- Функция log() в Python
- Понимание функции
- Варианты функций
- 1. log2(x) – основание логарифма 2
- 2. log(n, Base) – основание логарифма n
- 3. log10(x) – основание логарифма 10
- 4. log1p(x)
- Понимание журнала в NumPy
- Модуль math
- How to Use Python numpy to Calculate the Natural Logarithm (ln)
- How to Import the Log Function to Make It Clearer as ln
- How to Graph the Natural Log Function in Python
- Conclusion
Функция log() в Python
Логарифмы используются для изображения и представления больших чисел. Журнал – это величина, обратная экспоненте. В этой статье мы подробно рассмотрим функции log(). Логарифмические функции в Python помогают пользователям находить логарифм чисел намного проще и эффективнее.
Понимание функции
Чтобы использовать функциональные возможности журнала, нам необходимо импортировать модуль math, используя приведенный ниже оператор.
Нам всем необходимо принять во внимание тот факт, что к функциям журнала нельзя получить прямой доступ. Нам нужно использовать модуль math для доступа к функциям журнала в коде.
Функция math.log(x) используется для вычисления натурального логарифмического значения, т.е. логарифма с основанием e (число Эйлера), которое составляет около 2,71828 переданного ему значения параметра (числовое выражение).
import math print("Log value: ", math.log(2)) В приведенном выше фрагменте кода мы запрашиваем логарифмическое значение 2.
Log value: 0.6931471805599453
Варианты функций
Ниже приведены варианты базовой функции журнала в Python:
1. log2(x) – основание логарифма 2
Функция math.log2(x) используется для вычисления логарифмического значения числового выражения с основанием 2.
math.log2(numeric expression)
import math print ("Log value for base 2: ") print (math.log2(20)) Log value for base 2: 4.321928094887363
2. log(n, Base) – основание логарифма n
Функция math.log(x, Base) вычисляет логарифмическое значение x, т.е. числовое выражение для определенного (желаемого) базового значения.
math.log(numeric_expression,base_value)
Эта функция принимает два аргумента:
Примечание. Если функции не задано базовое значение, math.log(x, (Base)) действует как базовая функция журнала и вычисляет журнал числового выражения по основанию e.
import math print ("Log value for base 4 : ") print (math.log(20,4)) Log value for base 4 : 2.1609640474436813
3. log10(x) – основание логарифма 10
Функция math.log10(x) вычисляет логарифмическое значение числового выражения с точностью до 10.
math.log10(numeric_expression)
import math print ("Log value for base 10: ") print (math.log10(15)) В приведенном выше фрагменте кода вычислено логарифмическое значение от 15 до основания 10.
Log value for base 10 : 1.1760912590556813
4. log1p(x)
Функция math.log1p(x) вычисляет журнал (1 + x) определенного входного значения, т.е. x.
Примечание: math.log1p(1 + x) эквивалентно math.log (x).
math.log1p(numeric_expression)
import math print ("Log value(1+15) for x = 15 is: ") print (math.log1p(15)) В приведенном выше фрагменте кода вычисляется значение журнала (1 + 15) для входного выражения 15.
Таким образом, math.log1p(15) эквивалентен math.log(16).
Log value(1+15) for x = 15 is: 2.772588722239781
Понимание журнала в NumPy
NumPy позволяет нам одновременно вычислять натуральные логарифмические значения входных элементов массива NumPy.
Чтобы использовать метод numpy.log(), нам нужно импортировать модуль NumPy, используя приведенный ниже оператор.
