- Java Methods
- Declaring a Java Method
- Calling a Method in Java
- Example 1: Java Methods
- Java Method Return Type
- Example 2: Method Return Type
- Method Parameters in Java
- Example 3: Method Parameters
- Standard Library Methods
- Example 4: Java Standard Library Method
- What are the advantages of using methods?
- Example 5: Java Method for Code Reusability
- Table of Contents
- Java Program to Illustrate a Method without Parameters and Return Type
- Syntax
- Example
- Output
- Example
- Output
- Conclusion
- Java Program to Illustrate a Method without Parameters but with Return Type
- Syntax
- Steps
- Example
- Output
- Example
- Output
- Conclusion
- Java Program to Illustrate a Method without Parameters But with Return Type
Java Methods
A method is a block of code that performs a specific task.
Suppose you need to create a program to create a circle and color it. You can create two methods to solve this problem:
Dividing a complex problem into smaller chunks makes your program easy to understand and reusable.
In Java, there are two types of methods:
- User-defined Methods: We can create our own method based on our requirements.
- Standard Library Methods: These are built-in methods in Java that are available to use.
Let’s first learn about user-defined methods.
Declaring a Java Method
The syntax to declare a method is:
- returnType — It specifies what type of value a method returns For example if a method has an int return type then it returns an integer value.
In the above example, the name of the method is adddNumbers() . And, the return type is int . We will learn more about return types later in this tutorial.
This is the simple syntax of declaring a method. However, the complete syntax of declaring a method is
modifier static returnType nameOfMethod (parameter1, parameter2, . ) < // method body >- modifier — It defines access types whether the method is public, private, and so on. To learn more, visit Java Access Specifier.
- static — If we use the static keyword, it can be accessed without creating objects.
- parameter1/parameter2 — These are values passed to a method. We can pass any number of arguments to a method.
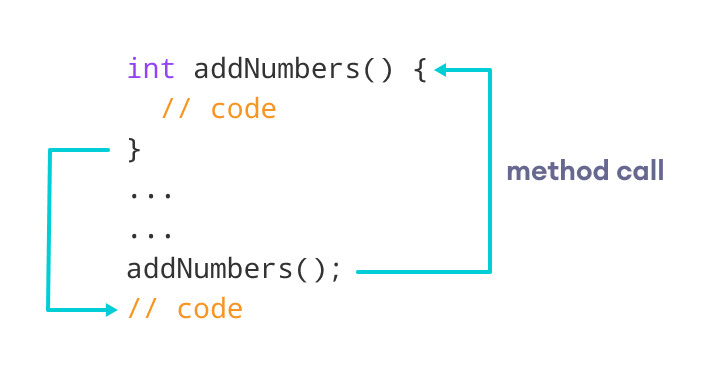
Calling a Method in Java
In the above example, we have declared a method named addNumbers() . Now, to use the method, we need to call it.
Here’s is how we can call the addNumbers() method.
// calls the method addNumbers();Example 1: Java Methods
class Main < // create a method public int addNumbers(int a, int b) < int sum = a + b; // return value return sum; >public static void main(String[] args) < int num1 = 25; int num2 = 15; // create an object of Main Main obj = new Main(); // calling method int result = obj.addNumbers(num1, num2); System.out.println("Sum is: " + result); >>In the above example, we have created a method named addNumbers() . The method takes two parameters a and b . Notice the line,
int result = obj.addNumbers(num1, num2);Here, we have called the method by passing two arguments num1 and num2 . Since the method is returning some value, we have stored the value in the result variable.
Note: The method is not static. Hence, we are calling the method using the object of the class.
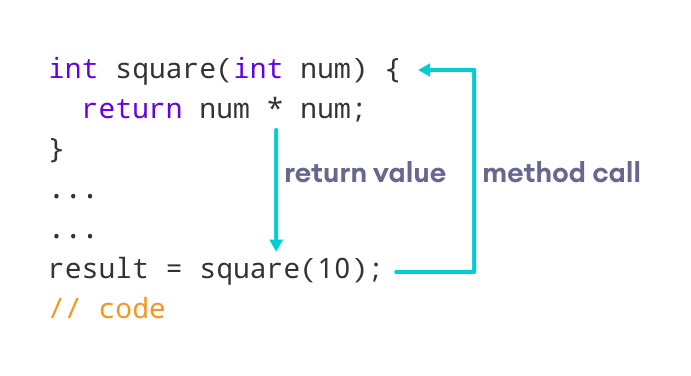
Java Method Return Type
A Java method may or may not return a value to the function call. We use the return statement to return any value. For example,
Here, we are returning the variable sum . Since the return type of the function is int . The sum variable should be of int type. Otherwise, it will generate an error.
Example 2: Method Return Type
class Main < // create a method public static int square(int num) < // return statement return num * num; >public static void main(String[] args) < int result; // call the method // store returned value to result result = square(10); System.out.println("Squared value of 10 is: " + result); >>Squared value of 10 is: 100
In the above program, we have created a method named square() . The method takes a number as its parameter and returns the square of the number.
Here, we have mentioned the return type of the method as int . Hence, the method should always return an integer value.
Note: If the method does not return any value, we use the void keyword as the return type of the method. For example,
Method Parameters in Java
A method parameter is a value accepted by the method. As mentioned earlier, a method can also have any number of parameters. For example,
// method with two parameters int addNumbers(int a, int b) < // code >// method with no parameter int addNumbers()< // code >If a method is created with parameters, we need to pass the corresponding values while calling the method. For example,
// calling the method with two parameters addNumbers(25, 15); // calling the method with no parameters addNumbers()Example 3: Method Parameters
class Main < // method with no parameter public void display1() < System.out.println("Method without parameter"); >// method with single parameter public void display2(int a) < System.out.println("Method with a single parameter: " + a); >public static void main(String[] args) < // create an object of Main Main obj = new Main(); // calling method with no parameter obj.display1(); // calling method with the single parameter obj.display2(24); >>Method without parameter Method with a single parameter: 24
Here, the parameter of the method is int . Hence, if we pass any other data type instead of int , the compiler will throw an error. It is because Java is a strongly typed language.
Note: The argument 24 passed to the display2() method during the method call is called the actual argument.
The parameter num accepted by the method definition is known as a formal argument. We need to specify the type of formal arguments. And, the type of actual arguments and formal arguments should always match.
Standard Library Methods
The standard library methods are built-in methods in Java that are readily available for use. These standard libraries come along with the Java Class Library (JCL) in a Java archive (*.jar) file with JVM and JRE.
- print() is a method of java.io.PrintSteam . The print(«. «) method prints the string inside quotation marks.
- sqrt() is a method of Math class. It returns the square root of a number.
Example 4: Java Standard Library Method
To learn more about standard library methods, visit Java Library Methods.
What are the advantages of using methods?
1. The main advantage is code reusability. We can write a method once, and use it multiple times. We do not have to rewrite the entire code each time. Think of it as, «write once, reuse multiple times».
Example 5: Java Method for Code Reusability
public class Main < // method defined private static int getSquare(int x)< return x * x; >public static void main(String[] args) < for (int i = 1; i > >Square of 1 is: 1 Square of 2 is: 4 Square of 3 is: 9 Square of 4 is: 16 Square of 5 is: 25
In the above program, we have created the method named getSquare() to calculate the square of a number. Here, the method is used to calculate the square of numbers less than 6.
Hence, the same method is used again and again.
2. Methods make code more readable and easier to debug. Here, the getSquare() method keeps the code to compute the square in a block. Hence, makes it more readable.
Table of Contents
Java Program to Illustrate a Method without Parameters and Return Type
First, let us get acquainted with the syntax, and examples, and then finally the implementation.
The methods in Java are of great importance since it allows reusability of the same code, reducing the number of statements to be written within the code.
There are three main parts of the method in order to make it executable.
Method invoking is the last step, while the other two can be interchanged. The only thing to be kept in mind here is, the method must be declared before invoking it.
Syntax
To create a method without any parameter and return type, the following syntax is considered.
Class class_name < function _name() < Statement 1; Statement 2; . . Statement n; //an optional return return; >Main function() < // invoking the above function function_name(); >>
A method is created within a class with an empty parameter list. The statements are written inside the method which may be followed by an empty return. The method thus created is invoked in the main method.
Example
The following program is written to show how a method is created that neither has parameters nor any return type.
A class named Wish is created within which, a method named wish() with return type void is created denoting it does not return any value, also it does not consist of any parameter. A statement is written within the wish() method and is displayed by invoking this method in the main method.
// Java Program to demonstrate a method without Parameters and Return Type public class Wish < // Declaration and Definition of the method public static void wish()< System.out.println("Good Morning! Have a nice day"); >public static void main(String args[]) < // Calling the method without any parameters wish (); >> Output
Good Morning! Have a nice day
Example
The following program is written to show how a method is created that neither has parameters nor any return type.
A class named Wish is created within which, a method named wish() with return type void is created denoting it does not return any value, also it does not consist of any parameter. The statements written inside the wish() method are displayed by invoking the method in the main method.
// Java Program to demonstrate a method without Parameters and Return Type public class Wish < // Declaration and Definition of the method public static void wish()< System.out.println("Congratulations! Have a great professional life"); //It is optional to use a return statement here. return; >public static void main(String args[]) < // Calling the method without any parameters wish(); >> Output
Congratulations! Have a great professional life
Conclusion
This article throws light on how a method is defined in Java without any parameters and return value. We started with the syntax and further saw an example and two java programs to have a clear picture of the topic.
Java Program to Illustrate a Method without Parameters but with Return Type
In Java, a method is a block of code that performs a specific task. Methods can take zero or more parameters and can also return a value. When a method returns a value, we call it a method with a return type.
A method without parameters but with a return type is a method that does not take any parameters, but it returns a value. This type of method is useful when we need to perform a specific task that does not require any input parameters, but we need to get a result from that task.
First, let us get acquainted with the syntax, examples, and then implementation.
Syntax
The syntax for defining a method without parameters but with a return type is as follows −
- class_name − It is the name of the class preceded by a keyword class.
- data_type − It is the type of data upon which the method works.
- method_name − It is the name or tag of the method. This method can be invoked in the latter part of the program using the method name only.
- Statements − These are the lines of code written within the method.
- return − The value to be returned by the method is written here. It can contain any numeral or variable name.
Here is an illustration of the above syntax −
Steps
- Start the program by declaring the class.
- Within the class, define a method as per the requirement.
- Within the method, declare and initialize the required variable.
- Perform the required task.
- Return the calculated value and close this method.
- Define the main method and create an object of the class inside it.
- Invoke the method created above through an object.
Example
The following program is written to demonstrate how a method is written without any parameters but 1 return type. A method named addition () containing no parameter but return type as double is created within a class named Add. The add () method gets invoked in the main method through the creation of an object of the created class and the value is displayed.
public class Add < // creation of method named addition without any parameter and 1 return value public double addition() < double sum = 567.98 + 34.76; // return value return sum; >public static void main(String[] args) < // creation of an object of class Add Add a = new Add(); // calling the addition method double sum = a.addition(); System.out.println("Sum is: " + sum); >> Output
Example
The following program is written to demonstrate how a method is written without any parameters but 1 return type. a method named area_semicircle () containing no parameter but return type as double is created within a class named Area. The area_semicircle () method gets invoked in the main method through the creation of an object of the created class and the calculated value of the area is displayed on the screen.
public class Area < // creation of an area method without any parameter and 1 return value public double area_semicircle() < double r = 16.0; double area = (3.14 * r * r)/2.0; // return value return area; >public static void main(String[] args) < //creation of an object of class Add Area a = new Area(); // calling the area_semicircle method double area = a.area_semicircle(); System.out.println("The area of semi circle is: " + area); >> Output
The area of semi circle is: 401.92
Conclusion
This article throws light on how a method is defined in Java without any parameters and 1 return value. We started with the syntax and further saw an example and two java programs.
Java Program to Illustrate a Method without Parameters But with Return Type
The task is to illustrate a method that does not contain any parameter but should return some value. Methods are used to break a complete program into a number of modules that can be executed one by one. Considering any random shape to illustrate: Circle
Example: First a class named ‘Circle’ is supposed to be created, then with the help of this class, it can calculate the area and circumference of a circle.
Inside the class Circle, we will declare a variable called radius to take the value of the radius from the user so that by using this value of radius we will be able to calculate the area and circumference of a circle. Now, for calculating the area and circumference, we need to create two separate methods called area() and circumference(), which does not take any value as a parameter but will definitely return some value, and the value which this method will return are the final values of area and circumference of the circle. The methods will return the values after calculating it with the help of the values of variables. The most important thing to calculate the area and circumference, and to use these methods are first to need is to call those methods which are known as calling a function, for this we have to create an object of Circle class because in the main method, and we want to access them, methods of another class hence we need to make the object of that class which contains our methods area() and circumference() and by using the object of the class Circle, we will easily call the methods and those methods will return some value, and we will display it by using our predefined function.
Implementation:
Example 1: Area calculation