- Java super
- Uses of super keyword
- 1. Access Overridden Methods of the superclass
- Example 1: Method overriding
- Example 2: super to Call Superclass Method
- 2. Access Attributes of the Superclass
- Example 3: Access superclass attribute
- 3. Use of super() to access superclass constructor
- Example 4: Use of super()
- Example 5: Call Parameterized Constructor Using super()
- Table of Contents
- super and this keywords in Java
- Java
- super keyword
- Java
- Similarities in this and super
- Java
- Java
- Java
- Can we use both this() and super() in the same constructor?
Java super
The super keyword in Java is used in subclasses to access superclass members (attributes, constructors and methods).
Before we learn about the super keyword, make sure to know about Java inheritance.
Uses of super keyword
- To call methods of the superclass that is overridden in the subclass.
- To access attributes (fields) of the superclass if both superclass and subclass have attributes with the same name.
- To explicitly call superclass no-arg (default) or parameterized constructor from the subclass constructor.
Let’s understand each of these uses.
1. Access Overridden Methods of the superclass
If methods with the same name are defined in both superclass and subclass, the method in the subclass overrides the method in the superclass. This is called method overriding.
Example 1: Method overriding
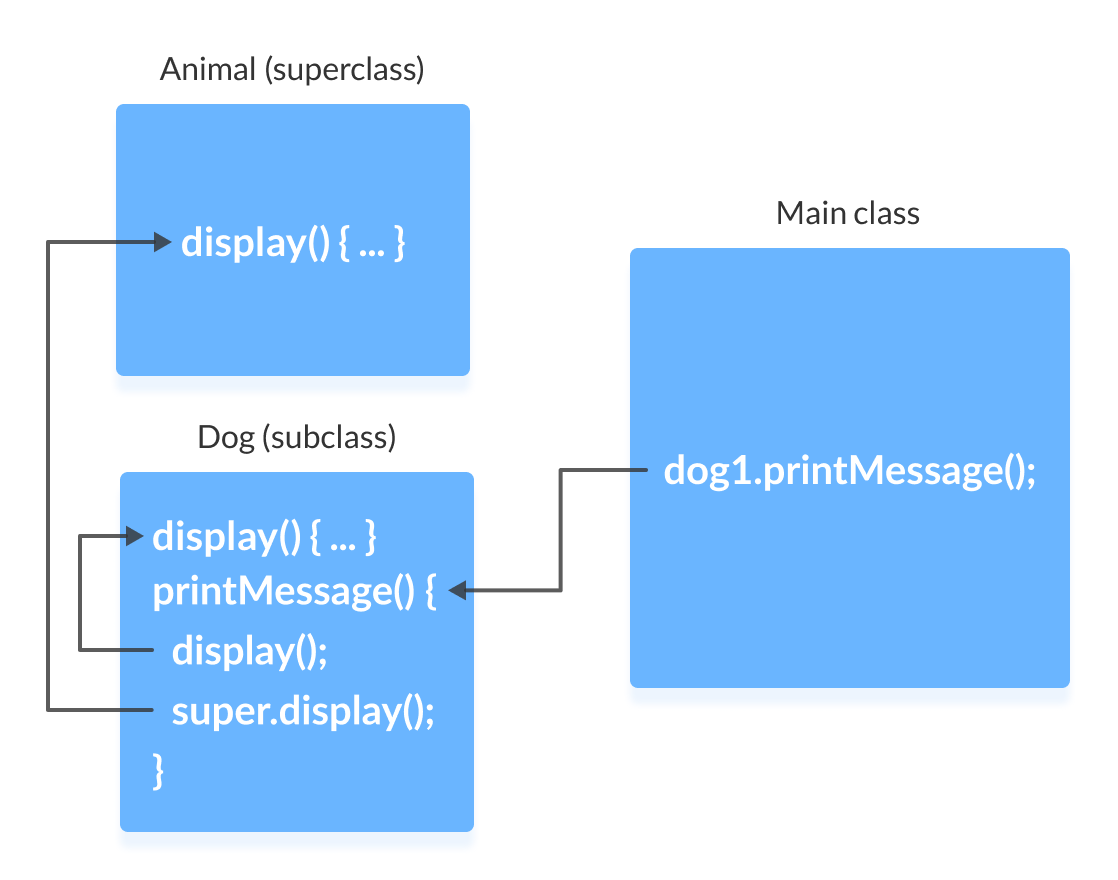
class Animal < // overridden method public void display()< System.out.println("I am an animal"); >> class Dog extends Animal < // overriding method @Override public void display()< System.out.println("I am a dog"); >public void printMessage() < display(); >> class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < Dog dog1 = new Dog(); dog1.printMessage(); >> In this example, by making an object dog1 of Dog class, we can call its method printMessage() which then executes the display() statement.
