- New String Class Functions in Java 11
- New methods in the String Class
- 1. isBlank() method:
- 2. lines() method:
- 3. strip() , stripLeading() and stripTrailing() methods
- 4. repeat(int) method:
- Conclusion:
- You may also like:
- Java Inline Function
- Java Inline Function
- Java String lines() Method to Get the Stream of Lines
- 1. String lines to List
- 2. Count the Lines in a String
- 3. Print all the Lines in a String
- 4. String Lines to Array
- Conclusion
- References:
New String Class Functions in Java 11
Java 11 is the second long time support release after Java 8.
We are all very familiar with Java 8 and its amazing features, but 4 years have passed since the release of Java 8 and Java has made a few major steps forward, in terms of syntax and features. And now, it’s high time to do some catching up with the new features because we already have Java 9, upgraded by Java 10 and Java 11 now, which is an important release because just like Java 8, it’s going to be a longer version of support.
With Java 11, Oracle JDK will no longer be free. Java 10 was the last free Oracle JDK download.
This version of Java has several new features including:
• The Java file can be executed in a single command
• Addition of new methods to be used in the String Class.
• Local-variable syntax is provided with the Lambda parameters
• Nested Applied Access Control
• Reading / Writing Strings to and from a file
New methods in the String Class
Following are the new methods added in the String class in Java 11:
Several new methods have been added to the String Class. Let’s cover it in detail:
1. isBlank() method:
The isBlank() method returns true if the string is empty or contains only white spaces, otherwise false.
Refer to the below program-1. Created input string with contents «WelcometoStudyTonight» and it is not blank. Hence, this method should return false.
String input = "WelcometoStudyTonight"; boolean isBlank = input.isBlank(); System.out.println(isBlank); Refer to the code below where we have created empty input string and then used the isBlank() which returns true.
String input2 = ""; isBlank = input2.isBlank(); System.out.println(isBlank);In the code example below, we have created a string variable with just some blank spaces, again the isBlank() method will return true.
String input3 = " "; isBlank = input3.isBlank(); System.out.println(isBlank);2. lines() method:
This method breaks the given string into rows.
Below example has a single line in string:
String value = "Welcome to StudyTonight"; Stream stream = value.lines(); Stream.forEach(line-> System.out.println(line));Only one line is printed as expected because the input has no end of the line.
In the code below, we have a string with multiple lines.
String s1 = " This is \n an article on \n Java 11"; Stream s2 = s1.lines(); s2.forEach(line -> System.out.println(line));This is
an article on
Java 11
Replacing \n with \r will also provide the same output.
String s1 = " This is \r an article on \r Java 11"; Stream s2 = s1.lines(); s2.forEach(line -> System.out.println(line));This is
an article on
Java 11
3. strip() , stripLeading() and stripTrailing() methods
The strip() method removes white space from both ends of the given string.
The strip() method is considered to appear in the «Unicode-aware» decoding
Unicode was not generated at the time trim() was introduced. Now, the new strip() method removes all types of spaces. ( Character.isWhiteSpace(c) is used to know whether Unicode is whitespace or not).
public class StringStripping < public static void main(String[] args) < String input = " welcome to studytonight "; System.out.println("Input string length : " + input.length()); String strippedStr = input.strip(); System.out.println("Stripped string length : " + strippedStr.length()); >>Input string length: 29
Stripped string length:23
The stripLeading() method returns a new string with all the leading spaces removed from the given string. Leading white/blank spaces refers to the white spaces before the string.
String input = " Welcome "; System.out.println("Input string length : " + input.length()); String sStr = input.stripLeading(); System.out.println("Stripped string length : " + sStr.length()); System.out.println("Input String : "+input); System.out.println("Output String : "+sStr);Input string length: 13
Stripped string length: 10
Input String: Welcome
Output String: Welcome
The stripTrailing() method returns a new string with all the trailing blank spaces removed. The trailing white spaces means if there are white/blank spaces after the string characters end.
String input = " mohit "; System.out.println("Input string length : " + input.length()); String stripStr = input.stripTrailing(); System.out.println("Stripped string length : " + stripStr.length()); System.out.println("Input String :"+input); System.out.println("Output String :"+stripStr);Input string length: 11
Stripped string length: 8
Input String : mohit
Output String: mohit
4. repeat(int) method:
It is used to simply multiply or repeat a string several times as specified by the int parameter.
Conclusion:
With this, we have covered the new String functions introduced in Java 11. These functions comes in handy when you are working with strings.
If we missed any function, please do share it with us in the comment section.
You may also like:
Java Inline Function
This tutorial demonstrates how to implement an inline function in Java.
Java Inline Function
When the compiler copies the code of a function and places it anywhere, it is considered an inline function. If we change the code of an inline function, the compiler would have to change the code in all the copied versions.
The HotSpot JVM just-in-time (JIT) compiler can perform a lot of optimizations which also include inlining, which is enabled by default, and we can use the following flags to enable or disable the inlining in JVM:
-XX:+Inline (+ means true, which enables the inlining) -XX:-Inline (- means false, which disables the inlining) Java doesn’t provide inline functions, but the JVM performs this operation at the execution time. As the compiler performs, we don’t have to use the inline function in Java.
