Поля ввода swing java
JTextField is a lightweight component that allows the editing of a single line of text. For information on and examples of using text fields, see How to Use Text Fields in The Java Tutorial. JTextField is intended to be source-compatible with java.awt.TextField where it is reasonable to do so. This component has capabilities not found in the java.awt.TextField class. The superclass should be consulted for additional capabilities. JTextField has a method to establish the string used as the command string for the action event that gets fired. The java.awt.TextField used the text of the field as the command string for the ActionEvent . JTextField will use the command string set with the setActionCommand method if not null , otherwise it will use the text of the field as a compatibility with java.awt.TextField . The method setEchoChar and getEchoChar are not provided directly to avoid a new implementation of a pluggable look-and-feel inadvertently exposing password characters. To provide password-like services a separate class JPasswordField extends JTextField to provide this service with an independently pluggable look-and-feel. The java.awt.TextField could be monitored for changes by adding a TextListener for TextEvent ‘s. In the JTextComponent based components, changes are broadcasted from the model via a DocumentEvent to DocumentListeners . The DocumentEvent gives the location of the change and the kind of change if desired. The code fragment might look something like:
DocumentListener myListener = ??; JTextField myArea = ??; myArea.getDocument().addDocumentListener(myListener); The horizontal alignment of JTextField can be set to be left justified, leading justified, centered, right justified or trailing justified. Right/trailing justification is useful if the required size of the field text is smaller than the size allocated to it. This is determined by the setHorizontalAlignment and getHorizontalAlignment methods. The default is to be leading justified. How the text field consumes VK_ENTER events depends on whether the text field has any action listeners. If so, then VK_ENTER results in the listeners getting an ActionEvent, and the VK_ENTER event is consumed. This is compatible with how AWT text fields handle VK_ENTER events. If the text field has no action listeners, then as of v 1.3 the VK_ENTER event is not consumed. Instead, the bindings of ancestor components are processed, which enables the default button feature of JFC/Swing to work. Customized fields can easily be created by extending the model and changing the default model provided. For example, the following piece of code will create a field that holds only upper case characters. It will work even if text is pasted into from the clipboard or it is altered via programmatic changes.
public class UpperCaseField extends JTextField < public UpperCaseField(int cols) < super(cols); >protected Document createDefaultModel() < return new UpperCaseDocument(); >static class UpperCaseDocument extends PlainDocument < public void insertString(int offs, String str, AttributeSet a) throws BadLocationException < if (str == null) < return; >char[] upper = str.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0; i < upper.length; i++) < upper[i] = Character.toUpperCase(upper[i]); >super.insertString(offs, new String(upper), a); > > > Warning: Swing is not thread safe. For more information see Swing’s Threading Policy. Warning: Serialized objects of this class will not be compatible with future Swing releases. The current serialization support is appropriate for short term storage or RMI between applications running the same version of Swing. As of 1.4, support for long term storage of all JavaBeans™ has been added to the java.beans package. Please see XMLEncoder .
Nested Class Summary
How to Use Text Fields
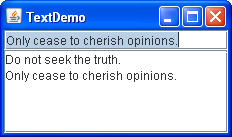
A text field is a basic text control that enables the user to type a small amount of text. When the user indicates that text entry is complete (usually by pressing Enter), the text field fires an action event. If you need to obtain more than one line of input from the user, use a text area.
| JTextField | What this section covers: basic text fields. |
| JFormattedTextField | A JTextField subclass that allows you to specify the legal set of characters that the user can enter. See How to Use Formatted Text Fields. |
| JPasswordField | A JTextField subclass that does not show the characters that the user types. See How to Use Password Fields. |
| JComboBox | Can be edited, and provides a menu of strings to choose from. See How to Use Combo Boxes. |
| JSpinner | Combines a formatted text field with a couple of small buttons that enables the user to choose the previous or next available value. See How to Use Spinners. |
The following example displays a basic text field and a text area. The text field is editable. The text area is not editable. When the user presses Enter in the text field, the program copies the text field’s contents to the text area, and then selects all the text in the text field.
Click the Launch button to run TextDemo using Java™ Web Start (download JDK 7 or later). Alternatively, to compile and run the example yourself, consult the example index.
You can find the entire code for this program in TextDemo.java . The following code creates and sets up the text field:
textField = new JTextField(20);
The integer argument passed to the JTextField constructor, 20 in the example, indicates the number of columns in the field. This number is used along with metrics provided by the field’s current font to calculate the field’s preferred width. It does not limit the number of characters the user can enter. To do that, you can either use a formatted text field or a document listener, as described in Text Component Features.
