- Environment Variables in PHP
- PHP Environment Variables
- More About PHP Environment Variables
- Example of Using Environment Variables in PHP
- Why $_ENV Is Empty
- Setting Environment Variables
- Related Functions of PHP Environment Variable
- How to Get and Set PHP Custom Environment Variables
- Setting Custom PHP Environment Variables
- Why We Need to User Custom Environment Variables
- How to Set Custom Environment Variables
- 1- Set Environment Variables Using putenv() function
- Set Environment Variables in PHP with PHP dotenv
- It makes it easier for malicious actors to access
- It makes it harder to deploy the code
- Prerequisites
- How does PHP dotenv work?
- How will the code work?
- Install PHP dotenv
- Create a dotenv file
- Use PHP dotenv to load the environment variables
- Use the environment variables in your application’s code
- Use a different dotenv file
- You might also be interested in.
Environment Variables in PHP
The most effective practice for application setup is by using PHP environment variables, whether its database credentials, secret data parameters, API keys, or anything between deploys are now visible to code through the environment. The PHP environment variable allows developers to gather specific types of data from existing servers dynamically. In this tutorial, you will learn how to use PHP environment variables and what their features are.
PHP Environment Variables
Various PHP frameworks such as Laravel, Symfony, and others use the PHP environment variable itself to store different security-related credentials and other configurations. An ENV var or environment variable is nothing but a key-value pair used in the global scope. These variables are explicitly stored for each environment. In other words, an environment variable can be defined as a dynamic-named variable that is provided in a program for affecting the way successively running processes will work in a system.
These variables are brought into the global namespace of PHP from the environment under which the PHP runs its parser. Many of them are provided by the shell under which PHP runs with different systems that are likely to run different kinds of shells. Other environment variables include the CGI variables, irrespective of whether they are running as a server module or as a CGI processor in PHP.
More About PHP Environment Variables
As a process starts in a program, it uses its defined variables or inherits from the parent process. These variables are used for discovering facts about the environment on which it is running. These variables include details about the preferred location where the temporary files are being saved or the path where the home directory resides within the system.
If you use a Unix operating system such as Linux, you can see this by typing the value of the $HOME environment variable in the terminal:
Command:
Result:
In case, you use the Windows OS; you have to open PowerShell and use the command:
Command:
Result:
Example of Using Environment Variables in PHP
He output will look something like:
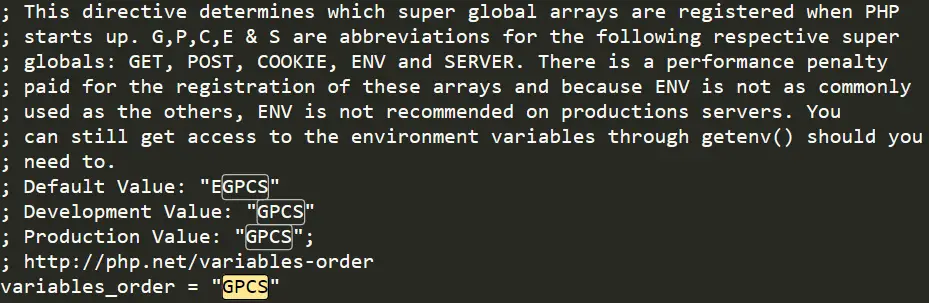
Why $_ENV Is Empty
I want to use $_ENV so that I can get the username of the logged-in user, but it is empty?
Everyone should use the getenv() function instead, but if you require $_ENV, you need to do so. To use $_ENV, you must activate it in your php.ini file. Find «variable_orders» and set it to:
Setting Environment Variables
Let us now discuss how to set an environment variable so that it can be made accessible from your PHP application.
Result:
But in case you want to include your variables in a PHP program, the simplest way to do this is to state the environment variable well before your run command, something like this:
» APP_ENV=local php -r 'var_dump(getenv("APP_ENV"));' Result:
Another well-known &convenient approach used in Unix systems is to make use of the «export» command. When the’export’ is used with an environment variable, it will be available in all successive commands until the shell exits.
