- How to read tab-separated values (TSV) files in Python
- Simple Ways to Read TSV Files in Python
- What is a TSV file?
- Reading TSV file in Python Using open Function
- The Entire Code is:
- Reading TSV file in Python Using Pandas
- The Entire Code is:
- Writing Over a TSV File with Pandas
- Writing TSV Without Pandas
- Reading TSV into dictionary with open()
- Must, Read
- Как читать TSV-файл с помощью Pandas (включая примеры)
- Чтение файла TSV с заголовком
- Чтение TSV-файла без заголовка
- Чтение файла TSV без заголовка и указание имен столбцов
- Дополнительные ресурсы
How to read tab-separated values (TSV) files in Python
To read tab-separated values files with Python, we’ll take advantage of the fact that they’re similar to CSVs. We’ll use Python’s csv library and tell it to split things up with tabs instead of commas. Just set the delimiter argument to «\t» .
For example, let’s say we have the following data in fruits.tsv :
Name Color Ranking Apple Red 5 Kiwi Green 9 Durian Brown 10 You can read it like this:
import csv with open("fruits.tsv", "r", encoding="utf8") as fruits_file: tsv_reader = csv.DictReader(fruits_file, delimiter="\t") for fruit in tsv_reader: name = fruit["Name"] ranking = fruit["Ranking"] print(f"name> is rank ranking>") Alternatively, you can read things by row:
import csv with open("fruits.tsv", "r", encoding="utf8") as fruits_file: tsv_reader = csv.reader(fruits_file, delimiter="\t") # Skip the first row, which is the header next(tsv_reader) for row in tsv_reader: (name, color, ranking) = row print(f"name> is rank ranking>") That’s it! Just tell the csv module that it’s a file split by tabs, not commas, and you’re all set.
- About me
- Contact
- Projects
- Guides
- Blog
Content is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial License and code under the Unlicense. The logo was created by Lulu Tang.
Simple Ways to Read TSV Files in Python
Files are used for storing information with the ability to read and write on them. The operations which can be performed on files in python are – read, write, open, close, rename and delete. There are two main types of files in python – binary file and text file. Binary files can be of various types such as image files like .png, .gif, .jpg or documents like .pdf, .xls, .doc, etc. The text file can be source code, web standards, tabular data, etc. In this article, we shall be looking into one such tabular data from the text file – .tsv file. We shall be seeing into how to read tsv file in python.
What is a TSV file?
The TSV file stands for tab-separated values file. It is a text file that stores data in a tabular form. The TSV file format is widely used for exchanging data between databases in the form of a database table or spreadsheet data. Here, each record is separated from the other by a tab character ( \t ). It acts as an alternate format to the .csv format. The difference between .tsv and .csv format is that the .csv format uses commas to separate columns in data whereas .tsv format uses tabs to separate columns.
Reading TSV file in Python Using open Function
We can read the tsv file in python using the open() function. We can read a given file with the help of the open() function. After reading, it returns a file object for the same. With open(), we can perform several file handling operations on the file such as reading, writing, appending, and creating files.
After opening the file, we shall make use of the reader() present in CSV to convert the file object into CSV.reader object. For using the reader, we shall be first importing CSV.
Then, we shall write the open() function. We shall be using a tsv file named ‘product.tsv’ , which consists of the sales count for three products over a span of 12 months. We will pass the tsv file as an argument to the open() function, and ‘file’ will be the file’s object.
Then we use csv.reader to convert the file object to csv.reader object. We pass the delimiter as ‘\t’ to the csv.reader. The delimiter is used to indicate the character which will be separating each field.
Since this is a tsv file, we shall be passing the tab character as the delimiter. The variable ‘tsv_file’ will be the object for the tsv file. Then, we shall iterate the entire file and print each statement line by line.
