- Python [WinError 3] The system cannot find the path specified
- 1. Typed the wrong name when calling os.listdir() method
- 2. Specifying non-existent path in os.rename() method.
- 3. Use absolute path instead of relative
- Take your skills to the next level ⚡️
- About
- Search
- Tags
- [SOLVED] Python filenotfounderror – A Quick Guide
- What is filenotfounderror
- How to Fix the Python filenotfounderror?
- Method 1: Specifying the complete file path
- Method 2: Using a .txt file to run Python script
- Method 3: Workaround for filenotfounderror
- Using an IDE to fix the filenotfounderror
- Conclusion
Python [WinError 3] The system cannot find the path specified
Python error [WinError 3] is a variation of the [WinError 2] error. The complete error message is as follows:
This error usually occurs when you use the Python os module to interact with the Windows filesystem.
While [WinError 2] means that a file can’t be found, [WinError 3] means that the path you specified doesn’t exist.
This article will show you several examples that can cause this error and how to fix it.
1. Typed the wrong name when calling os.listdir() method
Suppose you have the following directory structure on your computer:
Next, suppose you try to get the names of the files inside the assets/ directory using the os.listdir() method.
But you specified the wrong directory name when calling the method as follows:
Because you have an assets folder and not asset , the os module can’t find the directory:
To fix this error, make sure that the path you passed as the parameter to the listdir() method exists.
For our example, replacing asset with assets should fix the error.
2. Specifying non-existent path in os.rename() method.
The error also appears when you specified the wrong path name when calling the os.rename() method.
Suppose you have a different directory structure on your computer as follows:
Now, you want to rename the file.txt file into article.txt file.
You called the os.rename() method as follows:
The code above incorrectly specified the path docs/ as doc/ , so the error is triggered:
To fix this error, you need to specify the correct path to the file, which is docs/file.txt .
Please note that the extension of the file must be specified in the arguments. If you type file.txt as file , then you’ll get the same error.
This is because Python will think you’re instructing to rename a directory or folder and not a file.
When renaming a file, always include the file extension.
Also, keep in mind that directory and file names are case-sensitive, so you need to use the right capitalization.
3. Use absolute path instead of relative
At times, you might want to access a folder or file that’s a bit difficult to reach from the location of your script.
Suppose you have a directory structure as follows on your computer:
In this structure, the path to main.py is C:/scripts/test/main.py , while the file.txt is in C:/assets/text/file.txt
Suppose you want to rename file.txt to article.txt , this is how you specify the name with relative paths:
It’s easy for you to specify the wrong path when using relative paths, so it’s recommended to use absolute paths when the path is complex.
Here’s what the arguments look like using absolute paths:
As you can see, absolute paths are easier to read and understand. In Windows, the absolute path usually starts with the drive letter you have in your system like C: or D: .
