- Release Notes
- Named Arguments
- Support Policy
- Laravel 10
- PHP 8.1
- Types
- Laravel Pennant
- Process Interaction
- Test Profiling
- Pest Scaffolding
- Generator CLI Prompts
- Horizon / Telescope Facelift
- Installation
- Installing Laravel
- Via Laravel Installer
- Via Composer Create-Project
- Local Development Server
- Configuration
- Public Directory
- Configuration Files
- Directory Permissions
- Application Key
- Additional Configuration
- Web Server Configuration
- Directory Configuration
- Pretty URLs
- Apache
- Nginx
Release Notes
Laravel and its other first-party packages follow Semantic Versioning. Major framework releases are released every year (~Q1), while minor and patch releases may be released as often as every week. Minor and patch releases should never contain breaking changes.
When referencing the Laravel framework or its components from your application or package, you should always use a version constraint such as ^10.0 , since major releases of Laravel do include breaking changes. However, we strive to always ensure you may update to a new major release in one day or less.
Named Arguments
Named arguments are not covered by Laravel’s backwards compatibility guidelines. We may choose to rename function arguments when necessary in order to improve the Laravel codebase. Therefore, using named arguments when calling Laravel methods should be done cautiously and with the understanding that the parameter names may change in the future.
Support Policy
For all Laravel releases, bug fixes are provided for 18 months and security fixes are provided for 2 years. For all additional libraries, including Lumen, only the latest major release receives bug fixes. In addition, please review the database versions supported by Laravel.
| Version | PHP (*) | Release | Bug Fixes Until | Security Fixes Until |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 7.3 — 8.1 | September 8th, 2020 | July 26th, 2022 | January 24th, 2023 |
| 9 | 8.0 — 8.2 | February 8th, 2022 | August 8th, 2023 | February 6th, 2024 |
| 10 | 8.1 — 8.2 | February 14th, 2023 | August 6th, 2024 | February 4th, 2025 |
| 11 | 8.2 | Q1 2024 | August 5th, 2025 | February 3rd, 2026 |
Laravel 10
As you may know, Laravel transitioned to yearly releases with the release of Laravel 8. Previously, major versions were released every 6 months. This transition is intended to ease the maintenance burden on the community and challenge our development team to ship amazing, powerful new features without introducing breaking changes. Therefore, we have shipped a variety of robust features to Laravel 9 without breaking backwards compatibility.
Therefore, this commitment to ship great new features during the current release will likely lead to future «major» releases being primarily used for «maintenance» tasks such as upgrading upstream dependencies, which can be seen in these release notes.
Laravel 10 continues the improvements made in Laravel 9.x by introducing argument and return types to all application skeleton methods, as well as all stub files used to generate classes throughout the framework. In addition, a new, developer-friendly abstraction layer has been introduced for starting and interacting with external processes. Further, Laravel Pennant has been introduced to provide a wonderful approach to managing your application’s «feature flags».
PHP 8.1
Laravel 10.x requires a minimum PHP version of 8.1.
Types
Application skeleton and stub type-hints were contributed by Nuno Maduro.
On its initial release, Laravel utilized all of the type-hinting features available in PHP at the time. However, many new features have been added to PHP in the subsequent years, including additional primitive type-hints, return types, and union types.
Laravel 10.x thoroughly updates the application skeleton and all stubs utilized by the framework to introduce argument and return types to all method signatures. In addition, extraneous «doc block» type-hint information has been deleted.
This change is entirely backwards compatible with existing applications. Therefore, existing applications that do not have these type-hints will continue to function normally.
Laravel Pennant
Laravel Pennant was developed by Tim MacDonald.
A new first-party package, Laravel Pennant, has been released. Laravel Pennant offers a light-weight, streamlined approach to managing your application’s feature flags. Out of the box, Pennant includes an in-memory array driver and a database driver for persistent feature storage.
Features can be easily defined via the Feature::define method:
use Laravel\Pennant\Feature;use Illuminate\Support\Lottery; Feature::define('new-onboarding-flow', function () return Lottery::odds(1, 10);>); Once a feature has been defined, you may easily determine if the current user has access to the given feature:
if (Feature::active('new-onboarding-flow')) // . > Of course, for convenience, Blade directives are also available:
@feature('new-onboarding-flow') div> . --> div>@endfeature Pennant offers a variety of more advanced features and APIs. For more information, please consult the comprehensive Pennant documentation.
Process Interaction
The process abstraction layer was contributed by Nuno Maduro and Taylor Otwell.
