- How to Print a Newline in Python
- Print a Newline Character Using print() Statements
- Using an Escape Sequence to Print a Newline
- Practice Printing a Newline in Python!
- How to Print a Newline in Python
- Python Newline Statement Example
- Newlines in Python f-strings
- Create Two Line Breaks in Python
- Print without a Newline in Python
- Change the Newline Character in Python
- Print a newline in Python
- Use of newline in Python script:
- Example-1: Print the newline inside the string values
- Example-2: Print the newline inside the list items
- Example-3: Print the newline inside the dictionary items
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- Fahmida Yesmin
How to Print a Newline in Python
Do you know how to print a newline in Python? Do you struggle with multiple print() statements whenever you want to start a new line in your Python script? In this article, we’ll explore how to overcome this pitfall.
Newline is a feature related to the Python print() function. Maybe you already understand why you should learn Python but you’re unsure about Python printing techniques. That’s okay; this article will help you out.
To print multiple lines of text in Python, you can use either multiple print() statements or a single print() statement with newline characters ( \n ) inserted between the lines. We’ll give you some examples of these.
If you’re not familiar with the print() statement in Python, now might be a good time to take a look at our Python Basics track. It will give you the necessary foundations to start coding with confidence. Its 3 interactive courses will teach you Python data structures, control flow statements, and how to manipulate files. By the end of the course, you will know how to write and call your very own Python functions.
Ok, let’s suppose you know the basics of Python and you want to control how your results are displayed on the screen. For this, you’ll need the newline character.
Print a Newline Character Using print() Statements
The most basic way to print multiple lines of text in Python is to use multiple print() statements:
>>> print("Hello Pythonista!") >>> print("We love LearnPython.com") >>> print("Python is so fun!") Hello Pythonista! We love LearnPython.com Python is so fun!
In this example, each line of text is printed using a separate print() statement, causing each line to be printed on a separate line.
Note that you can use the end parameter of the print() function to change the default line-ending character. By default, the end parameter is set to » \n «, but you can set it to an empty string «» to remove the newline character. Or you can use a different character or string for a different line ending.
Using an Escape Sequence to Print a Newline
In Python, escape sequences are special characters that begin with a backslash ( \ ) and are used to represent certain special characters or behaviors. These escape sequences allow you to include characters in your strings that might otherwise be difficult or impossible to type directly in your code.
One common use of escape sequences is to include newline characters ( \n ) in your strings.
A newline character is a special character that represents the end of a line of text. It causes the next characters to be printed on a new line.
When a newline character is encountered in a string, it tells Python to start a new line in the output. This can be useful for formatting text in your Python programs or creating multi-line strings.
Here are some examples of how to use the escape sequence to print newlines in Python:
Example 1: Use the \n escape sequence to print a newline:
Example 2: Use multiple \n escape sequences to print multiple newlines:
>>> print("Hello Pythonista!\n\nWelcome to LearnPython.com!"") Hello Pythonista! Welcome to LearnPython.com!
Example 3: Use an f-string and include a newline character in a formatted string:
>>> name = "Alice" >>> print(f"Hello, !\nHow are you today?")
Hello, Alice! How are you today?
In each of these examples, the \n escape sequence is used to insert a newline character into the output produced by the print() function. This causes the following characters to be printed on a new line. You can use as many \n escape sequences as you like to produce multiple lines.
But at the end of the day, the main advantage of the newline character is to print multiple lines with a single Python print() statement.
>>> print("Hello Pythonista!\nWe love LearnPython.com\nPython is so fun!") Hello Pythonista! We love LearnPython.com Python is so fun!
In the example above, a single print() statement prints multiple lines of text by including newline characters ( \n ) between the lines. This causes the text to be printed with each line on a separate line.
Newlines can also be used to separate logical sections of code or data, such as in the case of a CSV or a text file where each row of data is separated by a newline character. You can verify this by opening a .txt file in Python, such as:
>>> file = open("example.txt", "rb") >>> print(file.readlines()) ['Hello Pythonista! \n', 'Welcome to LearnPython.com!\n', 'Python is awesome! ']
And if we type the following …
Hello Pythonista! Welcome to LearnPython.com! Python is awesome!