Функция numpy.log() принимает входной массив в качестве параметра и возвращает массив с логарифмическим значением элементов в нем.
import numpy as np inp_arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] print ("Array input elements:\n", inp_arr) res_arr = np.log(inp_arr) print ("Resultant array elements:\n", res_arr) Array input elements: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] Resultant array elements: [ 2.30258509 2.99573227 3.40119738 3.68887945 3.91202301]
Модуль math
Модуль math – один из наиважнейших в Python. Этот модуль предоставляет обширный функционал для работы с числами.
math.ceil(X) – округление до ближайшего большего числа.
math.copysign(X, Y) — возвращает число, имеющее модуль такой же, как и у числа X, а знак — как у числа Y.
math.factorial(X) — факториал числа X.
math.floor(X) — округление вниз.
math.fmod(X, Y) — остаток от деления X на Y.
math.frexp(X) — возвращает мантиссу и экспоненту числа.
math.ldexp(X, I) — X * 2 i . Функция, обратная функции math.frexp().
math.fsum(последовательность) — сумма всех членов последовательности. Эквивалент встроенной функции sum(), но math.fsum() более точна для чисел с плавающей точкой.
math.isfinite(X) — является ли X числом.
math.isinf(X) — является ли X бесконечностью.
math.isnan(X) — является ли X NaN (Not a Number — не число).
math.modf(X) — возвращает дробную и целую часть числа X. Оба числа имеют тот же знак, что и X.
math.trunc(X) — усекает значение X до целого.
math.expm1(X) — e X — 1. При X → 0 точнее, чем math.exp(X)-1.
math.log(X, [base]) — логарифм X по основанию base. Если base не указан, вычисляется натуральный логарифм.
math.log1p(X) — натуральный логарифм (1 + X). При X → 0 точнее, чем math.log(1+X).
math.log10(X) — логарифм X по основанию 10.
math.log2(X) — логарифм X по основанию 2.
math.sqrt(X) — квадратный корень из X.
math.acos(X) — арккосинус X. В радианах.
math.asin(X) — арксинус X. В радианах.
math.atan(X) — арктангенс X. В радианах.
math.atan2(Y, X) — арктангенс Y/X. В радианах. С учетом четверти, в которой находится точка (X, Y).
math.cos(X) — косинус X (X указывается в радианах).
math.sin(X) — синус X (X указывается в радианах).
math.tan(X) — тангенс X (X указывается в радианах).
math.hypot(X, Y) — вычисляет гипотенузу треугольника с катетами X и Y (math.sqrt(x * x + y * y)).
math.degrees(X) — конвертирует радианы в градусы.
math.radians(X) — конвертирует градусы в радианы.
math.cosh(X) — вычисляет гиперболический косинус.
math.sinh(X) — вычисляет гиперболический синус.
math.tanh(X) — вычисляет гиперболический тангенс.
math.acosh(X) — вычисляет обратный гиперболический косинус.
math.asinh(X) — вычисляет обратный гиперболический синус.
math.atanh(X) — вычисляет обратный гиперболический тангенс.
math.erf(X) — функция ошибок.
math.erfc(X) — дополнительная функция ошибок (1 — math.erf(X)).
math.gamma(X) — гамма-функция X.
math.lgamma(X) — натуральный логарифм гамма-функции X.
math.pi — pi = 3,1415926.
Для вставки кода на Python в комментарий заключайте его в теги
- Книги о Python
- GUI (графический интерфейс пользователя)
- Курсы Python
- Модули
- Новости мира Python
- NumPy
- Обработка данных
- Основы программирования
- Примеры программ
- Типы данных в Python
- Видео
- Python для Web
- Работа для Python-программистов
Python Natural Log: Calculate ln in Python
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to calculate the natural log in Python, thereby creating a way to calculate the mathematical values for ln() . You’ll receive a brief overview of what the natural logarithm is, how to calculate it in Python with the math library and with the numpy library. Finally, you’ll learn how to import it differently to make your code a little easier to read.
The Quick Answer: Use numpy.log()
What is the natural logarithm?
The natural logarithm is the logarithm of any number to the base e . This is often written either as loge(x) or ln(x) . Sometimes, the e is implicit, and the function is written as log(x) .
The natural logarithm has a number of unique attributes, such as:
The natural logarithm (ln) is often used in solving time and growth problems. Because the phenomenon of the logarithm to the base e occurs often in nature, it is called the natural logarithm, as it mirrors many natural growth problems.