Laravel 10.x introduces a beautiful abstraction layer for starting and interacting with external processes via a new Process facade:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Process; $result = Process::run('ls -la'); return $result->output(); Processes may even be started in pools, allowing for the convenient execution and management of concurrent processes:
use Illuminate\Process\Pool;use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Process; [$first, $second, $third] = Process::concurrently(function (Pool $pool) $pool->command('cat first.txt'); $pool->command('cat second.txt'); $pool->command('cat third.txt');>); return $first->output(); In addition, processes may be faked for convenient testing:
Process::fake(); // . Process::assertRan('ls -la'); For more information on interacting with processes, please consult the comprehensive process documentation.
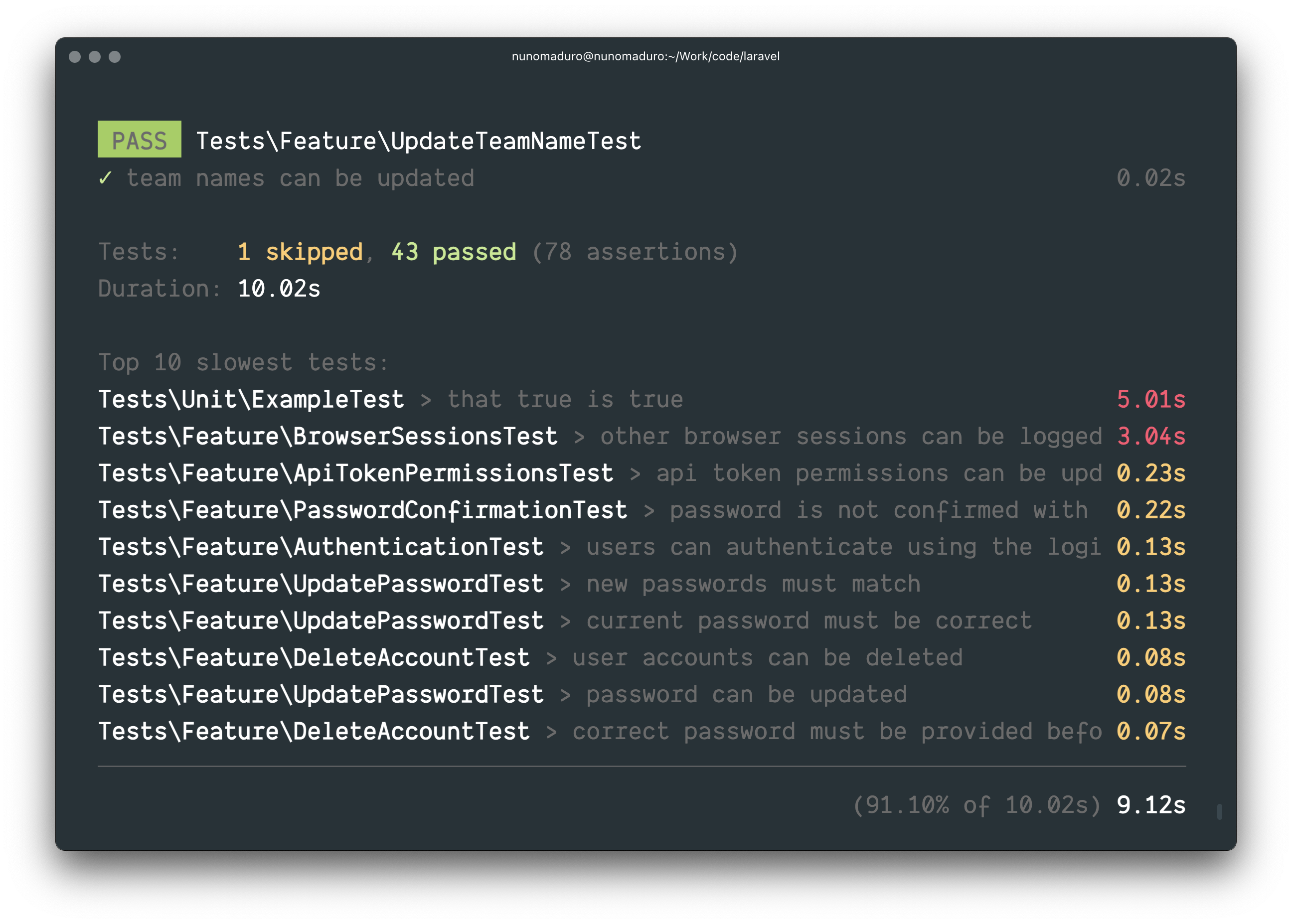
Test Profiling
Test profiling was contributed by Nuno Maduro.
