- How to Determine Which Element Has Focus in JavaScript
- JavaScript’s document.activeElement Property
- Focusable vs. Tabbable Elements in JavaScript
- Verify an Element Already Has Focus in JavaScript
- Checking a Specific Element for Focus in JavaScript
- Checking if the Document Has the Focus in JavaScript
- Final Thoughts on Element Focus in JavaScript
- Фокусировка: focus/blur
- События focus/blur
- Методы focus/blur
- Включаем фокусировку на любом элементе: tabindex
How to Determine Which Element Has Focus in JavaScript
Baking accessibility into your web apps should be second nature now, as we sail through the third decade of the 21st century. One of the key components of accessibility is keyboard navigation, allowing users who have difficulty using a mouse to navigate your application. Unfortunately, ensuring that all interactive elements are accessible via the keyboard is a task that is all-too-often overlooked by web developers. A prime example of poor focus management is not resetting the focus on the triggering element upon closing a modal dialog. Even an application built using a framework like Angular is not immune to such oversights. I recently worked on a bug where the developer disabled the triggering element after clicking it, thereby breaking the control’s built-in focus handling. Should you need to take charge of the focus in your application, this web development tutorial will show you how to do it with ease!
Looking to learn web development in a course or class format? Check out our tutorial listing some of the Best Online Courses to Learn HTML.
JavaScript’s document.activeElement Property
You may have already heard about the document.activeElement property, since it has been around for a while, but in case you have not been properly acquainted, the document.activeElement property returns the HTML element that is currently focused.
To give you an idea of how it works, here’s some (jQuery-assisted) code, that tracks the focus as you click on the various page elements:
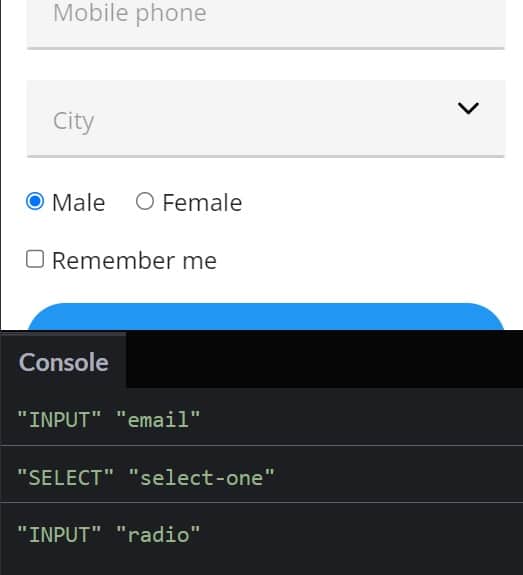
$(document).ready(function()< $(this).click(function() < var activeElement = document.activeElement; console.log(activeElement.tagName, activeElement.type || 'N/A'); >); >);
Since click events bubble up from the originating element, we can capture them at the document level. In the bound function, we obtain a reference to the focused element from the document.activeElement property and print its tag name and type to the console. Here is some sample output:
What is great about document.activeElement is that programmers do not need any type of event listener or Observable style subscribe handler to keep track of what element is focused; you can check the activeElement property any time you need to know which element currently has the focus.
Focusable vs. Tabbable Elements in JavaScript
Now would be an opportune time to cover the difference between focusable and tabbable elements. Some elements are natively focusable, while others require explicitly setting a tab index. In all cases, the element must be visible in order to be focusable.
Form controls like input, select, textarea, and button are all focusable if they are not disabled, as are objects. Other elements, such as anchors, are focusable if they have an href or tabindex attribute. Meanwhile, area elements are focusable if they are inside a named map, have an href attribute, and there is a visible image using the map. Other elements are focusable based solely on their tabindex attribute and visibility. Elements with a negative tabindex are said to be focusable, but not tabbable.
And now for the good news; the activeElement property will not only identify traditionally focusable elements, like form fields and links, but any element with a zero or positive tabIndex value – in other words, any focusable element, whether tabbable or not.
Verify an Element Already Has Focus in JavaScript
Sometimes web developers have to set the focus programmatically so that it does not get lost. Nothing wrong with that, but you may want to check that no other element already has the focus before setting it. Otherwise, you run the risk of moving the focus, which will annoy the user to no end.