Overall, the newline character is an important concept in Python. It’s used extensively in text formatting and manipulation.
Practice Printing a Newline in Python!
In this article, we explored how to print a newline in Python. It’s good practice to use newlines in your Python code. This can make it easier to read and understand, especially for code containing multiple lines or long strings. It also avoids the pitfall of writing multiple print() statements.
Once you’re confident using newlines in your code, I encourage you to read our tips for Python scripts. You may also want to practice your Python skills using our practice set, which is specifically designed to help you reach the next level of programming proficiency.
Last but not least, remember to regularly visit LearnPython.com and keep learning!
How to Print a Newline in Python
In this tutorial, we will look at how to print newlines in Python and change the character that is at the end of a line.
Python Newline Statement Example
To print a new line in Python use \n (backslash n) keyword. When the code is rendered \n will become a newline. Here is an example of printing a string with a newline inside it:
A thing to watch out for is Python will not automatically remove the leading whitespace on the newline. You can use \n without a space after and it will work:
Newlines in Python f-strings
Newlines work in the same way with Python f-strings. Add \n wherever you need it to be:
Create Two Line Breaks in Python
To create more than one newline use multiple \n next to each other like this:
Print without a Newline in Python
The default behaviour of the Python print() statement is to put a newline ( \n ) at the end of a line. To print without newlines add the end= argument and set it to an empty string like this:
print('hello ', end='') print('world') Change the Newline Character in Python
You can change what is put at the end of each line by the Python print() statement using the end= argument. In the example below a space will be used instead of \n :
print('hello', end=' ') print('world') Print a newline in Python
The newline(\n) or line break is required to add different parts of the python script, such as inside the string, list or dictionary or tuple items, etc. Different ways to print the newline(\n) in Python script have shown in this tutorial.
Use of newline in Python script:
Adding newline in different parts of the python script has been shown in this tutorial.
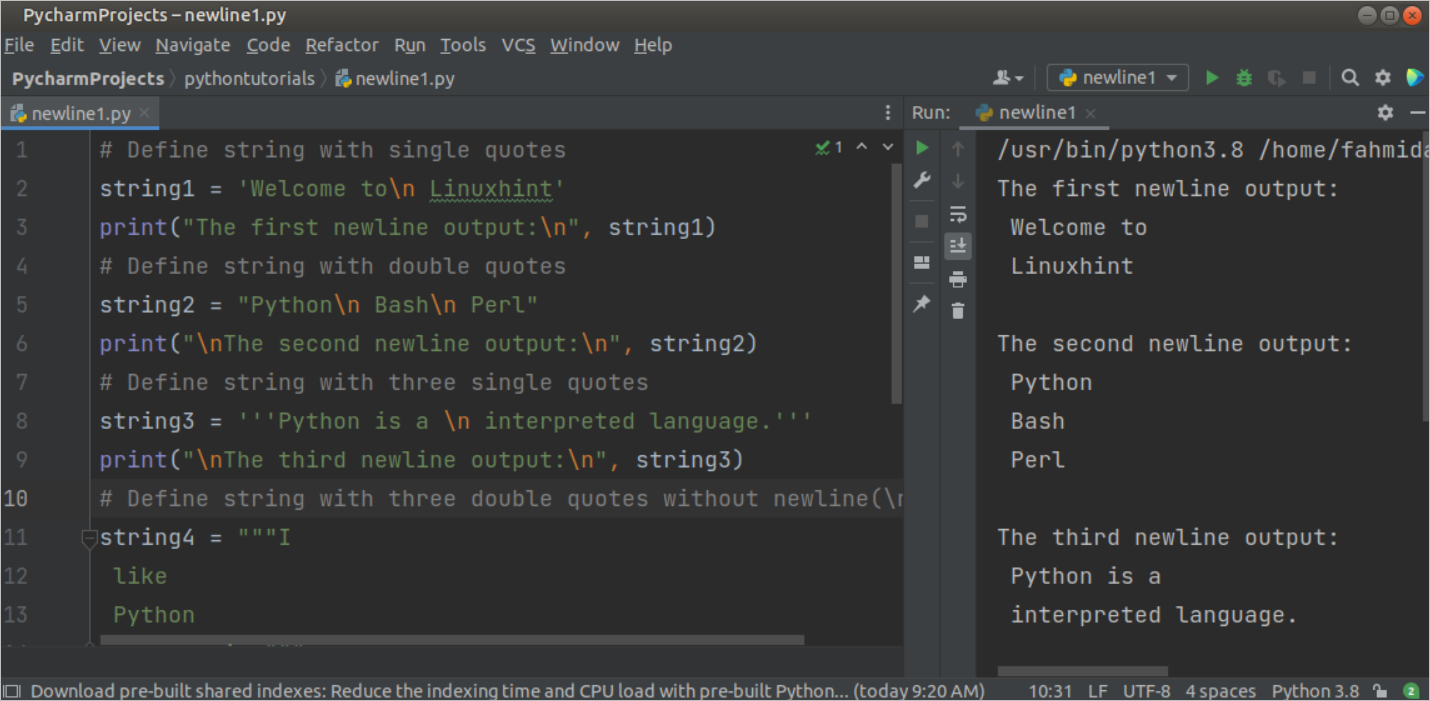
Example-1: Print the newline inside the string values
Adding a new line inside the string value is a very common task of the python script. Create a python file with the following script to know how to add newline in different parts of the string value. In the string1 variable, the newline character (\n) has used in the middle of the single-quoted string value. In the string2 variable, the newline character (\n) has used two times in the middle of the double-quoted string value. In the string3 variable, the newline character (\n) has used in the middle of the triple single-quoted string value. In the string4 variable, the newline character (\n) has used in the middle of the triple double-quoted string value. In the string5 variable, the variable containing newline character (\n) has been used inside the formatted string.