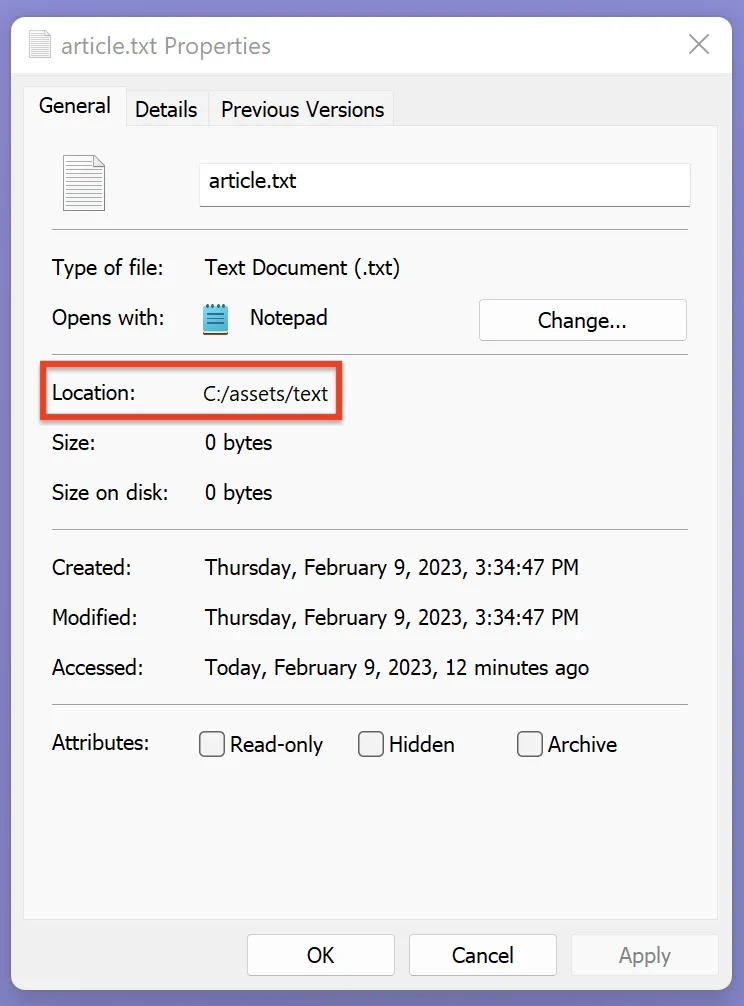
To find the absolute path of a file, right-click on the file and select Properties from the context menu.
You’ll see the location of the file as follows:
Add the file name at the end of the location path, and you get the absolute path.
I hope this tutorial is helpful. See you in other articles! 👋
Take your skills to the next level ⚡️
I’m sending out an occasional email with the latest tutorials on programming, web development, and statistics. Drop your email in the box below and I’ll send new stuff straight into your inbox!
About
Hello! This website is dedicated to help you learn tech and data science skills with its step-by-step, beginner-friendly tutorials.
Learn statistics, JavaScript and other programming languages using clear examples written for people.
Search
Type the keyword below and hit enter
Tags
Click to see all tutorials tagged with:
[SOLVED] Python filenotfounderror – A Quick Guide
In this article, we will be addressing a very common error – filenotfounderror – in Python . If you have worked with Python before, you would have faced this situation too, where you write all your code, maintain proper indents in it, put comments line, double-check for mistypes, and after making sure that everything is right and in its place, you run the code and end up getting ‘filenotfounderror’ in the compiler line.
Frustrating, isn’t it? Don’t worry, we will make sure to cover all possible ways to resolve this problem so that you do not encounter it ever again.
What is filenotfounderror
It is a system message that the compiler throws when you are trying to execute a command that requires a file that the system cannot find. It can be for various reasons like – wrong file path specified, the file is present in another directory, or an extension error. We will address the points in this article. But let’s first recreate the problem in our system.
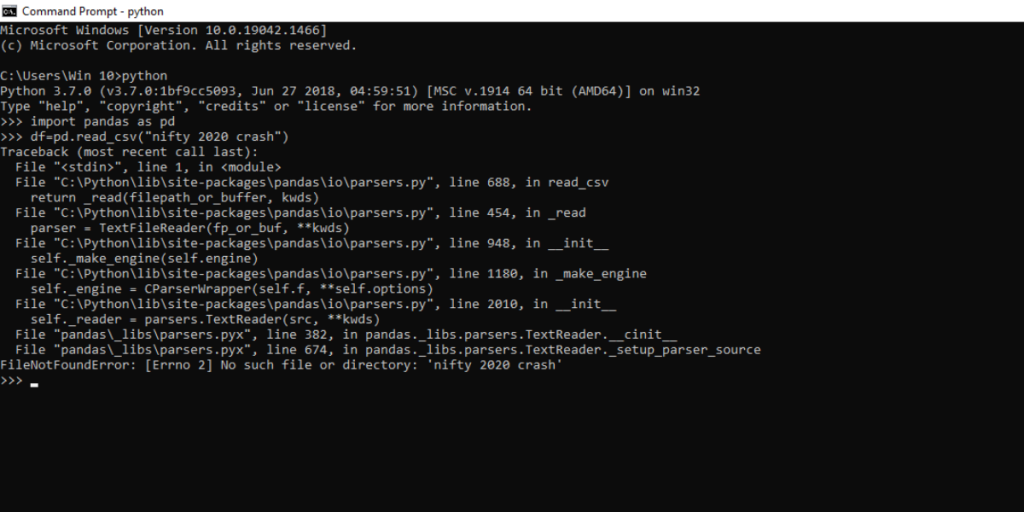
We will be writing a program to load a .csv file into a pandas data frame and then print that data frame.