Since display() is defined in both the classes, the method of subclass Dog overrides the method of superclass Animal . Hence, the display() of the subclass is called.
What if the overridden method of the superclass has to be called?
We use super.display() if the overridden method display() of superclass Animal needs to be called.
Example 2: super to Call Superclass Method
class Animal < // overridden method public void display()< System.out.println("I am an animal"); >> class Dog extends Animal < // overriding method @Override public void display()< System.out.println("I am a dog"); >public void printMessage() < // this calls overriding method display(); // this calls overridden method super.display(); >> class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < Dog dog1 = new Dog(); dog1.printMessage(); >> I am a dog I am an animal
Here, how the above program works.
2. Access Attributes of the Superclass
The superclass and subclass can have attributes with the same name. We use the super keyword to access the attribute of the superclass.
Example 3: Access superclass attribute
class Animal < protected String type="animal"; >class Dog extends Animal < public String type="mammal"; public void printType() < System.out.println("I am a " + type); System.out.println("I am an " + super.type); >> class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < Dog dog1 = new Dog(); dog1.printType(); >> I am a mammal I am an animal
In this example, we have defined the same instance field type in both the superclass Animal and the subclass Dog .
We then created an object dog1 of the Dog class. Then, the printType() method is called using this object.
Inside the printType() function,
- type refers to the attribute of the subclass Dog .
- super.type refers to the attribute of the superclass Animal.
Hence, System.out.println(«I am a » + type); prints I am a mammal . And, System.out.println(«I am an » + super.type); prints I am an animal .
3. Use of super() to access superclass constructor
As we know, when an object of a class is created, its default constructor is automatically called.
To explicitly call the superclass constructor from the subclass constructor, we use super() . It’s a special form of the super keyword.
super() can be used only inside the subclass constructor and must be the first statement.
Example 4: Use of super()
class Animal < // default or no-arg constructor of class Animal Animal() < System.out.println("I am an animal"); >> class Dog extends Animal < // default or no-arg constructor of class Dog Dog() < // calling default constructor of the superclass super(); System.out.println("I am a dog"); >> class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < Dog dog1 = new Dog(); >> I am an animal I am a dog
Here, when an object dog1 of Dog class is created, it automatically calls the default or no-arg constructor of that class.
Inside the subclass constructor, the super() statement calls the constructor of the superclass and executes the statements inside it. Hence, we get the output I am an animal .
The flow of the program then returns back to the subclass constructor and executes the remaining statements. Thus, I am a dog will be printed.
However, using super() is not compulsory. Even if super() is not used in the subclass constructor, the compiler implicitly calls the default constructor of the superclass.
So, why use redundant code if the compiler automatically invokes super()?
It is required if the parameterized constructor (a constructor that takes arguments) of the superclass has to be called from the subclass constructor.
The parameterized super() must always be the first statement in the body of the constructor of the subclass, otherwise, we get a compilation error.
Example 5: Call Parameterized Constructor Using super()
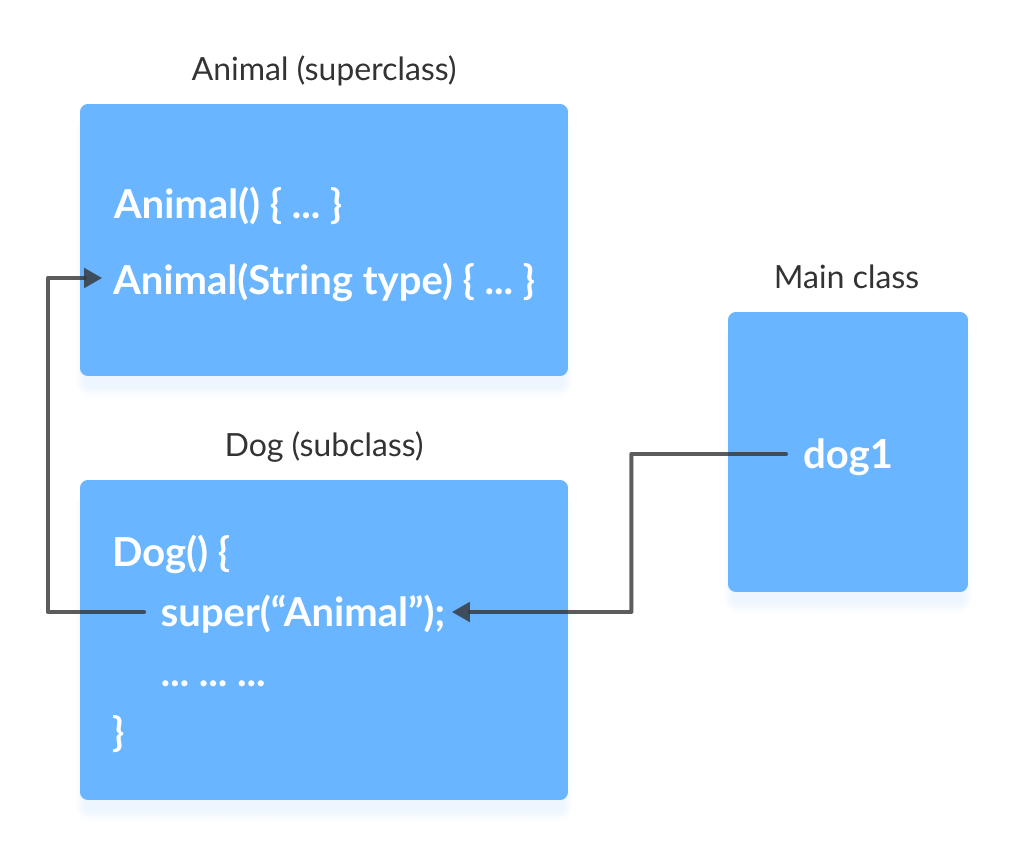
class Animal < // default or no-arg constructor Animal() < System.out.println("I am an animal"); >// parameterized constructor Animal(String type) < System.out.println("Type: "+type); >> class Dog extends Animal < // default constructor Dog() < // calling parameterized constructor of the superclass super("Animal"); System.out.println("I am a dog"); >> class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < Dog dog1 = new Dog(); >> The compiler can automatically call the no-arg constructor. However, it cannot call parameterized constructors.