with open("product.tsv") as file: tsv_file = csv.reader(file, delimiter="\t") for line in tsv_file: print(line) The tsv file is printed line by line as the output:
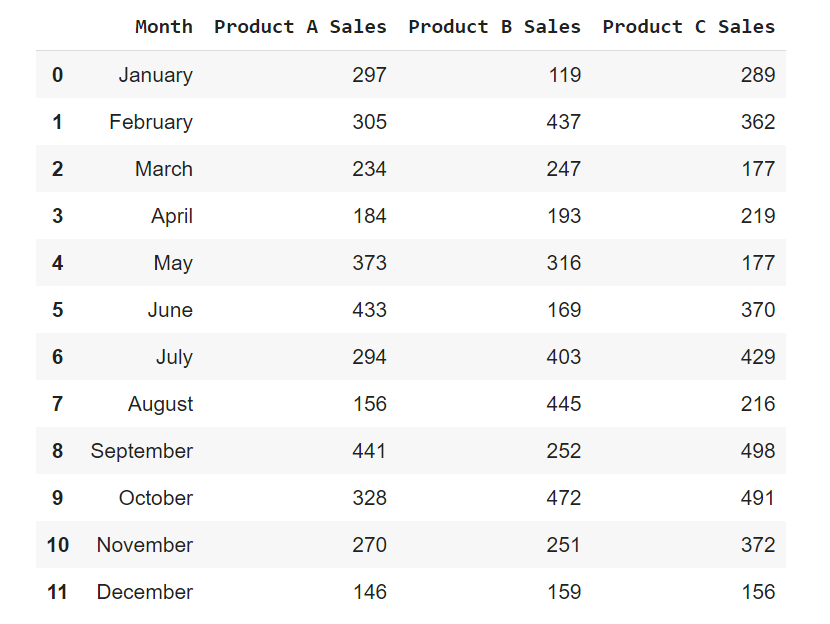
['Month', 'Product A Sales', 'Product B Sales', 'Product C Sales'] ['January', '297', '119', '289'] ['February', '305', '437', '362'] ['March', '234', '247', '177'] ['April', '184', '193', '219'] ['May', '373', '316', '177'] ['June', '433', '169', '370'] ['July', '294', '403', '429'] ['August', '156', '445', '216'] ['September', '441', '252', '498'] ['October', '328', '472', '491'] ['November', '270', '251', '372'] ['December', '146', '159', '156']
The Entire Code is:
import csv with open("product.tsv") as file: tsv_file = csv.reader(file, delimiter="\t") for line in tsv_file: print(line) Reading TSV file in Python Using Pandas
There is another way to read the tsv file which is using the pandas library. Pandas library in python is used for performing data analysis and data manipulation. It is a powerful library for manipulating numerical tables.
First, we shall be importing the pandas library.
Now, we shall be making use of the read_csv() function from the pandas library. We shall be passing the tsv file to the read_csv(). Along with the file, we shall be passing separator as ‘\t’ for the tab character because, for tsv files, the tab character will separate each field.
tsv_data = pd.read_csv('product.tsv', sep='\t') tsv_data The output will be the tsv file:
The Entire Code is:
import pandas as pd tsv_data = pd.read_csv('product.tsv', sep='\t') tsv_data Now, to read the first five rows from the product.tsv, we shall make use of head() function. This will get the first n rows from the tsv file.
By default, if you don’t specify the number of rows, head() will print 5 rows.
Month Product A Sales Product B Sales Product C Sales 0 January 297 119 289 1 February 305 437 362 2 March 234 247 177 3 April 184 193 219 4 May 373 316 177
To print all the entries of a particular column, we shall be using the following code. We will print the entire ‘Product A Sales’ column.
print(tsv_data['Product A Sales'])
The output will be:
0 297 1 305 2 234 3 184 4 373 5 433 6 294 7 156 8 441 9 328 10 270 11 146 Name: Product A Sales, dtype: int64
Writing Over a TSV File with Pandas
Now, we shall see how to write over an already existing tsv file. We shall make use of the open() function but this time we shall open the file in ‘wt’ mode. Using ‘wt’ mode, we can write the file as text. Instead of the csv.reader(), here we shall be using csv.writer(). We shall pass the tsv file and the delimiter as ‘\t’ to the writer() function.
After that, we shall use writerow() to write individual rows to the file. Finally, we shall insert two rows using the same function.
import csv with open('product.tsv', 'wt') as file: tsv_writer = csv.writer(file, delimiter='\t') tsv_writer.writerow(['January', 324, 122, 191]) tsv_writer.writerow(['February', 291, 322, 291]) Now, let us try to again read the ‘product.tsv’ file. Again, we shall use the same piece of code as used before for reading.
with open("product.tsv") as file: tsv_file = csv.reader(file, delimiter="\t") for line in tsv_file: print(line) For the output, we can see that the file has been overwritten and it only contains two rows instead of the twelve rows which were present before.