We encourage you to specify the number of columns for each text field. If you do not specify the number of columns or a preferred size, then the field’s preferred size changes whenever the text changes, which can result in unwanted layout updates.
The next line of code registers a TextDemo object as an action listener for the text field.
textField.addActionListener(this);
The actionPerformed method handles action events from the text field:
private final static String newline = «\n»; . public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent evt)
Notice the use of JTextField ‘s getText method to retrieve the text currently contained by the text field. The text returned by this method does not include a newline character for the Enter key that fired the action event.
You have seen how a basic text field can be used. Because the JTextField class inherits from the JTextComponent class, text fields are very flexible and can be customized almost any way you like. For example, you can add a document listener or a document filter to be notified when the text changes, and in the filter case you can modify the text field accordingly. Information on text components can be found in Text Component Features. Before customizing a JTextField , however, make sure that one of the other components based on text fields will not do the job for you.
Often text fields are paired with labels that describe the text fields. See Examples That Use Text Fields for pointers on creating these pairs.
Another Example: TextFieldDemo
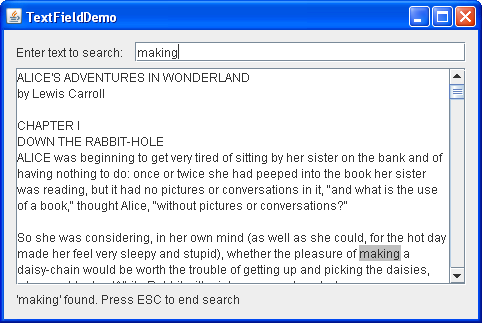
The TextFieldDemo example introduces a text field and a text area. You can find the entire code for this program in TextFieldDemo.java .
As you type characters in the text field the program searches for the typed text in the text area. If the entry is found it gets highlighted. If the program fails to find the entry then the text field’s background becomes pink. A status bar below the text area displays a message whether text is found or not. The Escape key is used to start a new search or to finish the current one. Here is a picture of the TextFieldDemo application.
Click the Launch button ro run TextFieldDemo using Java™ Web Start (download JDK 7 or later). Alternatively, to compile and run the example yourself, consult the example index.
To highlight text, this example uses a highlighter and a painter. The code below creates and sets up the highlighter and the painter for the text area.
final Highlighter hilit; final Highlighter.HighlightPainter painter; . hilit = new DefaultHighlighter(); painter = new DefaultHighlighter.DefaultHighlightPainter(HILIT_COLOR); textArea.setHighlighter(hilit);
This code adds a document listener to the text field’s document.
entry.getDocument().addDocumentListener(this);
Document listener’s insertUpdate and removeUpdate methods call the search method, which not only performs a search in the text area but also handles highlighting. The following code highlights the found text, sets the caret to the end of the found match, sets the default background for the text field, and displays a message in the status bar.
hilit.addHighlight(index, end, painter); textArea.setCaretPosition(end); entry.setBackground(entryBg); message("'" + s + "' found. Press ESC to end search"); The status bar is a JLabel object. The code below shows how the message method is implemented.
private JLabel status; . void message(String msg)
If there is no match in the text area, the following code changes the text field’s background to pink and displays a proper information message.
entry.setBackground(ERROR_COLOR); message("'" + s + "' not found. Press ESC to start a new search"); The CancelAction class is responsible for handling the Escape key as follows.
class CancelAction extends AbstractAction < public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent ev) < hilit.removeAllHighlights(); entry.setText(""); entry.setBackground(entryBg); >> The Text Field API
The following tables list the commonly used JTextField constructors and methods. Other methods you are likely to call are defined in the JTextComponent class. Refer to The Text Component API.
You might also invoke methods on a text field inherited from the text field’s other ancestors, such as setPreferredSize , setForeground , setBackground , setFont , and so on. See The JComponent Class for tables of commonly used inherited methods.
The API for using text fields falls into these categories:
Examples That Use Text Fields
This table shows a few of the examples that use text fields and points to where those examples are described. For examples of code that are similar among all varieties of text fields such as dealing with layout, look at the example lists for related components such as formatted text fields and spinners.
addLabelTextRows(JLabel[] labels, JTextField[] textFields, GridBagLayout gridbag, Container container)
makeCompactGrid(Container parent, int rows, int cols, int initialX, int initialY, int xPad, int yPad)
If you are programming in JavaFX, see Text Field.