How to Use Python math to Calculate the Natural Logarithm (ln)
The Python library, math , comes with a function called log() . The function takes two parameters:
An interesting aspect of this function is that the base is an optional value. If no value is provided, the value defaults to e , meaning that by only provided a number, you are automatically calculating the natural logarithm.
This may seem counterintuitive – however, recall from the introduction that in many cases the base e is implicit, and many times is omitted when referring to a log() function without a specified base.
Let’s see how we can use the Python math library to calculate the natural log. We’ll verify some of the key attributes to see how this works in practise.
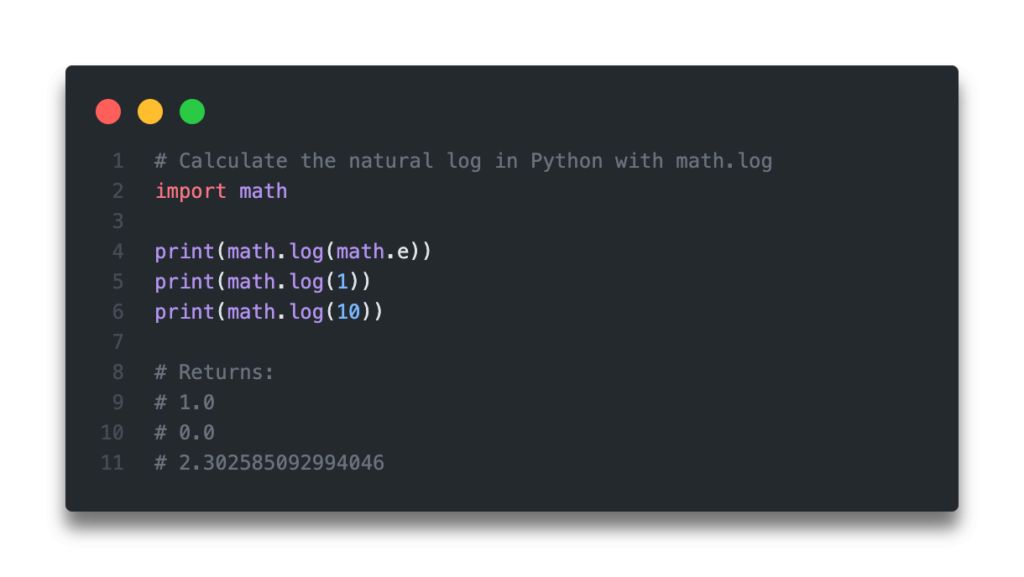
# Calculate the natural log in Python with math.log import math print(math.log(math.e)) print(math.log(1)) print(math.log(10)) # Returns: # 1.0 # 0.0 # 2.302585092994046In the next section, you’ll learn how to use the numpy library to calculate the natural logarithm in Python.
Want to learn how to use the Python zip() function to iterate over two lists? This tutorial teaches you exactly what the zip() function does and shows you some creative ways to use the function.
How to Use Python numpy to Calculate the Natural Logarithm (ln)
Another helpful way in Python to calculate the natural log is to the use the popular numpy library. The numpy library comes with many different ways in which you can manipulate numerical data. One of these functions is the numpy.log() function.
Similar to the function you learned in the previous section, the numpy.log() function takes two parameters:
- The number to calculate the logarithm for,
- The base to use in the logarithm calculation
Similar to the math library’s function, the base is an optional parameter. If it is left blank, the value of e is used. Because of this, the function defaults to calculating the natural logarithm.
Let’s see how we can use the numpy.log() function to calculate the natural logarithm in Python. We’ll calculate the natural logarithm for Euler’s constant and some other values.
# Calculate the natural log in Python with numpy.log import numpy as np import math print(np.log(math.e)) print(np.log(1)) print(np.log(10)) # Returns: # 1.0 # 0.0 # 2.302585092994046In the next section, you’ll learn how to import the log() function in a different manner to make it easier to read.
How to Import the Log Function to Make It Clearer as ln
Python makes importing functions easy and intuitive. In both examples, we’ve simply imported the whole library, but importing the log() function may not make it clear that we’re referring to natural logs.
One thing that we can do is provide an alias for the function, to make it clear that we are referring to a natural logarithm.