The Artisan test command has received a new —profile option that allows you to easily identify the slowest tests in your application:
For convenience, the slowest tests will be displayed directly within the CLI output:
Pest Scaffolding
New Laravel projects may now be created with Pest test scaffolding by default. To opt-in to this feature, provide the —pest flag when creating a new application via the Laravel installer:
laravel new example-application --pest Generator CLI Prompts
Generator CLI prompts were contributed by Jess Archer.
To improve the framework’s developer experience, all of Laravel’s built-in make commands no longer require any input. If the commands are invoked without input, you will be prompted for the required arguments:
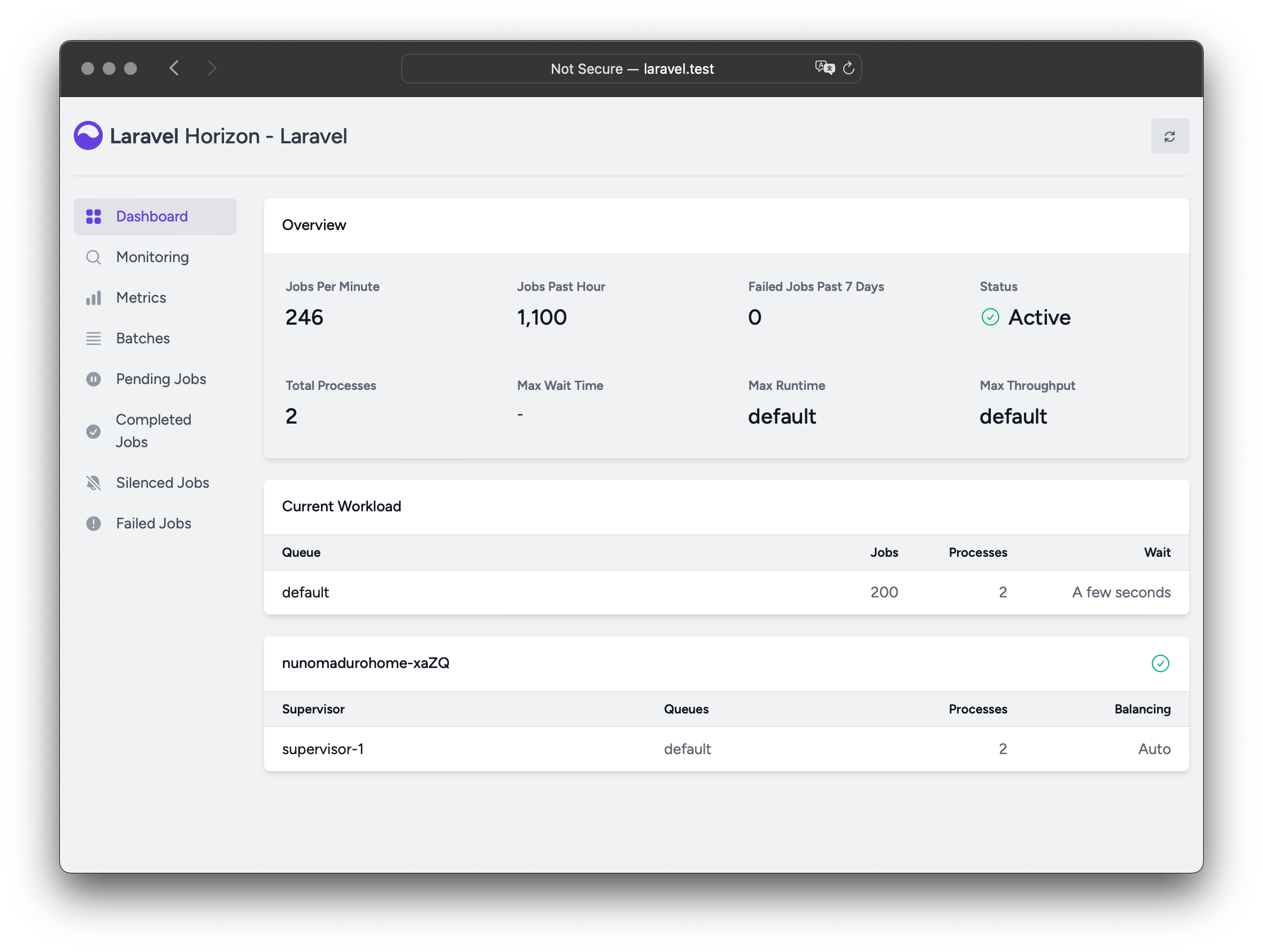
php artisan make:controller Horizon / Telescope Facelift
Horizon and Telescope have been updated with a fresh, modern look including improved typography, spacing, and design:
Laravel is a web application framework with expressive, elegant syntax. We believe development must be an enjoyable and creative experience to be truly fulfilling. Laravel attempts to take the pain out of development by easing common tasks used in most web projects.