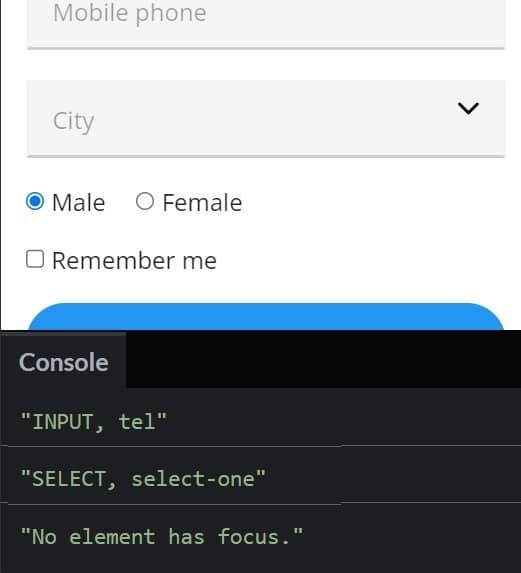
A big clue to determining whether or not any element is currently focused was provided in the above code. If you click somewhere in the document that is not occupied by a form control, you will see the output “BODY N/A“. That is because the document.body retains the focus as long as you are on that page. With that in mind, let’s refactor our callback function to print a different message when no form element has the focus:
Here’s some sample output with our new message:
Checking a Specific Element for Focus in JavaScript
Sometimes you do not want to know which element currently has the focus, only whether or not a particular element has it. For those situations, you can simply compare the activeElement against the one in question, much like we did above with the document.body:
// dummy element var myElement = document.getElementById('myElement'); // check for focus var isFocused = (document.activeElement === myElement); Other times, programmers may be interested in checking if an element does not currently have the focus. For instance, perhaps a developer would like to know if an element does not have the focus before setting it programmatically. The following code snippet shows how you might go about doing that:
var activeElement = document.activeElement; var myElement = document.getElementById('my-element'); if (activeElement !== myElement) < myElement.focus(); >); Checking if the Document Has the Focus in JavaScript
Although an element with focus is always the active element in the document, an active element does not necessarily have focus. For example, an active element within a popup window that is not the foreground does not have focus. In such cases, you will also want to check if the entire document has the focus. To do that, you can use the hasFocus() method of the Document interface. It returns a boolean value indicating whether the document or any element inside the document has focus.
The following code invokes document.hasFocus() every 300 milliseconds and presents a message displaying the result. In addition, it also changes the page’s background color from white to gray whenever the page loses the focus:
function checkPageFocus() < const log = document.getElementById('log'); if (document.hasFocus()) < log.textContent = 'This document has the focus.'; document.body.style.background = '#fff'; >else < log.textContent = 'This document does not have the focus.'; document.body.style.background = '#ccc'; >> // Check page focus every 300 milliseconds setInterval(checkPageFocus, 300); You can see the above code in action in the codepen demo. There, you can see it in action by clicking the “Open a new window” button. Once the new window receives the focus, the triggering page color and message change. Closing the new window then changes them back as the focus returns to the main document.
Final Thoughts on Element Focus in JavaScript
In this JavaScript tutorial we learned how to determine which element has the focus, which is a crucial factor in focus management. In the process, we also covered the difference between focusable and tabbable elements, as well as how to check if the entire document has the focus. Armed with that knowledge, you’ll be able to make your web pages and applications more accessible to those who have difficulty in using a mouse.
Фокусировка: focus/blur
Элемент получает фокус, когда пользователь кликает по нему или использует клавишу Tab . Также существует HTML-атрибут autofocus , который устанавливает фокус на элемент, когда страница загружается. Есть и другие способы получения фокуса, о них – далее.
Фокусировка обычно означает: «приготовься к вводу данных на этом элементе», это хороший момент, чтобы инициализовать или загрузить что-нибудь.
Момент потери фокуса («blur») может быть важнее. Это момент, когда пользователь кликает куда-то ещё или нажимает Tab , чтобы переключиться на следующее поле формы. Есть другие причины потери фокуса, о них – далее.