To understand how it works, let’s try to create the inline function functionality in Java. See the example:
package delftstack; public class Inline_Example public static final class Points private int a = 0; private int b = 0; public int getA() return a; > public void setA(int a) this.a = a; > public int getB() return b; > public void setB(int b) this.b = b; > @Override public String toString() return String.format("%s[a=%d, b=%d]", getClass().getSimpleName(), a, b); > > public static void main(String[] args) final Points NotInlinedPoints = new Points(); NotInlinedPoints.setA( NotInlinedPoints.getA() + 2); NotInlinedPoints.setB( NotInlinedPoints.getA() * 6/2); final Points InlinedPoints = new Points(); InlinedPoints.a = InlinedPoints.a + 2; InlinedPoints.b = InlinedPoints.a * 6/2; System.out.println("The Non Inlined Points "+NotInlinedPoints); System.out.println("The Inlined Points "+InlinedPoints); > > The code above shows the method inlining. The optimization is performed, and the method call is replaced with simple statements, as shown in our code.
Both NotInlinedPoints and InlinedPoints are performing the same operation, as shown in the output:
The Non Inlined Points Points[a=2, b=6] The Inlined Points Points[a=2, b=6] As we can see here, we don’t have to perform the inlining by declaring an inline function in Java. The JVM does it with some complex structure behind the scene.
By default, the inlining is enabled in JVM. Let’s try to run the code by disabling the inlining by using the above flags.
Run the above code in cmd:
C:\Users\DelftStack>javac Inline_Example.java C:\Users\DelftStack> Java -XX:-Inline Inline_Example.java The Non Inlined Points Points[a=2, b=6] The Inlined Points Points[a=2, b=6] As we can see, the code doesn’t show any difference in the result after disabling the inlining, but the process ids and the time elapsed will be more for this compilation.
Sheeraz is a Doctorate fellow in Computer Science at Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xian, China. He has 7 years of Software Development experience in AI, Web, Database, and Desktop technologies. He writes tutorials in Java, PHP, Python, GoLang, R, etc., to help beginners learn the field of Computer Science.
Java String lines() Method to Get the Stream of Lines
Let’s look at some examples of using String lines() method.
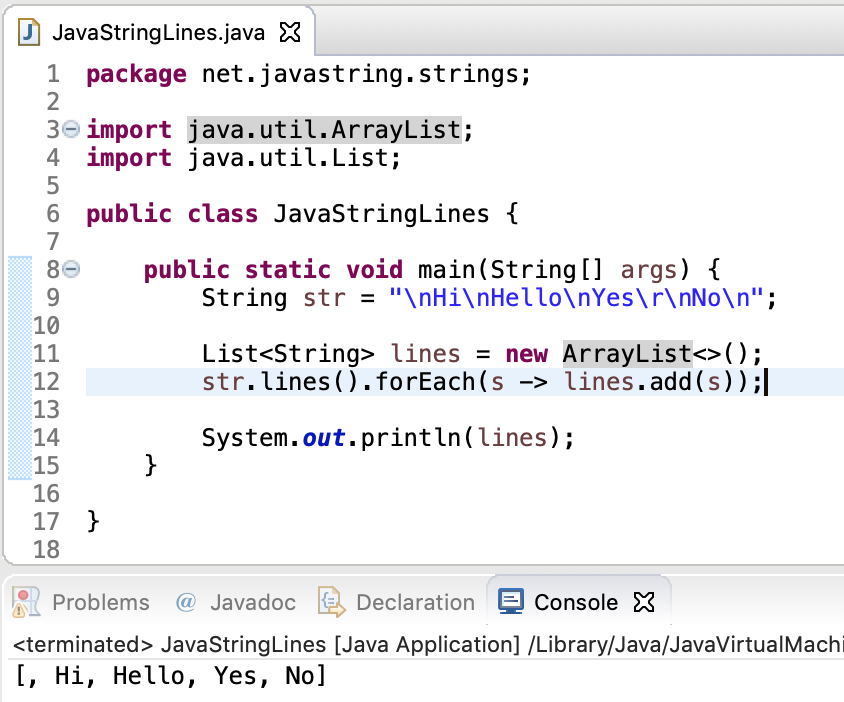
1. String lines to List
We can use lines() method to get the stream of lines. Then use the forEach() method to add all these lines to a list.