If a parameterized constructor has to be called, we need to explicitly define it in the subclass constructor.
Note that in the above example, we explicitly called the parameterized constructor super(«Animal») . The compiler does not call the default constructor of the superclass in this case.
Table of Contents
super and this keywords in Java
In java, super keyword is used to access methods of the parent class while this is used to access methods of the current class.
this keyword is a reserved keyword in java i.e, we can’t use it as an identifier. It is used to refer current class’s instance as well as static members. It can be used in various contexts as given below:
- to refer instance variable of current class
- to invoke or initiate current class constructor
- can be passed as an argument in the method call
- can be passed as argument in the constructor call
- can be used to return the current class instance
Java
super keyword
- super is a reserved keyword in java i.e, we can’t use it as an identifier.
- super is used to refer super-class’s instance as well as static members.
- super is also used to invoke super-class’s method or constructor.
- super keyword in java programming language refers to the superclass of the class where the super keyword is currently being used.
- The most common use of super keyword is that it eliminates the confusion between the superclasses and subclasses that have methods with same name.
super can be used in various contexts as given below:
- it can be used to refer immediate parent class instance variable
- it can be used to refer immediate parent class method
- it can be used to refer immediate parent class constructor.
Java
Similarities in this and super
- We can use this as well as superanywhere except static area. Example of this is already shown above where we use this as well as super inside public static void main(String[]args) hence we get Compile Time Error since cannot use them inside static area.
- We can use this as well as superany number of times in a program.
- Both are non-static keyword.
Java
See above we have used this 3 times. So this can be used any number of times.
Java
See above we have used super 2 times. So super can be used any number of times.
Note: We can use ‘this’ as well as ‘super’ any number of times but main thing is that we cannot use them inside static context.
Let us consider a tricky example of this keyword:
Java
//it is of S.O.P(first) of garcia method 22 //it is of S.O.P(second) of garcia method 33 //it is of S.O.P(a) of garcia method 22 //it is of S.O.P(b) of garcia method 33 //it is of S.O.P(first) of louis method 1 //it is of S.O.P(second) of louis method 2 //it is of S.O.P(m) of louis method 1 //it is of S.O.P(n) of louis method 2
Flow of program : First, it start from main and then we have new RR().garcia(100, 200) then flow goes to garcia method of RR class and then in that we have:
a = this.first b = this.second
Here, what is happening is that the value of instance variable(i.e, first) and the value of static variable(i.e, second) are assigned to the garcia method’s local variables a and b respectively. Hence value of a and b comes out to be 22 and 33 respectively. Next we have new RR().louis(1, 2) hence here flow goes to the louis method of RR class and in that we have:
this.first = m this.second = n
Here, above what happens is that the value of the louis method’s local variables i.e, m and n are assigned to the instance as well as static variables i.e, first and second respectively.
Hence, the value of first and second variables are same which we have passed into the louis method i.e, 1 and 2 respectively.
Can we use both this() and super() in the same constructor?
An interesting thing to note here is that according to Java guidelines, this() or super() must be the first statement in the constructor block for it to be executed. So we cannot have them together in the same constructor as both need to be the first statement in the block for proper execution, which is not possible. Trying to do so would raise a compiler error.