- How To Create, Modify, Append ByteArray Object In Python
- 1. What Is Python ByteArray.
- 2. How To Create Python ByteArray Object Examples.
- 2.1 Example 1.
- 2.2 Example 2.
- 2.3 Example 3.
- 2.4 Example 4.
- 3. How To Modify A Python ByteArray Object.
- 4. Python ByteArray Append Example.
- 4.1 Use append() Method Example.
- 4.2 Use extend() Method Example.
- Python Byte Arrays: A Comprehensive Guide
- Manipulating Byte Arrays in Python
- Complexity of Byte Arrays in Python
- Real-Life Applications of Byte Arrays
- a. File Handling
- b. Cryptography
- c. Networking
- Conclusion
- Questions for Interactivity and Testing Knowledge
- Akshat Sunil Pande
- Python
- Introduction to Android Development
- Different ways to Redirect a webpage
How To Create, Modify, Append ByteArray Object In Python
In this article, I will tell you what is python ByteArray, how to create or modify a python ByteArray object, how to append data to a python ByteArray object with examples.
1. What Is Python ByteArray.
- In Python, bytearray is a mutable sequence of bytes. It is similar to a list, but each element in a bytearray is an integer between 0 and 255, representing a single byte of data.
- One of the main benefits of bytearray over other Python data types is that it is mutable.
- This means that you can change the values of individual elements in the bytearray after it has been created.
- This can be useful in situations where you need to modify data that is represented as a sequence of bytes, such as in network communication or file I/O.
2. How To Create Python ByteArray Object Examples.
- In Python, the bytearray() function is used to create a mutable sequence of bytes. The function can take one of the following arguments:
- If no argument is provided, an empty bytearray object is created.
- If an integer argument is provided, a bytearray object of the specified length is created, with all elements initialized to zero.
- If an iterable argument is provided, a bytearray object is created with the same elements as the iterable.
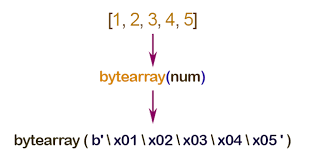
2.1 Example 1.
- A bytearray object can be created by calling the bytearray() function with an optional argument that specifies the length of the bytearray or an iterable that contains the elements of the bytearray .
- Here is an example of how to create and use a bytearray object in Python:
# Create a bytearray object from a string my_string = "hello world" my_bytearray = bytearray(my_string, "utf-8") # Print the bytearray object print(my_bytearray) # Output: bytearray(b'hello world') # Modify an element of the bytearray object my_bytearray[0] = 72 # Change the first element to the ASCII code for 'H' # Print the modified bytearray object print(my_bytearray) # Output: bytearray(b'Hello world')
2.2 Example 2.
my_bytearray = bytearray() print(my_bytearray) # Output: bytearray(b'') print('bytearray length is : ' + str(len(my_bytearray))) bytearray(b'') bytearray length is : 0
2.3 Example 3.
my_bytearray = bytearray(5) print(my_bytearray) # Output: bytearray(b'\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00') print('bytearray length is : ' + str(len(my_bytearray))) bytearray(b'\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00') bytearray length is : 5
2.4 Example 4.
my_list = [97, 98, 99, 100] my_bytearray = bytearray(my_list) print(my_bytearray) # Output: bytearray(b'abcd')
3. How To Modify A Python ByteArray Object.
- You can also modify a bytearray object, since it is mutable.
- Here is an example of how to modify a bytearray object:
my_bytearray = bytearray(b"hello") print("Before modify : ") print(my_bytearray) # Output: bytearray(b'dello') my_bytearray[0] = 100 # Change the first element to from 'h' to 'd' with the new ascii code. print("After modify : ") print(my_bytearray) # Output: bytearray(b'dello') Before modify : bytearray(b'hello') After modify : bytearray(b'dello')
4. Python ByteArray Append Example.
4.1 Use append() Method Example.
- In Python, you can append elements to a bytearray object using the append() method.
- The append() method adds a single element to the end of the bytearray.
- Here’s an example of how to use the append() method to add elements to a bytearray object:
# Create an empty bytearray my_bytearray = bytearray() # Append elements to the bytearray my_bytearray.append(72) # Append the ASCII code for 'H' my_bytearray.append(101) # Append the ASCII code for 'e' my_bytearray.append(108) # Append the ASCII code for 'l' my_bytearray.append(108) # Append the ASCII code for 'l' my_bytearray.append(111) # Append the ASCII code for 'o' # Print the final bytearray print(my_bytearray) # Output: bytearray(b'Hello')
4.2 Use extend() Method Example.
- You can also append multiple elements to a bytearray using the extend() method.
- The extend() method takes an iterable as an argument, and adds each element of the iterable to the end of the bytearray .
- Here’s an example of how to use the extend() method:
# Create an empty bytearray my_bytearray = bytearray() # Append multiple elements to the bytearray my_bytearray.extend([72, 101, 108, 108, 111]) # Print the final bytearray print(my_bytearray) # Output: bytearray(b'Hello')
Python Byte Arrays: A Comprehensive Guide
In this example, we created a byte array containing the ASCII-encoded string «hello world». The ‘b’ prefix before the string indicates that it should be treated as a sequence of bytes rather than characters.
my_bytes = bytes([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) This creates a byte array with eight bytes, each containing the corresponding integer value.
my_bytearray = bytearray([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) This creates a mutable byte array that can be modified in-place, unlike the bytes() function, which creates an immutable byte array.
Manipulating Byte Arrays in Python
- Byte arrays in Python offer several methods to manipulate the data they contain, such as slicing, concatenation, appending, inserting, and modifying.
