- How to use java codes
- How to use java codes
- Trails Covering the Basics
- Creating Graphical User Interfaces
- Specialized Trails and Lessons
- Getting Started with Java in VS Code
- Setting up VS Code for Java development
- Coding Pack for Java
- Installing extensions
- Installing and setting up a Java Development Kit (JDK)
- Supported Java versions
- Installing a Java Development Kit (JDK)
- Creating a source code file
- Editing source code
- Running and debugging your program
- More features
How to use java codes
- Introduction to Java
- The complete History of Java Programming Language
- C++ vs Java vs Python
- How to Download and Install Java for 64 bit machine?
- Setting up the environment in Java
- How to Download and Install Eclipse on Windows?
- JDK in Java
- How JVM Works – JVM Architecture?
- Differences between JDK, JRE and JVM
- Just In Time Compiler
- Difference between JIT and JVM in Java
- Difference between Byte Code and Machine Code
- How is Java platform independent?
- Decision Making in Java (if, if-else, switch, break, continue, jump)
- Java if statement with Examples
- Java if-else
- Java if-else-if ladder with Examples
- Loops in Java
- For Loop in Java
- Java while loop with Examples
- Java do-while loop with Examples
- For-each loop in Java
- Continue Statement in Java
- Break statement in Java
- Usage of Break keyword in Java
- return keyword in Java
- Object Oriented Programming (OOPs) Concept in Java
- Why Java is not a purely Object-Oriented Language?
- Classes and Objects in Java
- Naming Conventions in Java
- Java Methods
- Access Modifiers in Java
- Java Constructors
- Four Main Object Oriented Programming Concepts of Java
- Inheritance in Java
- Abstraction in Java
- Encapsulation in Java
- Polymorphism in Java
- Interfaces in Java
- ‘this’ reference in Java
How to use java codes
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8. Examples and practices described in this page don’t take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available.
See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated language features in Java SE 9 and subsequent releases.
See JDK Release Notes for information about new features, enhancements, and removed or deprecated options for all JDK releases.
The Java Tutorials are practical guides for programmers who want to use the Java programming language to create applications. They include hundreds of complete, working examples, and dozens of lessons. Groups of related lessons are organized into «trails».
Trails Covering the Basics
- Getting Started — An introduction to Java technology and lessons on installing Java development software and using it to create a simple program.
- Learning the Java Language — Lessons describing the essential concepts and features of the Java Programming Language.
- Essential Java Classes — Lessons on exceptions, basic input/output, concurrency, regular expressions, and the platform environment.
- Collections — Lessons on using and extending the Java Collections Framework.
- Date-Time APIs — How to use the java.time pages to write date and time code.
- Deployment — How to package applications and applets using JAR files, and deploy them using Java Web Start and Java Plug-in.
- Preparation for Java Programming Language Certification — List of available training and tutorial resources.
Creating Graphical User Interfaces
- Creating a GUI with Swing — A comprehensive introduction to GUI creation on the Java platform.
- Creating a JavaFX GUI — A collection of JavaFX tutorials.
Specialized Trails and Lessons
These trails and lessons are only available as web pages.
- Custom Networking — An introduction to the Java platform’s powerful networking features.
- The Extension Mechanism — How to make custom APIs available to all applications running on the Java platform.
- Full-Screen Exclusive Mode API — How to write applications that more fully utilize the user’s graphics hardware.
- Generics — An enhancement to the type system that supports operations on objects of various types while providing compile-time type safety. Note that this lesson is for advanced users. The Java Language trail contains a Generics lesson that is suitable for beginners.
- Internationalization — An introduction to designing software so that it can be easily adapted (localized) to various languages and regions.
- JavaBeans — The Java platform’s component technology.
- JAXB — Introduces the Java architecture for XML Binding (JAXB) technology.
- JAXP — Introduces the Java API for XML Processing (JAXP) technology.
- JDBC Database Access — Introduces an API for connectivity between the Java applications and a wide range of databases and data sources.
- JMX— Java Management Extensions provides a standard way of managing resources such as applications, devices, and services.
- JNDI— Java Naming and Directory Interface enables accessing the Naming and Directory Service such as DNS and LDAP.
- Reflection — An API that represents («reflects») the classes, interfaces, and objects in the current Java Virtual Machine.
- RMI — The Remote Method Invocation API allows an object to invoke methods of an object running on another Java Virtual Machine.
- Security — Java platform features that help protect applications from malicious software.
- Sockets Direct Protocol — How to enable the Sockets Direct Protocol to take advantage of InfiniBand.
- Sound — An API for playing sound data from applications.
- 2D Graphics — How to display and print 2D graphics in applications.