Installation
The Laravel framework has a few system requirements. All of these requirements are satisfied by the Laravel Homestead virtual machine, so it’s highly recommended that you use Homestead as your local Laravel development environment.
However, if you are not using Homestead, you will need to make sure your server meets the following requirements:
- PHP >= 7.2.5
- BCMath PHP Extension
- Ctype PHP Extension
- Fileinfo PHP extension
- JSON PHP Extension
- Mbstring PHP Extension
- OpenSSL PHP Extension
- PDO PHP Extension
- Tokenizer PHP Extension
- XML PHP Extension
Installing Laravel
Laravel utilizes Composer to manage its dependencies. So, before using Laravel, make sure you have Composer installed on your machine.
Via Laravel Installer
First, download the Laravel installer using Composer:
composer global require laravel/installer Make sure to place Composer’s system-wide vendor bin directory in your $PATH so the laravel executable can be located by your system. This directory exists in different locations based on your operating system; however, some common locations include:
- macOS: $HOME/.composer/vendor/bin
- Windows: %USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\Composer\vendor\bin
- GNU / Linux Distributions: $HOME/.config/composer/vendor/bin or $HOME/.composer/vendor/bin
You could also find the composer’s global installation path by running composer global about and looking up from the first line.
Once installed, the laravel new command will create a fresh Laravel installation in the directory you specify. For instance, laravel new blog will create a directory named blog containing a fresh Laravel installation with all of Laravel’s dependencies already installed:
Via Composer Create-Project
Alternatively, you may also install Laravel by issuing the Composer create-project command in your terminal:
composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel:^7.0 blog Local Development Server
If you have PHP installed locally and you would like to use PHP’s built-in development server to serve your application, you may use the serve Artisan command. This command will start a development server at http://localhost:8000 :
More robust local development options are available via Homestead and Valet.
Configuration
Public Directory
After installing Laravel, you should configure your web server’s document / web root to be the public directory. The index.php in this directory serves as the front controller for all HTTP requests entering your application.
Configuration Files
All of the configuration files for the Laravel framework are stored in the config directory. Each option is documented, so feel free to look through the files and get familiar with the options available to you.
Directory Permissions
After installing Laravel, you may need to configure some permissions. Directories within the storage and the bootstrap/cache directories should be writable by your web server or Laravel will not run. If you are using the Homestead virtual machine, these permissions should already be set.
Application Key
The next thing you should do after installing Laravel is set your application key to a random string. If you installed Laravel via Composer or the Laravel installer, this key has already been set for you by the php artisan key:generate command.
Typically, this string should be 32 characters long. The key can be set in the .env environment file. If you have not copied the .env.example file to a new file named .env , you should do that now. If the application key is not set, your user sessions and other encrypted data will not be secure!
Additional Configuration
Laravel needs almost no other configuration out of the box. You are free to get started developing! However, you may wish to review the config/app.php file and its documentation. It contains several options such as timezone and locale that you may wish to change according to your application.
You may also want to configure a few additional components of Laravel, such as:
Web Server Configuration
Directory Configuration
Laravel should always be served out of the root of the «web directory» configured for your web server. You should not attempt to serve a Laravel application out of a subdirectory of the «web directory». Attempting to do so could expose sensitive files present within your application.
Pretty URLs
Apache
Laravel includes a public/.htaccess file that is used to provide URLs without the index.php front controller in the path. Before serving Laravel with Apache, be sure to enable the mod_rewrite module so the .htaccess file will be honored by the server.
If the .htaccess file that ships with Laravel does not work with your Apache installation, try this alternative:
Options +FollowSymLinks -IndexesRewriteEngine On RewriteCond %HTTP:Authorization> .RewriteRule .* - [E=HTTP_AUTHORIZATION:%HTTP:Authorization>] RewriteCond %REQUEST_FILENAME> !-dRewriteCond %REQUEST_FILENAME> !-fRewriteRule ^ index.php [L] Nginx
If you are using Nginx, the following directive in your site configuration will direct all requests to the index.php front controller:
location / try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$query_string;> When using Homestead or Valet, pretty URLs will be automatically configured.
Laravel is a web application framework with expressive, elegant syntax. We believe development must be an enjoyable and creative experience to be truly fulfilling. Laravel attempts to take the pain out of development by easing common tasks used in most web projects.