- For instance, we can slice a byte array to extract a subset of its elements as follows:
my_bytes = bytes([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]) slice_bytes = my_bytes[2:6] print(slice_bytes) # Output: b'\x02\x03\x04\x05' This extracts the elements from index 2 to 5 and returns them as a new byte array.
my_bytes1 = bytes([0, 1, 2]) my_bytes2 = bytes([3, 4, 5, 6]) concat_bytes = my_bytes1 + my_bytes2 print(concat_bytes) # Output: b'\x00\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05\x06' This creates a new byte array that combines the elements of both byte arrays.
- We can also append or insert elements into a byte array using the append() and insert() methods , respectively. For instance:
my_bytearray = bytearray([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]) my_bytearray.append(5) my_bytearray.insert(1, 6) print(my_bytearray) # Output: bytearray(b'\x00\x06\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05') This adds the element 5 at the end of the byte array and inserts the element 6 at index 1, shifting the other elements to the right.
Complexity of Byte Arrays in Python
- Byte arrays in Python are efficient data structures that offer several advantages over other data types, such as strings or lists, for storing and manipulating binary data. For instance, byte arrays use less memory than strings because they only store the raw data without any additional metadata or encoding. Additionally, byte arrays offer faster performance than lists because they are implemented as a contiguous block of memory that can be easily accessed and modified.
- To illustrate the performance benefits of byte arrays, let’s compare the time it takes to manipulate a byte array versus a list of integers using the following code :
import time # Using byte array start = time.time() my_bytes = bytearray(range(1000000)) my_bytes[500000] = 255 end = time.time() print("Time taken with byte array: ", end-start) # Using list of integers start = time.time() my_list = list(range(1000000)) my_list[500000] = 255 end = time.time() print("Time taken with list of integers: ", end-start) In this example, we create a byte array and a list of integers with one million elements each and then modify the element at index 500000. Running this code on a typical machine gives the following output:
Time taken with byte array: 0.00032591819763183594 Time taken with list of integers: 0.016950130462646484 - As we can see, manipulating a byte array is almost 50 times faster than manipulating a list of integers. This is because a byte array is implemented as a contiguous block of memory that can be accessed and modified in constant time, while a list of integers is implemented as a dynamic array that requires reallocating memory and copying elements whenever it grows or shrinks.
Real-Life Applications of Byte Arrays
- Byte arrays in Python have several real-life applications, particularly in data processing, network programming, and cryptography. For instance, byte arrays are commonly used to read and write binary files such as images, audio, video, and other multimedia files. They are also used in network programming to send and receive data over sockets, where the data needs to be serialized and deserialized as byte arrays.
- Byte arrays are also essential in cryptography, where they are used to encrypt and decrypt data, generate and verify digital signatures, and perform other cryptographic operations. For instance, the popular RSA algorithm uses byte arrays to represent the plaintext, ciphertext, and keys. Similarly, the AES algorithm uses byte arrays to represent the blocks of data that are encrypted or decrypted using the key.
- Let’s take a look at a few examples to see how they can be used in practice.
a. File Handling
- Byte arrays can be used to read and write binary data from files. For example, let’s say you have an image file called «my_image.jpg» and you want to read its contents into a byte array. Here’s how you can do it:
with open('my_image.jpg', 'rb') as f: image_data = bytearray(f.read()) The «rb» mode argument indicates that the file should be opened in binary mode. The ‘read()’ method reads the entire contents of the file into a byte array.
b. Cryptography
- Byte arrays are also useful for cryptography, which involves encrypting and decrypting data. Let’s say you have a plaintext message that you want to encrypt using the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm . Here’s how you can do it using the PyCryptodome library:
from Crypto.Cipher import AES plaintext = b'my secret message' key = b'this is a secret key' iv = b'initialization vec' cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_CBC, iv) ciphertext = cipher.encrypt(plaintext) In this example, we created a byte array containing the plaintext message, as well as byte arrays for the secret key and initialization vector (IV). We then created an AES cipher object using the key and IV, and encrypted the plaintext message using the encrypt() method.
c. Networking
- Finally, byte arrays can be used for networking applications, such as sending and receiving data over a network socket. Let’s say you want to send a message over a TCP socket. Here’s how you can do it:
import socket message = b'hello world' host = 'localhost' port = 1234 s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) s.connect((host, port)) s.sendall(message) s.close() In this example, we created a byte array containing the message to be sent.
Conclusion
- In conclusion, byte arrays in Python are versatile and efficient data structures that allow for storing and manipulating binary data with ease. They offer several advantages over other data types, such as strings or lists, in terms of memory usage and performance. Byte arrays have numerous real-life applications in data processing, network programming, and cryptography, making them an essential tool for any Python programmer.
Questions for Interactivity and Testing Knowledge
- Here are some questions to test your knowledge and understanding of byte arrays in Python:
- What is a byte array in Python, and how is it different from bytes and strings?
- How do you create a byte array in Python, and what methods can be used to modify it?
- What are some applications of byte arrays in Python, and in what scenarios would you prefer to use them over other data types?
- How can you convert a byte array to a string or vice versa in Python?
- What are memory-mapped files, and how can they be used to handle large binary data in Python?
Akshat Sunil Pande
Shri Ramdeobaba College of Engineering and Management, Nagpur
OpenGenus Tech Review Team
Python
Introduction to Android Development
In this article, we will take a closer look at Android Development and explore what it takes to become an Android developer.
King Immanuel
Different ways to Redirect a webpage
In this article at OpenGenus, we have explained how to redirect a webpage using JavaScript and natively in HTML. We have developed demos to demonstrate the ideas with code examples.
Oluwafunsho Anthony