.
def hello(): try: return 'hello try' finally: print('finally block') def hello_new(): try: raise TypeError except TypeError as te: return 'hello except' finally: print('finally block') print(hello()) print(hello_new()) finally block hello try finally block hello except
Если в блоке finally есть оператор return, то предыдущий оператор return игнорируется и возвращается значение из блока finally.
def hello(): try: return 'hello try' finally: print('finally block') return 'hello from finally' print(hello()) finally block hello from finally
Оператор return в Python: возврат значений из функции
Оператор return в Python используется для возврата значения из функции. Пользователь может использовать оператор возврата только в функции. Его нельзя использовать вне функции Python. Оператор возврата включает ключевое слово return и значение, которое будет возвращено после этого.
Синтаксис оператора возврата:
def funtion_name(): statements . . . return [expression]
def adding(x, y): i = x + y return i result = adding(16, 25) print(f'Output of adding(16, 25) function is ')
def adding(a, b): # this function is return the value of(a + b) return a + b def boolean_function(a): # this function is return the Boolean value return bool(a) # calling function flag = adding(2, 3) print("Output of first function is <>".format(flag)) flag = boolean_function(9 < 5) print("\nOutput of second function is <>".format(flag)) Возврат нескольких значений
В языке программирования Python пользователь может возвращать несколько значений из функции. Ниже приведены различные методы для этого.
1. Использование объекта: этот метод похож на C / C ++ и Java. Пользователь может создать класс для хранения нескольких значений в функции и возврата объекта этого класса.
class a: def __init__(self): self.omg = "javatpoint is the best website to learn" self.i = 122 # This function will return an object of the class a def test(): return a() # Driver code to test the above method z = test() print(z.omg) print(z.i)
2. Использование кортежа: кортеж похож на список, но есть небольшая разница между кортежем и списком. В кортеже значения объекта нельзя изменить, а в списке – можно.
def test(): omg = "javatpoint is the best website to learn" i = 122 return omg, i; # Return tuple, we could also. # Driver code to test the above method. omg, i = test() # Assign return tuple print(omg) print(i)
3. Использование списка: список аналогичен массиву динамического размера. В списке пользователь может хранить все в одной переменной.
def test(): omg = "javatpoint" i = 122 return [omg, i]; # Driver code to test the above method list = test() print(list)
4. Использование словаря. В языке Python словарь – это набор неструктурированных элементов, которые используются для хранения значений данных, таких как хэш или карта.
def test(): a = dict(); a['omg'] = "javatpoint" a['i'] = 122 return a # Driver code to test the above method a = test() print(a)
5. Использование класса данных(Python 3.7+)
from dataclasses import dataclass @dataclass class Book_list: bookname: str cost: float quantity_of_book_available: int = 0 # This function is used to calculate the total cost of the books def total_cost_of_book(self) -> float: return self.cost * self.quantity_of_book_available book = Book_list("Python programming language.", 499, 10) i = book.total_cost_of_book() # print the total cost print(i) # print the details of the book print(book) Функция, возвращающая другую функцию
В языке программирования Python функция имеет форму объекта. Следовательно, пользователь может вернуть функцию из другой функции.
В приведенной ниже программе функция first_add возвращает функцию second_add.
def first_add(x): def second_add(y): return x + y return second_add i = first_add(20) print("The value of x + y is", i(10)) # second function def outer_func(x): return x * 5 def func(): # return the value in the different function return outer_func # storing the function in z z = func() print("\nThe value of x * y is", z(10)) Python return statement
While we believe that this content benefits our community, we have not yet thoroughly reviewed it. If you have any suggestions for improvements, please let us know by clicking the “report an issue“ button at the bottom of the tutorial.
The python return statement is used to return values from the function. We can use the return statement in a function only. It can’t be used outside of a Python function.
Python Function without return statement
Every function in Python returns something. If the function doesn’t have any return statement, then it returns None .
def print_something(s): print('Printing::', s) output = print_something('Hi') print(f'A function without return statement returns ') Output:
Python Return Statement Example
We can perform some operation in a function and return the result to the caller using the return statement.
def add(x, y): result = x + y return result output = add(5, 4) print(f'Output of add(5, 4) function is ') Output:
Python return statement with expression
We can have expressions also in the return statement. In that case, the expression is evaluated and the result is returned.
def add(x, y): return x + y output = add(5, 4) print(f'Output of add(5, 4) function is ') Output:
Python return boolean
Let’s look at an example where we will return the boolean value of the argument of a function. We will use bool() function to get the boolean value of the object.
def bool_value(x): return bool(x) print(f'Boolean value returned by bool_value(False) is ') print(f'Boolean value returned by bool_value(True) is ') print(f'Boolean value returned by bool_value("Python") is ') Output:
Python return string
Let’s look at an example where our function will return the string representation of the argument. We can use the str() function to get the string representation of an object.
def str_value(s): return str(s) print(f'String value returned by str_value(False) is ') print(f'String value returned by str_value(True) is ') print(f'String value returned by str_value(10) is ') Output:
Python return tuple
Sometimes we want to convert a number of variables into a tuple. Let’s see how to write a function to return a tuple from a variable number of arguments.
def create_tuple(*args): my_list = [] for arg in args: my_list.append(arg * 10) return tuple(my_list) t = create_tuple(1, 2, 3) print(f'Tuple returned by create_tuple(1,2,3) is ') Output: Further Reading: Python *args and **kwargs
Python function returning another function
We can return a function also from the return statement. This is similar to Currying, which is the technique of translating the evaluation of a function that takes multiple arguments into evaluating a sequence of functions, each with a single argument.
def get_cuboid_volume(h): def volume(l, b): return l * b * h return volume volume_height_10 = get_cuboid_volume(10) cuboid_volume = volume_height_10(5, 4) print(f'Cuboid(5, 4, 10) volume is ') cuboid_volume = volume_height_10(2, 4) print(f'Cuboid(2, 4, 10) volume is ') Output:
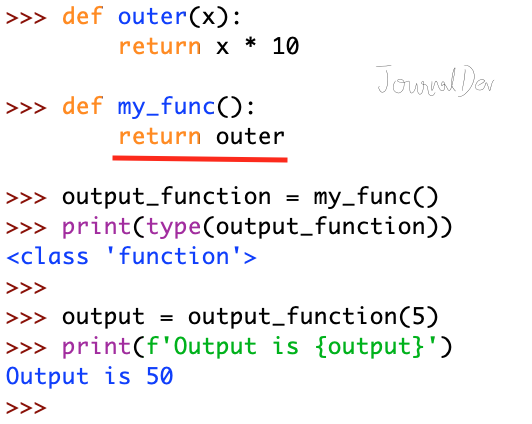
Python function returning outer function
def outer(x): return x * 10 def my_func(): return outer output_function = my_func() print(type(output_function)) output = output_function(5) print(f'Output is ') Output:
Python return multiple values
If you want to return multiple values from a function, you can return tuple, list, or dictionary object as per your requirement. However, if you have to return a huge number of values then using sequence is too much resource hogging operation. We can use yield, in this case, to return multiple values one by one.
def multiply_by_five(*args): for arg in args: yield arg * 5 a = multiply_by_five(4, 5, 6, 8) print(a) # showing the values for i in a: print(i) Output:
Summary
The python return statement is used to return the output from a function. We learned that we can also return a function from another function. Also, expressions are evaluated and then the result is returned from the function. You can checkout complete python script and more Python examples from our GitHub Repository.
Thanks for learning with the DigitalOcean Community. Check out our offerings for compute, storage, networking, and managed databases. Learn more about us