# Define string with single quotes
string1 = ‘Welcome to \n Linuxhint’
print ( «The first newline output: \n » , string1 )
# Define string with double quotes
string2 = «Python \n Bash \n Perl»
print ( » \n The second newline output: \n » , string2 )
# Define string with three single quotes
string3 = »’Python is a \n interpreted language.»’
print ( » \n The third newline output: \n » , string3 )
# Define string with three double quotes without newline(\n)
print ( » \n The fourth newline output: \n » , string4 )
# Assign newline(\n) character into a variable
# Use the variable in the string
print ( » \n The fourth newline output: \n » , string5 )
The following output will appear after executing the above script.
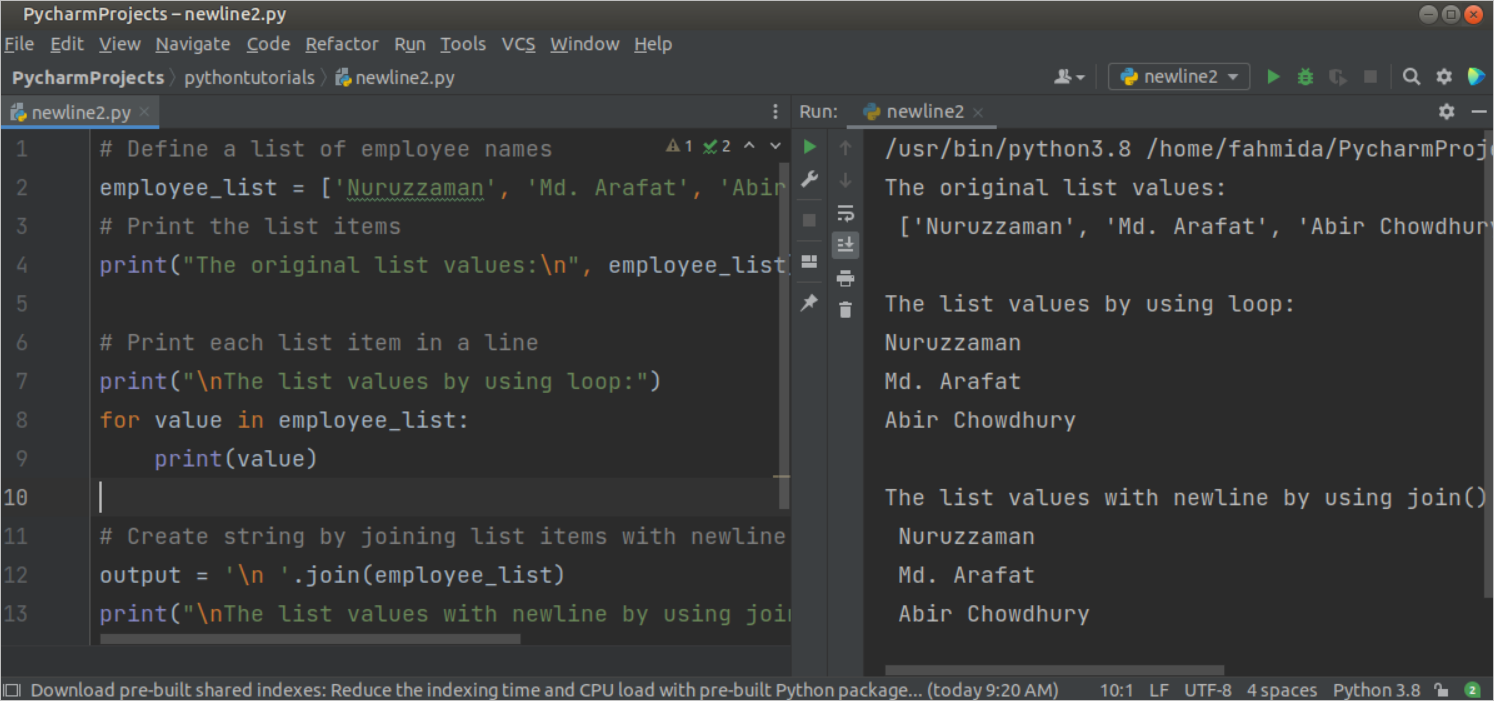
Example-2: Print the newline inside the list items
Create a python file with the following script to print each list value in a line by using for loop and joining the list items with the newline character (\n). A list of three elements has been declared in the script, and the values of this list have been printed by using for loop and the join() function.
# Define a list of employee names
employee_list = [ ‘Nuruzzaman’ , ‘Md. Arafat’ , ‘Abir Chowdhury’ ]
# Print the list items
print ( «The original list values: \n » , employee_list )
# Print each list item in a line
print ( » \n The list values by using loop:» )
for value in employee_list:
print ( value )
# Create string by joining list items with newline
output = ‘ \n ‘ . join ( employee_list )
print ( » \n The list values with newline by using join() function: \n » , output )
The following output will appear after executing the above script.