» php -r ‘var_dump(getenv(«APP_ENV»));’
Result:
Related Functions of PHP Environment Variable
- getenv() is a PHP function used for returning the specific environment variable’s value
- putenv() is a PHP function that is used for setting the value of a particular environment variable
How to Get and Set PHP Custom Environment Variables
like windows Environment Variables we have some variables at Apache/PHP level, there are some default Environment Variables while we can also set our custom variables according to need of our application.
Scope wise these are Super Global Variables, although we can limit our custom vars to our application only we have discussed it step 4 below.
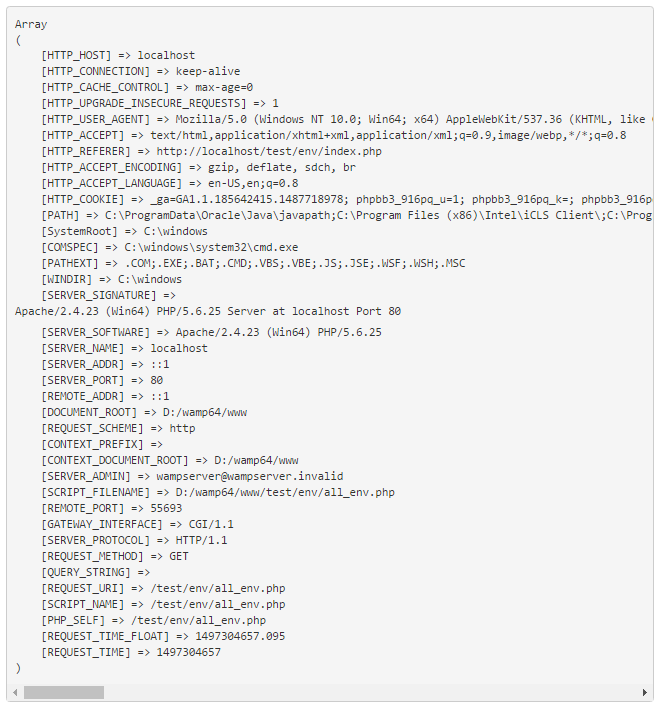
Lets have a look at PHP Default Environment Variables, we can view all Environment Variables executing the following code.
it will give us the following array of different variables
we can access single variable by using $_SERVER array or getenv() function as below
Setting Custom PHP Environment Variables
Yes we can store our custom variables too, and that can be accessed and used in the same manner as default Environment Variables.
Why We Need to User Custom Environment Variables
In short we need to use Custom Environment Variables to make our application more secure.
While developing dynamic websites we connect to database, email systems and other external components or services through their credentials like Host, User, Password, Port etc.
It is bad practice to write these credentials inside our PHP coding because if somehow someone got access to our code he/she can gain access to our database, email or other connected service and can make unwanted changes or steel our sensitive information.
To avoid it we have an option to keep these credentials as variables outside PHP code in some secure directory of our server, Environment variables gives us this facility.
How to Set Custom Environment Variables
There are several ways to set Custom Environment Variables few of them are given below.
- Using putenv() function
- using .htaccess file
- using Apache config files (httpd.conf)
- using virtual hosts (httpd-vhosts.conf)
1- Set Environment Variables Using putenv() function
This method sets Environment Variable temporarily, once script is ended, Variable(s) set by this method will no longer exist. it can be set and accessed as the following code snippet.
Set Environment Variables in PHP with PHP dotenv
There are a number of ways to set environment variables in PHP. But the approach I use most often in development is a wonderful package called PHP dotenv. In this tutorial, I’m going to step you through how to install and use it.
Before we dive right on in, why would you set and use environment variables anyway? Why wouldn’t you just store credentials in your code, where you can see and quickly edit them?
Honestly? Because you should never store credentials or any form of sensitive data in your code. Ever! Among others, here are two key reasons.
It makes it easier for malicious actors to access
Firstly, if anyone ever gets access to your source code, whether that be a malicious actor or a disgruntled former co-worker, etc, they have access to secret keys, API keys, usernames, passwords – everything. Given that, they can make authenticated requests and no one would be any the wiser.