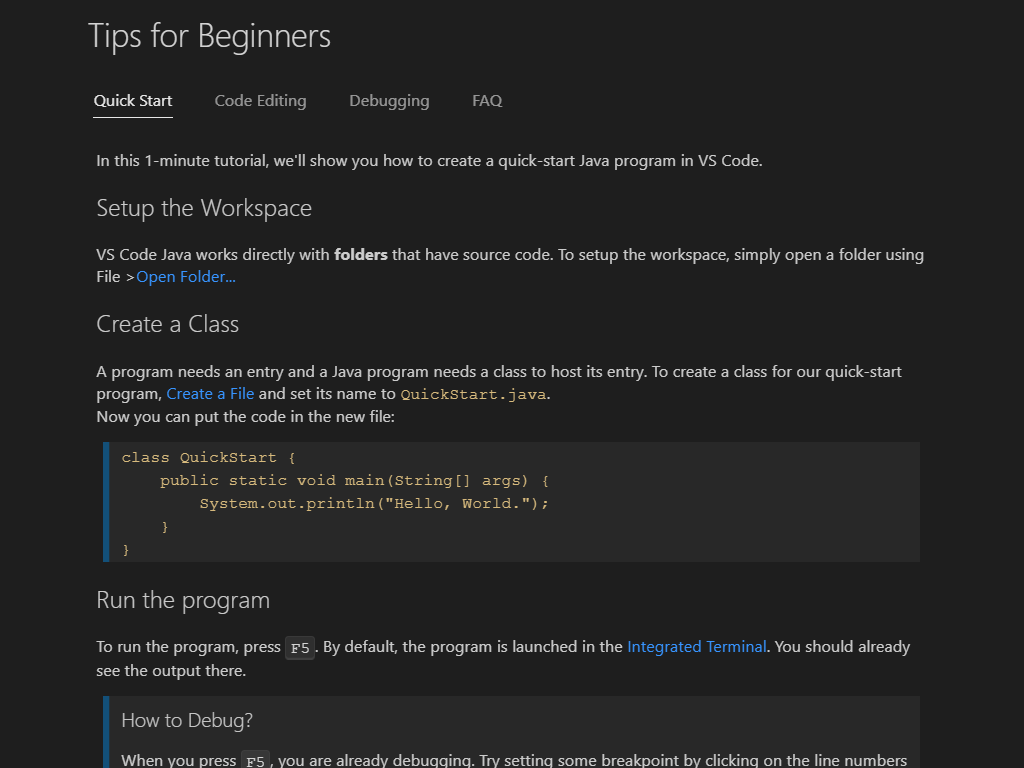
Getting Started with Java in VS Code
This tutorial shows you how to write and run Hello World program in Java with Visual Studio Code. It also covers a few advanced features, which you can explore by reading other documents in this section.
For an overview of the features available for Java in VS Code, see Java Language Overview.
If you run into any issues when following this tutorial, you can contact us by entering an issue.
Setting up VS Code for Java development
Coding Pack for Java
To help you set up quickly, you can install the Coding Pack for Java, which includes VS Code, the Java Development Kit (JDK), and essential Java extensions. The Coding Pack can be used as a clean installation, or to update or repair an existing development environment.
Note: The Coding Pack for Java is only available for Windows and macOS. For other operating systems, you will need to manually install a JDK, VS Code, and Java extensions.
Installing extensions
If you are an existing VS Code user, you can also add Java support by installing the Extension Pack for Java, which includes these extensions:
The Extension Pack for Java provides a Quick Start guide and tips for code editing and debugging. It also has a FAQ that answers some frequently asked questions. Use the command Java: Tips for Beginners from the Command Palette ( ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P ) ) to launch the guide.
You can also install extensions separately. The Extensions Guide is provided to help you. You can launch the guide with the Java: Extensions Guide command.
For this tutorial, the only required extensions are:
Installing and setting up a Java Development Kit (JDK)
To use Java within Visual Studio Code, you need to install a Java Development Kit (JDK) on your local environment. JDK is a software development environment used for developing Java applications.
Supported Java versions
The Extension Pack for Java supports Java version 1.5 or above.
Note: To configure JDKs for your projects, see Configure Runtime for Projects. To enable Java preview features, see How can I use VS Code with new Java versions.
Installing a Java Development Kit (JDK)
If you have never installed a JDK before and need to install one, we recommend you to choose from one of these sources:
Creating a source code file
Create a folder for your Java program and open the folder with VS Code. Then in VS Code, create a new file and save it with the name Hello.java . When you open that file, the Java Language Server automatically starts loading, and you should see a language status item with a loading icon on the right side of the Status Bar showing the language status is busy. After it finishes loading, you can hover on the language status item and find the loading process has been finished successfully. You can also choose to pin the status item in the status bar.
Note: If you open a Java file in VS Code without opening its folder, the Java Language Server might not work properly.
VS Code will also try to figure out the correct package for the new type and fill the new file from a template. See Create new file.
You can also create a Java project using the Java: Create Java Project command. Bring up the Command Palette ( ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P ) ) and then type java to search for this command. After selecting the command, you will be prompted for the location and name of the project. You can also choose your build tool from this command.
Visual Studio Code also supports more complex Java projects — see Project Management.
Editing source code
You can use code snippets to scaffold your classes and methods. VS Code also provides IntelliSense for code completion, and various refactor methods.
To learn more about editing Java, see Java Editing.
Running and debugging your program
To run and debug Java code, set a breakpoint, then either press F5 on your keyboard or use the Run > Start Debugging menu item. You can also use the Run|Debug CodeLens option in the editor. After the code compiles, you can see all your variables and threads in the Run and Debug view.
The debugger also supports advanced features such as Hot Code Replace and conditional breakpoints.
More features
The editor also has many more capabilities to assist with your Java workload.
- Editing Java explains how to navigate and edit Java in more details
- Debugging illustrates all the key features of the Java Debugger
- Testing provides comprehensive support for JUnit and TestNG framework
- Java Project Management shows you how to use a project view and work with Maven
- Spring Boot and Tomcat and Jetty demonstrate great framework support
- Java Web Apps shows how to work with Java Web App in VS Code