import pandas as pd df=pd.read_csv("nifty 2020 crash") print(df) How to Fix the Python filenotfounderror?
When you run your python code in the terminal, it searches for the file in the root directory from where the terminal is running. A common misconception people have is that when you run a python code to read a file, the terminal searches that file in the whole computer, which is incorrect.
All your files that are needed for your program should be present in the root directory from where the terminal is activated.
This problem can be resolved in two ways:
Method 1: Specifying the complete file path
When we run our program, we state the file name in the program. The compiler searches for it in the root directory and throws errors. The solution to this problem is specifying the whole file path in the code.
import pandas as pd df = pd.read_csv(r"C:\Users\Win 10\Desktop\python_errorsolving\nifty 2020 crash.csv") print(df)
Note: Observe, while specifying the file path, we added an r before writing the path, pd.read_csv(r»C:\. ) . It is used to convert simple strings to raw strings. If we do not add r before specifying our file path, the system is gonna treat that line of code as a normal string input instead of a file path.
Method 2: Using a .txt file to run Python script
In this method, we use a very simple but effective approach to this problem. We write our code in a .txt file and store it in the directory where the file we require is present. When we run this .txt file with python, the compiler searches for that file only in that directory. This method does not require us to specify the whole file path but we need to make sure that the terminal has been run from the right directory.
To illustrate this example, we have created a directory in our desktop named, ‘python_errorsolving’. This directory contains two files, – the .txt file containing python codes and the .csv file we needed for our code.
To run this file from the terminal, go to the directory manually using cd , and then run this file with syntax python error_crt.txt or whatever your file name is.
As you can see, this method does not require us to specify the whole file path. It is useful when you have to work with multiple files because specifying the whole path for each specific file can be a tedious job.
Method 3: Workaround for filenotfounderror
This is not a solution but rather a workaround for this problem. Suppose you are in a certain situation where the file path is the same but you have to load consecutive different files. In that case, you can store your filename and file path in two different variables and then concatenate them in a third variable. This way you can make combinations of multiple different files, and then load them easily.
To illustrate this solution, we will create a .txt file, with the codes:
import pandas as pd filename = "nifty 2020 crash.csv" filepath = "C:\\Users\\Win 10\\Desktop\\python_errorsolving\\" file = filepath+filename df = pd.read_csv(file) print(df)
Using an IDE to fix the filenotfounderror
Integrated development environments or IDE’s are a great way to manage our files and environment variables. This helps to create virtual environments for your codes so that the needed libraries and environment variables do not interact with our other projects. In this section, we will create a project in PyCharm IDE, and see how easily we can store and interact with our files.
To demonstrate this example, we have created a .csv file containing school records, and it is named ‘book1.csv’. To import it in PyCharm, follow these steps:
Step 1: Go to File>new project…>give a file name>create.
Step 2: Copy your .csv file and paste it into that project.
Once you paste the file, you can directly access that file with your codes, without having to specify the whole path. You can simply work with the filename.
import pandas as pd df = pd.read_csv('Book1.csv', sep='|') print(df) Conclusion
In this article, we have observed the different cases where the system cannot locate your files. We also looked at the different solutions that are possible to these problems, from manually specifying paths, to using IDE’s for a better outcome. I hope this article solved your problem