Потеря фокуса обычно означает «данные введены», и мы можем выполнить проверку введённых данных или даже отправить эти данные на сервер и так далее.
В работе с событиями фокусировки есть важные особенности. Мы постараемся разобрать их далее.
События focus/blur
Событие focus вызывается в момент фокусировки, а blur – когда элемент теряет фокус.
Используем их для валидации(проверки) введённых данных.
- Обработчик blur проверяет, введён ли email, и если нет – показывает ошибку.
- Обработчик focus скрывает это сообщение об ошибке (в момент потери фокуса проверка повторится):
.invalid < border-color: red; >#error Ваш email: >; input.onfocus = function() < if (this.classList.contains('invalid')) < // удаляем индикатор ошибки, т.к. пользователь хочет ввести данные заново this.classList.remove('invalid'); error.innerHTML = ""; >>; Современный HTML позволяет делать валидацию с помощью атрибутов required , pattern и т.д. Иногда – это всё, что нам нужно. JavaScript можно использовать, когда мы хотим больше гибкости. А ещё мы могли бы отправлять изменённое значение на сервер, если оно правильное.
Методы focus/blur
Методы elem.focus() и elem.blur() устанавливают/снимают фокус.
Например, запретим посетителю переключаться с поля ввода, если введённое значение не прошло валидацию:
.error Ваш email: Это сработает во всех браузерах, кроме Firefox (bug).
Если мы что-нибудь введём и нажмём Tab или кликнем в другое место, тогда onblur вернёт фокус обратно.
Отметим, что мы не можем «отменить потерю фокуса», вызвав event.preventDefault() в обработчике onblur потому, что onblur срабатывает после потери фокуса элементом.
Однако на практике следует хорошо подумать, прежде чем внедрять что-то подобное, потому что мы обычно должны показывать ошибки пользователю, но они не должны мешать пользователю при заполнении нашей формы. Ведь, вполне возможно, что он захочет сначала заполнить другие поля.
Потеря фокуса может произойти по множеству причин.
Одна из них – когда посетитель кликает куда-то ещё. Но и JavaScript может быть причиной, например:
- alert переводит фокус на себя – элемент теряет фокус (событие blur ), а когда alert закрывается – элемент получает фокус обратно (событие focus ).
- Если элемент удалить из DOM, фокус также будет потерян. Если элемент добавить обратно, то фокус не вернётся.
Из-за этих особенностей обработчики focus/blur могут сработать тогда, когда это не требуется.
Используя эти события, нужно быть осторожным. Если мы хотим отследить потерю фокуса, которую инициировал пользователь, тогда нам следует избегать её самим.
Включаем фокусировку на любом элементе: tabindex
Многие элементы по умолчанию не поддерживают фокусировку.
Какие именно – зависит от браузера, но одно всегда верно: поддержка focus/blur гарантирована для элементов, с которыми посетитель может взаимодействовать: , , , и т.д.
Это можно изменить HTML-атрибутом tabindex .
Любой элемент поддерживает фокусировку, если имеет tabindex . Значение этого атрибута – порядковый номер элемента, когда клавиша Tab (или что-то аналогичное) используется для переключения между элементами.
То есть: если у нас два элемента, первый имеет tabindex=»1″ , а второй tabindex=»2″ , то находясь в первом элементе и нажав Tab – мы переместимся во второй.
Порядок перебора таков: сначала идут элементы со значениями tabindex от 1 и выше, в порядке tabindex , а затем элементы без tabindex (например, обычный ).
При совпадающих tabindex элементы перебираются в том порядке, в котором идут в документе.
Есть два специальных значения:
- tabindex=»0″ ставит элемент в один ряд с элементами без tabindex . То есть, при переключении такие элементы будут после элементов с tabindex ≥ 1 . Обычно используется, чтобы включить фокусировку на элементе, но не менять порядок переключения. Чтобы элемент мог участвовать в форме наравне с обычными .
- tabindex=»-1″ позволяет фокусироваться на элементе только программно. Клавиша Tab проигнорирует такой элемент, но метод elem.focus() будет действовать.
Например, список ниже. Кликните первый пункт в списке и нажмите Tab :