package net.javastring.strings; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class JavaStringLines < public static void main(String[] args) < String str = "\nHi\nHello\nYes\r\nNo\n"; Listlines = new ArrayList<>(); str.lines().forEach(s -> lines.add(s)); System.out.println(lines); > >
Output: [, Hi, Hello, Yes, No]
The output is more clear if we write the string object like this:
String str = "\n" + "Hi\n" + "Hello\n" + "Yes\r\n" + "No\n";
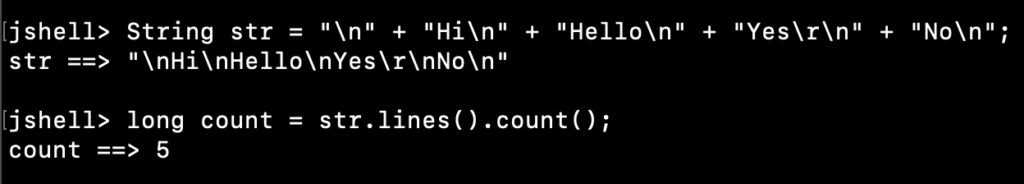
2. Count the Lines in a String
We can count the number of lines in a string using the lines() method followed by the Stream count() method.
jshell> String str = "\n" + "Hi\n" + "Hello\n" + "Yes\r\n" + "No\n"; str ==> "\nHi\nHello\nYes\r\nNo\n" jshell> long count = str.lines().count(); count ==> 5
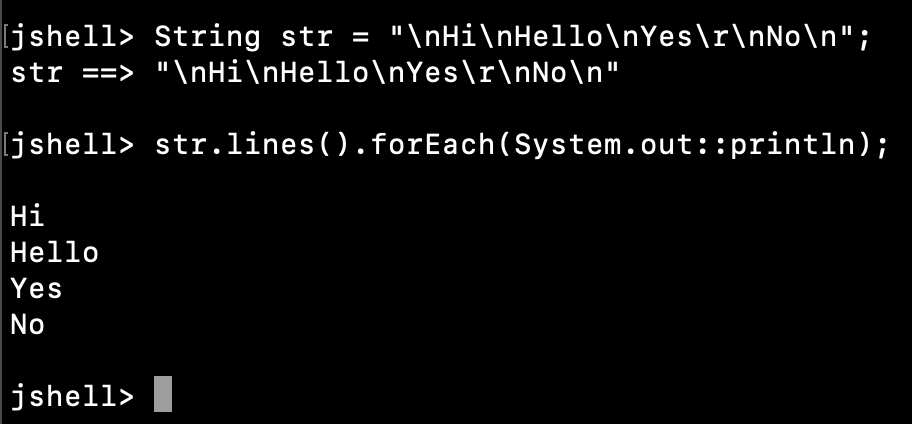
3. Print all the Lines in a String
We can print the lines in a string using the lines() method. It’s better than splitting and then printing the lines because it saves time and memory.
jshell> String str = "\nHi\nHello\nYes\r\nNo\n"; str ==> "\nHi\nHello\nYes\r\nNo\n" jshell> str.lines().forEach(System.out::println); Hi Hello Yes No jshell>
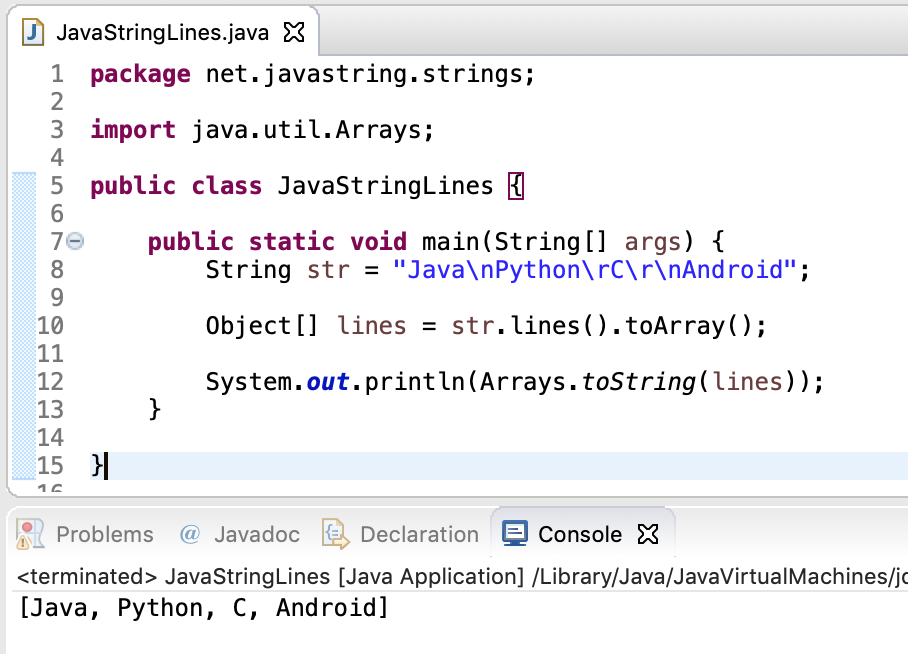
4. String Lines to Array
We can use toArray() method of Stream API to convert string lines into an array. Note that the output will be an Object array and not String array.
package net.javastring.strings; import java.util.Arrays; public class JavaStringLines < public static void main(String[] args) < String str = "Java\nPython\rC\r\nAndroid"; Object[] lines = str.lines().toArray(); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(lines)); >>
Conclusion
Java String lines() provides a stream of lines. We can use it to convert the string lines to list and array. It’s much better in performance than the split() method to get the string lines because of Stream API lazy initializations.