Let’s see how we can do this, by importing the function from the numpy library:
# Calculate the natural log in Python with numpy.log as ln from numpy import log as ln import math print(ln(math.e)) print(ln(1)) print(ln(10)) # Returns: # 1.0 # 0.0 # 2.302585092994046In the next section, you’ll learn how to graph the natural log function using Python.
Want to learn more about Python f-strings? Check out my in-depth tutorial, which includes a step-by-step video to master Python f-strings!
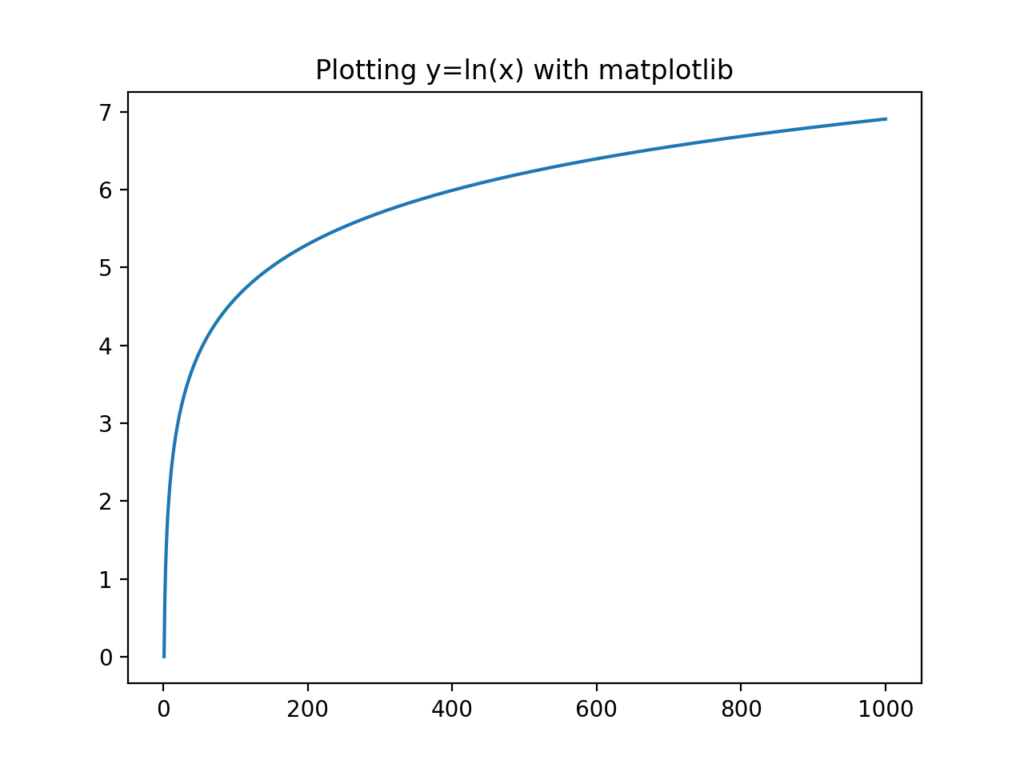
How to Graph the Natural Log Function in Python
In this section, you’ll learn how to plot the natural log function in Python using the popular graphing library, matplotlib .
In order to plot the data, what we’ll do is
- Generate an array of the numbers from 1 through to 30.
- We will then loop over the array and create an array of the natural log of that number.
- Finally, we will plot the two arrays using matplotlib.
Let’s see how we can do this in Python:
# Calculate the natural log in Python with numpy.log as ln import numpy as np import math import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = np.array(range(1, 1001)) y = np.log(x) plt.plot(x, y) plt.title('Plotting y=ln(x) with matplotlib') plt.show()This returns the following image:
Want to learn more about calculating the square root in Python? Check out my tutorial here, which will teach you different ways of calculating the square root, both without Python functions and with the help of functions.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to use Python to calculate the natural logarithm. You learned how to do this using both the math and numpy libraries, as well how to plot the natural log function using matplotlib .
To learn more about the math.log() function, check out the official documentation here.