I’m not trying to say that people are out to get you, or that you should be paranoid. However, there are people who, for a wide number of reasons, look for the opportunity to do malicious things. By storing secure credentials and sensitive data in your code, you’re making it pretty easy for them to do so. All it would take is an accidental server misconfiguration or a security breach and the secure data is available for all the world to see.
What’s more, if you put these credentials in your code, and you’re using version control, then they’re also stored there too. Yes, you can purge information from Git repositories that never should have been there, but it’s best to never put that kind of secure data under version control in the first place.
It makes it harder to deploy the code
Secondly, if secure credentials are stored directly in your code, then every deployment must use them. Think about:
- How challenging doing so would make deploying the application to different environments, such as one for testing, QA, and staging
- How hard it would be for new developers on a project to get up and running, even if they’re using tooling such as Docker Compose
- The risk that new developers run of clobbering the data of other developers – or of production!
- How hard it will be to maintain that code
By having code set in environment variables, the credentials are kept out of the code. And by having secure credentials and other details retrieved from environment variables:
- Developers don’t need to pull the latest copy of a codebase to update variables
- Developers don’t need to grep a codebase to find variables so that they can update them
- Secure credentials can never accidentally be stored under version control
- There’s a clear record of what variables need to be set for an application to work
- Each developer can use their own values
- It’s simpler to deploy applications to multiple environments
- Environment variables can be set, regardless of environment, using a range of high-quality tools such as HashiCorp Vault, GitHub Encrypted Secrets, or AWS Secrets Manager.
What other benefits can you think of? Let me know in the comments, or tweet me. Otherwise, let’s get in and write some code so you can see what I mean.
Prerequisites
To following along with this tutorial, you’re going to need the following:
How does PHP dotenv work?
PHP dotenv is, conceptually, quite simple. By default, it loads environment variables from a file named .env making them available to the getenv() method, and loads them in to $_ENV and $_SERVER . It does more than that, as you’ll see shortly, but for now that’s the essence of what it does.
How will the code work?
For the purposes of this tutorial, let’s say that your code needs an API key to make authenticated requests, such as to SendGrid or Twilio. The code will retrieve it from PHP’s $_SERVER superglobal using the key API_KEY , after PHP dotenv loads it there.
Install PHP dotenv
Thanks to Composer, there’s virtually nothing you need to install PHP dotenv, other than running the following command.
Create a dotenv file
In the top-level directory of your project, create a new file named .env. In it add the configuration below.
It’s a very strong API key, no? But seriously, set it to whatever you want. It’s not important for the purposes of this tutorial.
Use PHP dotenv to load the environment variables
Next, have PHP dotenv load API_KEY read .env and load the environment variables – as early in the lifecycle of your application as possible. To do that, add the following code to the top of your application’s main file, likely public/index.php, right after it includes Composer’s autoloader, as in the example below.
This way, your application’s code will always have access to the API key.
Use the environment variables in your application’s code
Now, all you need to do is to reference either $_ENV[‘API_KEY’] or $_SERVER[‘API_KEY’] in your application, when you need to reference the API key.
One way that I’ve become fond of when working with Mezzio, is to set the relevant configuration variables, which are stored in the DI (Dependency Injection) Container, from $_SERVER , and then use those configuration variables, as in the following example.
I find it simpler and it’s analagous to what other frameworks, such as Laravel and Symfony do.
Use a different dotenv file
By default, PHP dotenv will look for a dotenv file named .env in the directory passed to createImmutable() . However, you may prefer to name the file differently, for whatever reason. To use a different name or supply a range of potential file names, supply them as the second parameter to createImmutable() , as in the example below.
Another helpful thing you can do is require one or more environment variables to be set. I find this to be a good way to provide a documented list of all the environment variables which an application needs. To do this, use the required() method, as in the following example.
Now, if API_KEY is not set in the dotenv file, PHP dotenv will throw an exception. You can take this further by also requiring the variable to not be empty, as in the example below.
I hope that this short tutorial’s shown you both why it’s a good idea to keep secure credentials out of code, and how to do it, using PHP dotenv. If you’d like to learn several other ways of working with environment variables in PHP, check out this tutorial that I wrote.
Otherwise, have a play with PHP dotenv and the other functionality it has to offer. If you already use it, what’s your experience been with it?