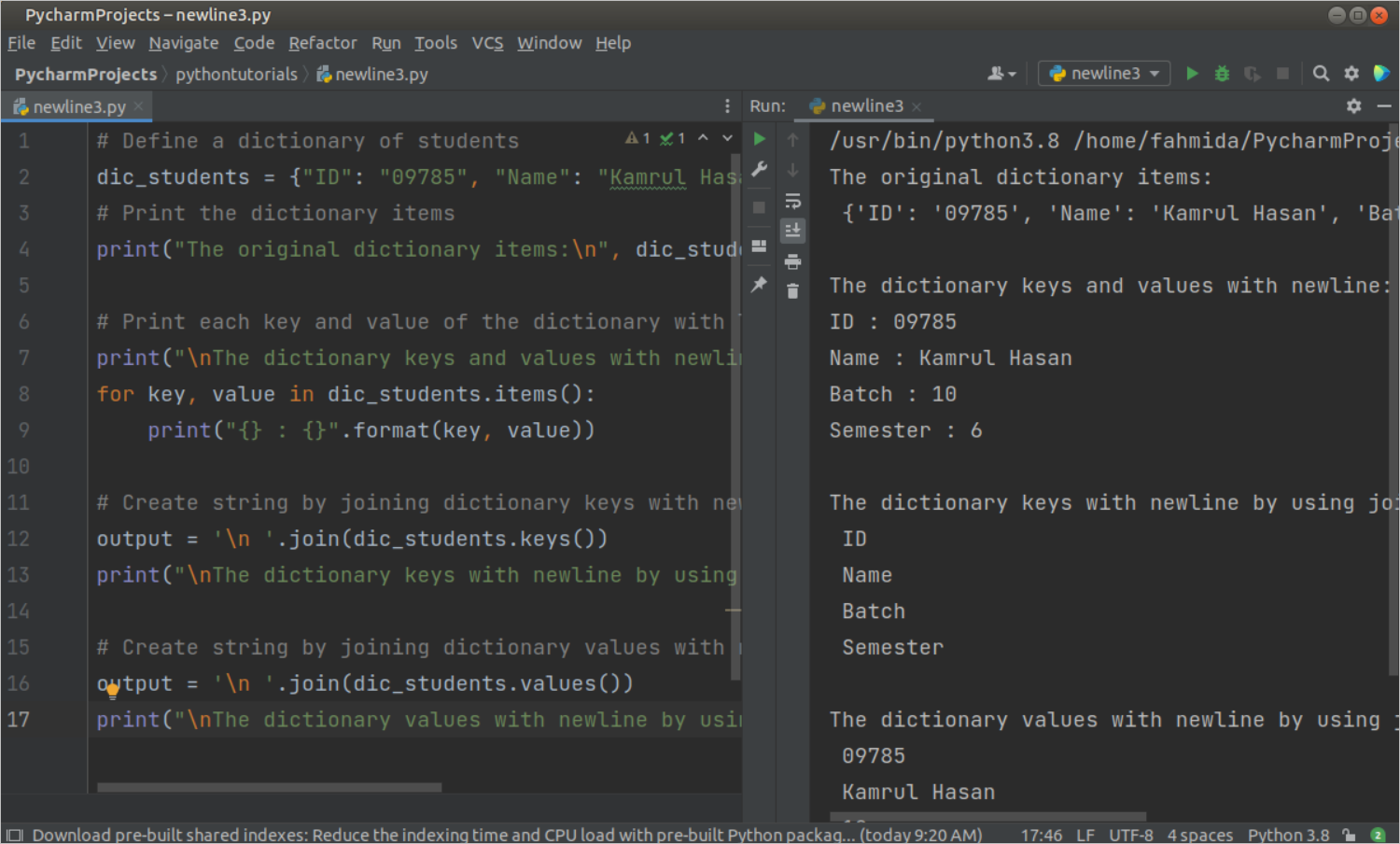
Example-3: Print the newline inside the dictionary items
Create a python file with the following script to print each key and value of a dictionary in a line by using for loop. Next, each key and value of the dictionary has been printed in a line separately by using the join() function.
# Define a dictionary of students
dic_students = { «ID» : «09785» , «Name» : «Kamrul Hasan» ,
«Batch» : «10» , «Semester» : «6» }
# Print the dictionary items
print ( «The original dictionary items: \n » , dic_students )
# Print each key and value of the dictionary with line break
print ( » \n The dictionary keys and values with newline:» )
for key , value in dic_students. items ( ) :
print ( «<> : <>» . format ( key , value ) )
# Create string by joining dictionary keys with newline
output = ‘ \n ‘ . join ( dic_students. keys ( ) )
print ( » \n The dictionary keys with newline by using join() function: \n » , output )
# Create string by joining dictionary values with newline
output = ‘ \n ‘ . join ( dic_students. values ( ) )
print ( » \n The dictionary values with newline by using join() function: \n » , output )
The following output will appear after executing the above script.
Conclusion:
The ways of adding newline (\n) inside the string, list, and dictionary variables have been shown in this tutorial using various examples.
About the author
Fahmida Yesmin
I am a trainer of web programming courses. I like to write article or tutorial on various IT topics. I have a YouTube channel where many types of tutorials based on Ubuntu, Windows, Word, Excel, WordPress, Magento, Laravel etc. are published: Tutorials4u Help.