['January', '324', '122', '191'] ['February', '291', '322', '291']
Writing TSV Without Pandas
To write over tsv files without using the pandas library, we shall use the following code. Here, we will append the contents of a file named ‘total_sales’ into another tsv file named ‘product’. The ‘total_sales’ consists of sales for all the products for a year, whereas the ‘product’ consists of sales for all in products individually.
with open("total_sales.tsv") as file: for line in file: with open('product.tsv', "a") as f: f.write(line) Now, to read the file:
import csv with open("product.tsv") as file: tsv_file = csv.reader(file, delimiter="\t") for line in tsv_file: print(line) The output is:
['Month', 'Product A Sales', 'Product B Sales', 'Product C Sales'] ['January', '297', '119', '289'] ['February', '305', '437', '362'] ['March', '234', '247', '177'] ['April', '184', '193', '219'] ['May', '373', '316', '177'] ['June', '433', '169', '370'] ['July', '294', '403', '429'] ['August', '156', '445', '216'] ['September', '441', '252', '498'] ['October', '328', '472', '491'] ['November', '270', '251', '372'] ['December', '146', '159', '156Month', 'Total Sales'] ['January', '558'] ['February', '871'] ['March', '756'] ['April', '509'] ['May', '987'] ['June', '625'] ['July', '862'] ['August', '548'] ['September', '669'] ['October', '827'] ['November', '776'] ['December', '955']
As seen above, the ‘product’ file has been appended with the contents of the ‘total_sales’ file.
Reading TSV into dictionary with open()
We can read a given tsv file and store its contents into a dictionary. To achieve that, we shall be taking a tsv file containing two columns – month and total sales. Then, with the help of the open() function, we shall store each month as the dictionary’s key and the total sales amount for the month as the values.
We shall split the month and sales using the tab character. Then, we shall enumerate over the dictionary and print its values.
sales_dictionary = <> with open("total_sales.tsv") as f: for line in f: (month, sales)=line.split('\t') sales_dictionary[month]=sales for i,month in enumerate(sales_dictionary): print(f' : ') The output is:
Month : Total Sales January : 558 February : 871 March : 756 April : 509 May : 987 June : 625 July : 862 August : 548 September : 669 October : 827 November : 776 December : 955
Must, Read
That sums up everything about the tsv file. If you have any questions, let us know in the comments below.
Until next time, Keep Learning!
Как читать TSV-файл с помощью Pandas (включая примеры)
Чтобы прочитать файл TSV с пандами в Python, вы можете использовать следующий базовый синтаксис:
df = pd.read_csv (" data.txt", sep=" \t ") В этом руководстве представлено несколько примеров использования этой функции на практике.
Чтение файла TSV с заголовком
Предположим, у нас есть следующий файл TSV с именем data.txt и заголовком:
Чтобы прочитать этот файл в DataFrame pandas, мы можем использовать следующий синтаксис:
import pandas as pd #read TSV file into pandas DataFrame df = pd.read_csv (" data.txt", sep=" \t ") #view DataFrame print(df) column1 column2 0 1 4 1 3 4 2 2 5 3 7 9 4 9 1 5 6 3 6 5 7 7 8 8 8 3 1 9 4 9 Мы можем распечатать класс DataFrame и найти количество строк и столбцов, используя следующий синтаксис:
#display class of DataFrame print(type(df)) #display number of rows and columns in DataFrame df.shape (10, 2) Мы видим, что df — это DataFrame pandas с 10 строками и 2 столбцами.
Чтение TSV-файла без заголовка
Предположим, у нас есть следующий TSV-файл с именем data.txt без заголовков:
Чтобы прочитать этот файл в DataFrame pandas, мы можем использовать следующий синтаксис:
#read TSV file into pandas DataFrame df = pd.read_csv (" data.txt", sep=" \t", header= None ) #view DataFrame print(df) 0 1 0 1 4 1 3 4 2 2 5 3 7 9 4 9 1 5 6 3 6 5 7 7 8 8 8 3 1 9 4 9 Поскольку в текстовом файле не было заголовков, Pandas просто назвали столбцы 0 и 1 .
Чтение файла TSV без заголовка и указание имен столбцов
При желании мы можем присвоить имена столбцам при импорте текстового файла с помощью аргумента имен :
#read TSV file into pandas DataFrame and specify column names df = pd.read_csv (" data.txt", sep=" \t", header= None, names=[" A", " B "] ) #display DataFrame print(df) A B 0 1 4 1 3 4 2 2 5 3 7 9 4 9 1 5 6 3 6 5 7 7 8 8 8 3 1 9 4 9 Дополнительные ресурсы
В следующих руководствах объясняется, как читать файлы других типов с помощью pandas: