- Python in LibreOffice Macros
- Macros and Security
- Install
- Create python directory
- APSO — Alternative Script Organizer for Python
- Write your script live
- Save your script and debug
- What next?
- Введение
- Установка
- Поддержка тестов для макросов Python
- Где хранятся макросы?
- Каталог с профилем пользователя, макросы доступны только для пользователя
- Profile USER folder, macros available only for USER
- Каталог LibreOffice, макросы доступны для всех пользователей
- Внутри документа
- Python Guide — My First Macro
- For Writer
- For Calc
- Execute macro
- For Writer
- For Calc
Python in LibreOffice Macros
Are macros still useful? I think yes. Macros give the users ability to programmatically script the content. This can be really useful in many situations to automate the stuff. Of course there are many reasons not use them. Historically they have been proven very dangerous. Specifically the documents that you receive through email or download from the web that have embedded macros. By default I consider any macro I receive from others as dangerous and wont run it. I usually use macros that only I have written or checked out from «official» git repo of the institution that I am involved with. With that caution, let’s proceed.
Macros are useful but writing macos in Basic is hard. Hence Python. In this how-to we will learn about the ways to
Macros and Security
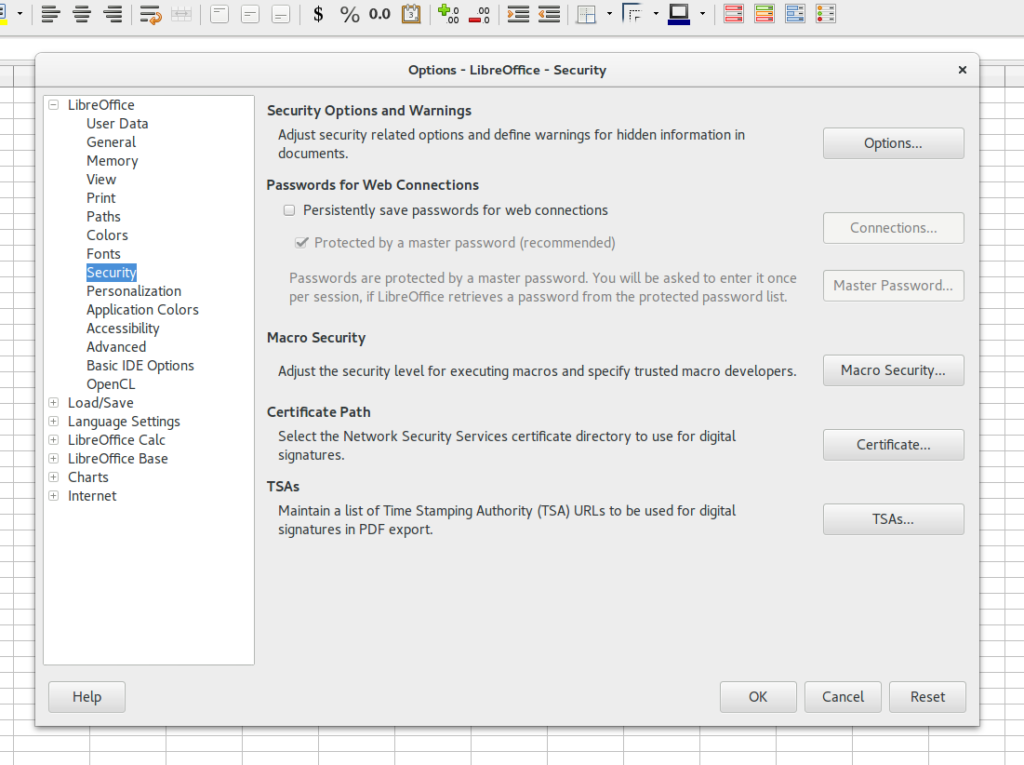
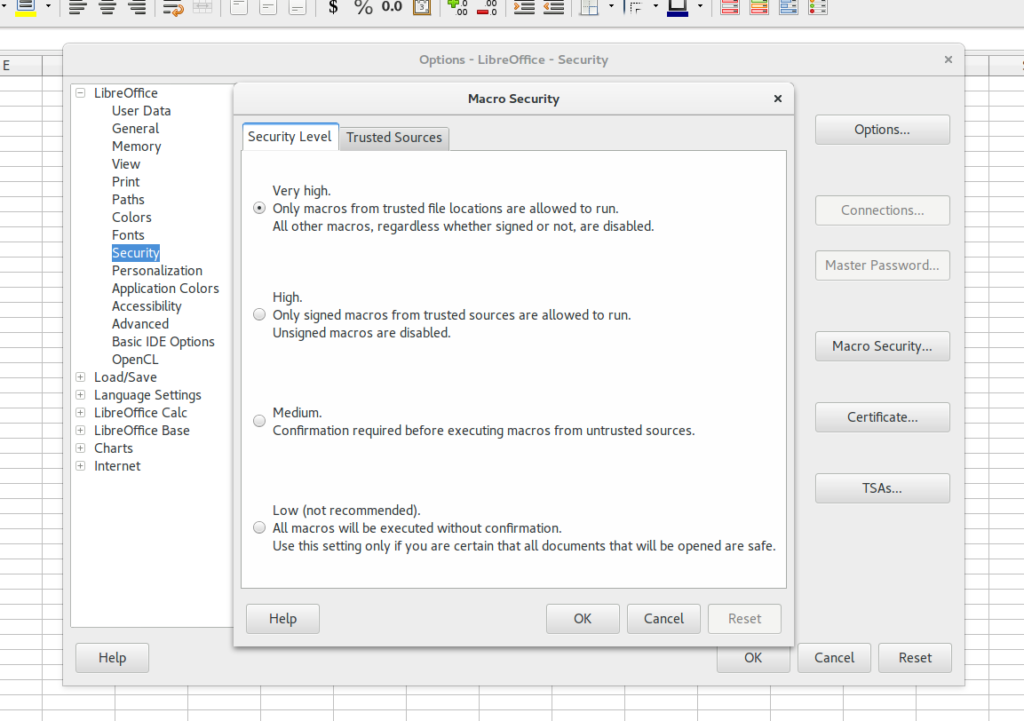
You can control the macro security from Tools-Options-Security-Macro Security. I always have the security at Very High or High . Very rarely I have it medium. And ⚠️ never at Low ⚠️. Even if I have the security level at High, Once I am done with the work, I make it Very High again. Also like I said I prefer manually running the macro than auto run and hence Very High works.
Libreoffice Option Settings
LibreOffice Macro Security settings
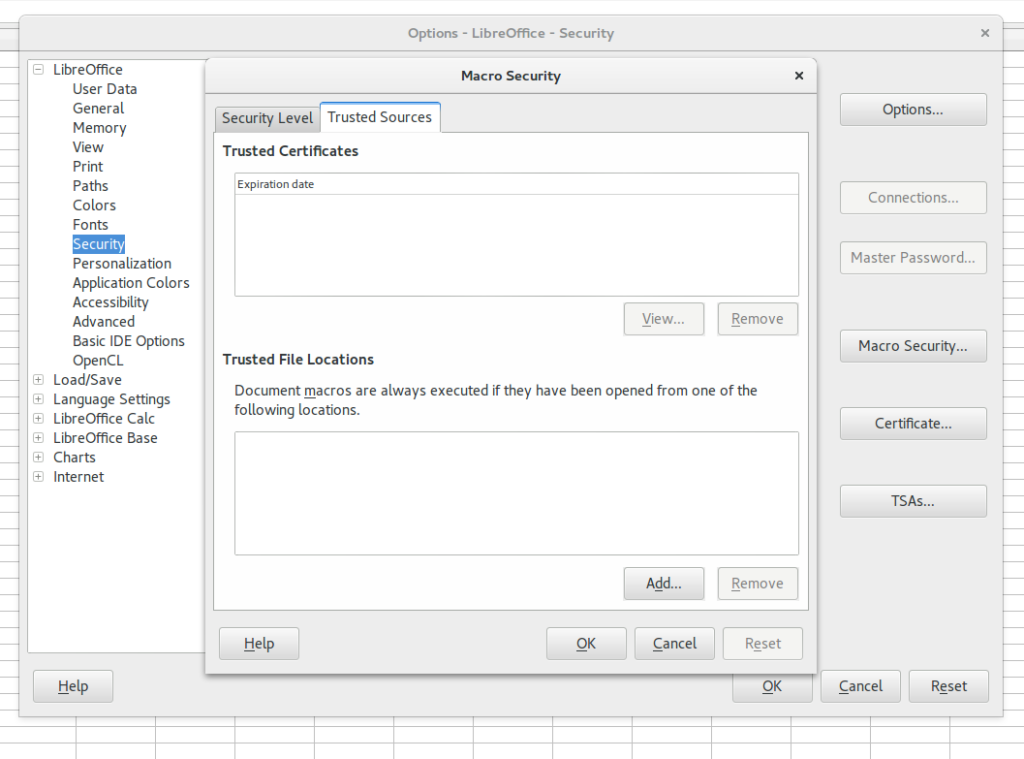
Libreoffice also allows you to have trusted paths on your computer. If a macro is opened from these paths then they are always executed. Its a good option if you like to run the macros often. This way you can have Very High Security level and also can run Macros without issues.
Install
LibreOffice comes with Basic Scripting built in. But to support any other scripting language you need to install the specific packaage. For python install
sudo apt-get install libreoffice-script-provider-python
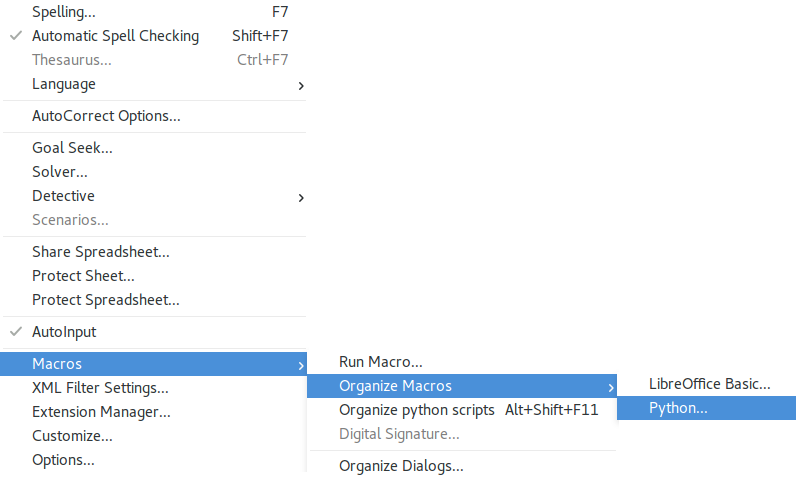
Once you install restart your LibreOffice (Calc or Writer) and Go to Tools and Macros, you will find Python Macros.
Create python directory
Create python directory inside the user folder. Where your all system level scripts will be store.
~/.config/libreoffice/4/user/Scripts/python
Now you should be ready to write your first script. Whatever you write in the Scripts folder should appear in the Menu to run. But these default screens are not useful enough to write any practical scripts. We need access to python REPL, IDE and Debugger. This is where the community is great. There are great tools available as extensions. We will install couple of extensions to make it developer friendly.
APSO — Alternative Script Organizer for Python
APSO — Alternative Script Organiser for Python. Its a great tool for developing and managing the python scripts. It gives you console and debugger access etc
- Create module (python file, each function is a macro) or library
- Standard Edit, rename, delete a module or library
- Embed module from application/local into current document. So it can be sent
- Export an embedded module for local editing
- Launch Python Console for REPL
- Debug the Scripts
First install the APSO Extension from LibreOffice website. Restart the libreOffice to see the menu item Organize Python Scripts (ALT+Shift+F11) in Tools — Macros folder.
Now you are ready to develop.
Write your script live
Let’s start developing like a Pythoner in REPL mode. Create a new LibreOffice Calc sheet. Save it some where. Create a sheet called welcome sheet. Now we will start a console and try to get the sheet name.
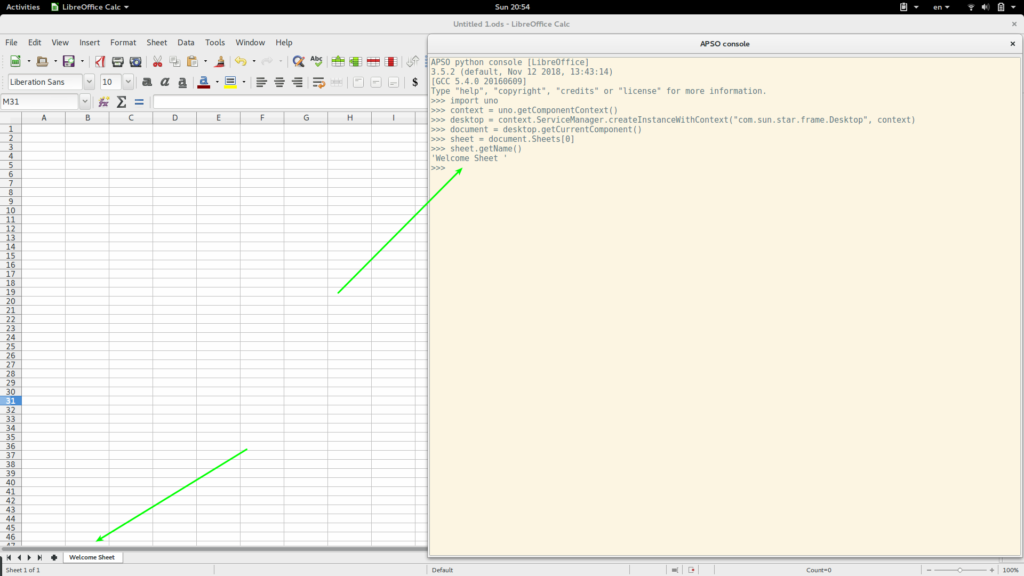
import uno context = uno.getComponentContext() desktop = context.ServiceManager.createInstanceWithContext("com.sun.star.frame.Desktop", context) document = desktop.getCurrentComponent() sheet = document.Sheets[0] sheet.getName() The code is above but we can run in REPL mode so we can experiment as we go. Launch APSO and click on Menu and Launch console. It should launch your standard Python console. Launch will also print Python Version. Make a note of this. This is the version you will develop for.
Save your script and debug
Now that you have a script. Create a module — Edit and save it as def hello_world. APSO usually opens your default editor (GEDIT) for you to edit.
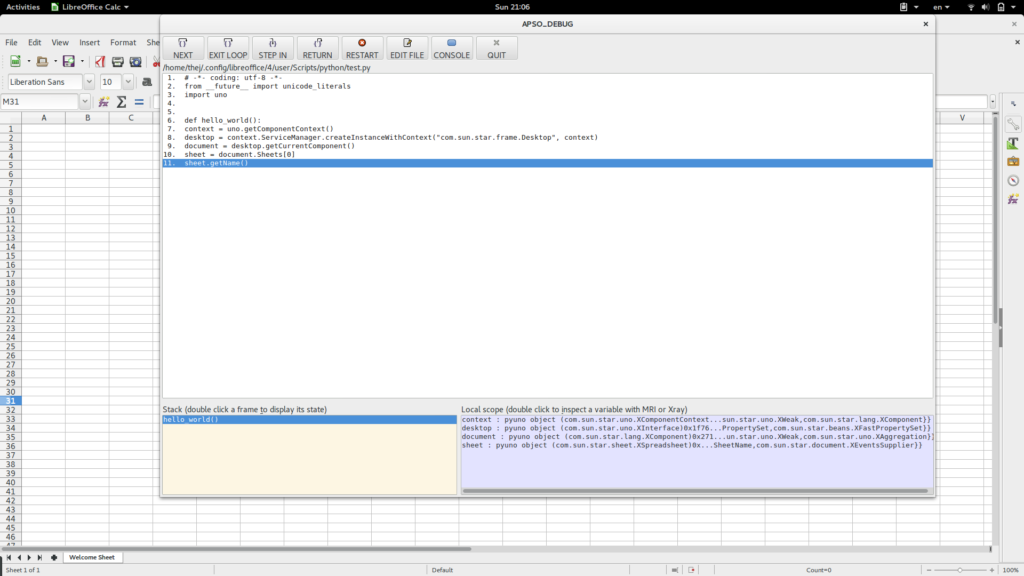
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from __future__ import unicode_literals import uno def hello_world(): context = uno.getComponentContext() desktop = context.ServiceManager.createInstanceWithContext("com.sun.star.frame.Desktop", context) document = desktop.getCurrentComponent() sheet = document.Sheets[0] sheet.getName() You can also start debugger from APSO menu. It opens a window and works just like any other debugger. Its simple and easy to use.
APSO debugger is simple and very friendly to use.
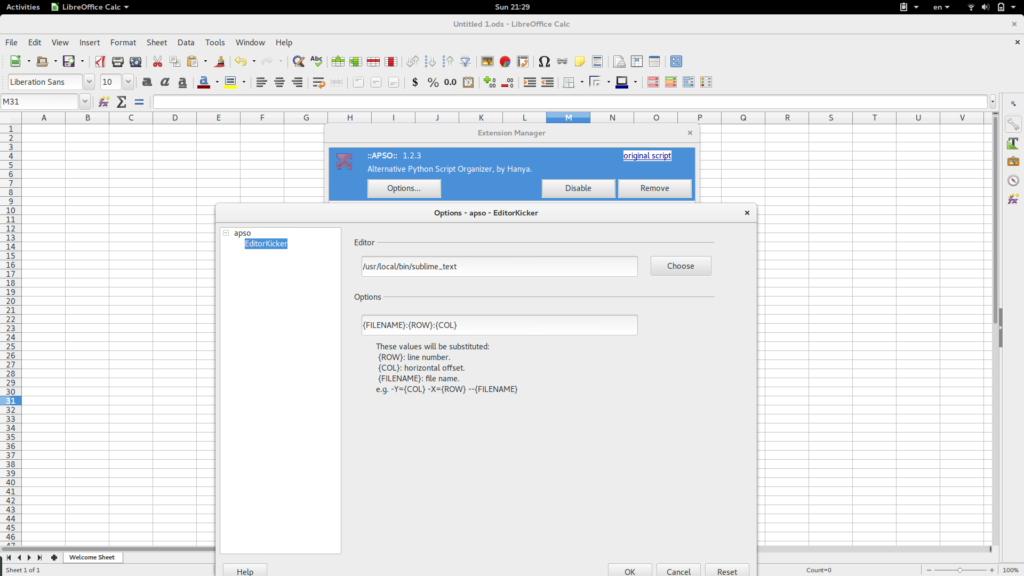
Also if you like to use a different editor then you can go to Extensions-APSO-Options and give the path of your favourite editor. I use sublime text.
APSO custom editor settings
What next?
That’s it for this tutorial. You can also refer LibreOffice Wiki for more details. In the next tutorial we will explore the uno objects and document structure. We will also develop a real and useful Python macro.
Введение
LibreOffice позволяет пользователям писать макросы на различных интерпретируемых языках, один из которых Python. PyUNO — это компонент, который дает пользователям доступ к API LibreOffice из Python.
Установка
На некоторых операционных системах, таких, как Ubuntu 18.04 LTS вам нужно установить дополнительный пакет OS. В Ubuntu такой пакет называется libreoffice-script-provider-python и содержит такие файлы, как scriptproviderforpython.rdb (метаданные XML) и pythonscript.py (инфраструктура Python).
sudo apt install libreoffice-script-provider-pythonПоддержка тестов для макросов Python
Откройте новый документ в Writer. Выберите пункт меню Сервис ▸ Макросыs ▸ Выполнить макрос. , откроется диалог «Выбор макроса». В списке «Библиотека» выберите Макросы LibreOffice ▸ HelloWorld , в списке «Имя макроса» выберите HelloWorldPython и нажмите кнопку Выполнить
Если вы видите этот результат, ваша система может выполнять макросы Python.

Где хранятся макросы?
Каталог с профилем пользователя, макросы доступны только для пользователя
/home/USER/.config/libreoffice/4/user/Scripts/python
%APPDATA%\LibreOffice\4\user\Scripts\python
~/Library/Application Support/LibreOffice/4/user/Scripts/python/
There is no built-in way to edit Python scripts so you have to use your own text editor. There are 3 places where you can put your code.
Profile USER folder, macros available only for USER
/home/USER/.config/libreoffice/4/user/Scripts/python
%APPDATA%\LibreOffice\4\user\Scripts\python
~/Library/Application Support/LibreOffice/4/user/Scripts/python/
Каталог LibreOffice, макросы доступны для всех пользователей
/usr/lib/libreoffice/share/Scripts/python/
/usr/lib/libreoffice/share/Scripts/python/
Это каталог по умолчанию, он может быть иным, если при установке был выбран иной каталог. Если каталог не существует, вы должны его создать с учётом заглавных символов.
Внутри документа
-
- Любой ODF файл — это в действительности ZIP-архив, который можно распаковать. В корне создайте каталог
myfile | . ├── META-INF │ └── manifest.xml ├── Scripts │ └── python │ └── mymacros.py .
- Отредактируйте файл manifest.xml в каталоге META-INF и добавьте строки, просто до закрывающего тэга
- Any ODF file, really is a ZIP file, you can extract this file like extract normally this type files. In the root, create folder
myfile | . ├── META-INF │ └── manifest.xml ├── Scripts │ └── python │ └── mymacros.py .
- Теперь, запакуйте каталог обратно. Внимание, не пакуйте внешний каталог, запакуйте только содержимое каталога.
Python Guide — My First Macro
All Python examples are stored as PC-based personal macros, as opposed to product Python scripts or document-based scripts. Any example in this guide assumes that you save in this place.
IMPORTANT Python’s syntax is very strict, be sure copy and paste correctly.
Use your favorite text editor, or better an IDE to edit your code.
For Writer
import uno def my_first_macro_writer(): doc = XSCRIPTCONTEXT.getDocument() text = doc.getText() # com.sun.star.text.Text text.setString('Hello World in Python in Writer') returnFor Calc
import uno def my_first_macro_calc(): doc = XSCRIPTCONTEXT.getDocument() cell = doc.Sheets[0]['A1'] # com.sun.star.sheet.XSpreadsheetDocument cell.setString('Hello World in Python in Calc') returnExecute macro
For Writer
- Open Writer, go to Tools ▸ Macros ▸ Run macro. in section Library select mymacros (or your name file), in section Macro Name, select macro my_first_macro_writer and click in command button Run
For Calc
- Open calc, go to Tools ▸ Macros ▸ Run macro. in section Library select mymacros (or your name file), in section Macro Name, select macro my_first_macro_calc and click in command button Run