- Difference between Factory and Abstract Factory Design Pattern in Java? Example
- Difference between Abstract Factory and Factory design pattern in Java
- When to use Abstract Factory and Factory method design pattern in Java
- 5 comments :
- Abstract Factory Design Pattern in Java
- Abstract Factory
- Abstract Factory Design Pattern Super Class and Subclasses
- Factory Class for Each subclass
- Abstract Factory Design Pattern Benefits
- Abstract Factory Design Pattern Examples in JDK
- Abstract Factory Design Pattern Video Tutorial
Difference between Factory and Abstract Factory Design Pattern in Java? Example
Both the Abstract Factory and Factory design pattern are creational design pattern and use to decouple clients from creating objects they need, But there is a significant difference between Factory and Abstract Factory design patterns, Factory design pattern produces implementation of Products like Garment Factory produce different kinds of clothes, On the other hand, Abstract Factory design pattern adds another layer of abstraction over Factory Pattern and Abstract Factory implementation itself like the AbstractFactory will allow you to choose a particular Factory implementation based upon need which will then produce different kinds of products.
2) Factory design pattern creates Products
Btw, If you are serious about learning design patterns and principles, I suggest you take a look at these Design Pattern Courses. This list contains best design pattern courses that cover both SOLID design principles like Open Closed and Liskov substitution, and all-important Object Oriented design patterns like Decorator, Observer, Chain of Responsibility, and much more .
Difference between Abstract Factory and Factory design pattern in Java
Let see another example of Abstract Factory and Factory design pattern in Java from JDK itself to get a better understanding. If you have done some XML work in Java e.g. reading XML files using DOM parser, you may be familiar with DocumentBuilderFactory class which is an example abstract factory design pattern because it returns a factory called DocumentBuilder which then used to create Document .
//Example of Abstract Factory and Factory design pattern in Java
DocumentBuilderFactory abstractFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory. newInstance () ;
DocumentBuilder factory = abstractFactory. newDocumentBuilder () ;
Document doc = factory. parse ( stocks )
In this example DocumentBuilderFactory (Abstract Factory) creates DocumentBuilder (Factory) which creates Documents (Products).
Let’s see some more difference between Abstract Factory and Factory design pattern in Java in point form :
1) One more difference between Abstract Factory and Factory design pattern is that AbstractFactory pattern uses composition to delegate responsibility of creating object to another class while Factory design pattern uses inheritance and relies on derived class or sub class to create object.
2) Abstract Factory may use Factory design pattern for creating objects but they are not just limited to that they can also use Builder design pattern to build object by doing series of steps or Prototype pattern to build object by copying or customizing the prototype of that object. It completely depends upon your implementation whether to use Factory pattern or Builder pattern for creating products.
When to use Abstract Factory and Factory method design pattern in Java
Factory method design patterns are a modern way of creating objects. It offers some notable advantages over new() operator to create Objects e.g. By using the Factory method design pattern client is completely decoupled with object creation code, which enforces Encapsulation, and the result is a loosely coupled and highly cohesive system.
Any change like a new product from Factory requires almost no change in existing clients. See When to use Factory method design pattern in Java for more scenarios.
On the other hand if you need an additional level of abstraction over your Factory pattern then Abstract Factory is the right design pattern to use. Abstract Factory allows you to use different Factory implementation for different purposes.
Abstract Factory pattern can be implemented using Factory method and Singleton design pattern in Java. One of the best examples of Abstract Factory and Factory patterns in Java is DocumentBuilderFactory and DocumentBuilder javax.xml.parsers package.
That’s all on the difference between Abstract Factory and Factory design pattern in Java. In short Abstract Factory, design pattern provides an abstraction over Factory pattern itself while Factory design pattern provides an abstraction over products.
5 comments :
Can you please explain more with some example on the following difference you mentioned:
«One more difference between Abstract Factory and Factory design pattern is that AbstractFactory pattern uses composition to delegate responsibility of creating object to another class while Factory design pattern uses inheritance and relies on derived class or sub class to create object.»
nice explanation.. SessionFactory is AbstractDesign pattern, and session is Factory design pattern, am i right.
I think that the approach is wrong. From what I understand, AbstractFactory is not a class that creates factories. Instead, it is a different class that creates families of related products.
With factory method, our class itself or its sublasses create the instance of the product.
With abstract factory, our class delegates the creation to another class or to subclasses of that class. This other class (or its subclasses) is the one that creates the object we need. It may also create some other related products as well (a family of products). Each product is created with its own kind of factory method.
@Anonymous, AbstractFactory as name state itself is to abstract Factory class, which is responsible for creating products e.g. A factory for creating Canadian Pizza could be different than factory for creating American or Italian Pizza. You can abstract this detail by using AbstractFactory pattern and depending upon whether your application is running it can pick corresponding implementation of abstract factory.
Abstract Factory is like a CarFactory, the class implementing the CarFactory decides whether it’s IndianCar, GermanCar or AmericanCar.
Abstract Factory Design Pattern in Java
While we believe that this content benefits our community, we have not yet thoroughly reviewed it. If you have any suggestions for improvements, please let us know by clicking the “report an issue“ button at the bottom of the tutorial.
Welcome to Abstract Factory Design Pattern in java example. Abstract Factory design pattern is one of the Creational patterns. Abstract Factory pattern is almost similar to Factory Pattern except the fact that its more like factory of factories.
Abstract Factory
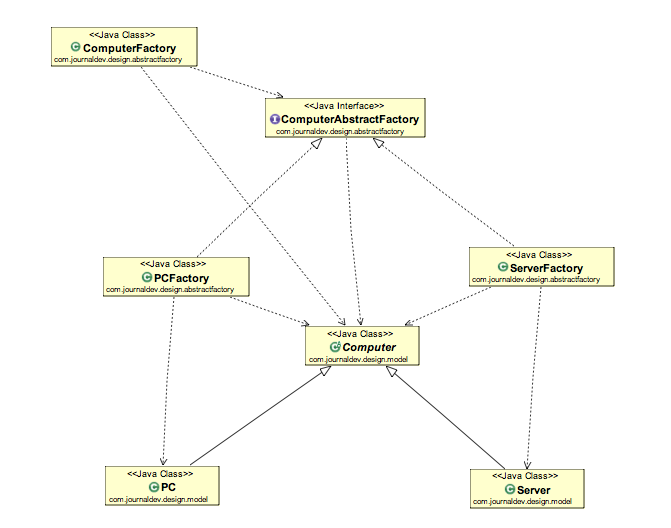
If you are familiar with factory design pattern in java, you will notice that we have a single Factory class. This factory class returns different subclasses based on the input provided and factory class uses if-else or switch statement to achieve this. In the Abstract Factory pattern, we get rid of if-else block and have a factory class for each sub-class. Then an Abstract Factory class that will return the sub-class based on the input factory class. At first, it seems confusing but once you see the implementation, it’s really easy to grasp and understand the minor difference between Factory and Abstract Factory pattern. Like our factory pattern post, we will use the same superclass and sub-classes.
Abstract Factory Design Pattern Super Class and Subclasses
package com.journaldev.design.model; public abstract class Computer < public abstract String getRAM(); public abstract String getHDD(); public abstract String getCPU(); @Override public String toString()< return "RAM= "+this.getRAM()+", HDD="+this.getHDD()+", CPU="+this.getCPU(); >> package com.journaldev.design.model; public class PC extends Computer < private String ram; private String hdd; private String cpu; public PC(String ram, String hdd, String cpu)< this.ram=ram; this.hdd=hdd; this.cpu=cpu; >@Override public String getRAM() < return this.ram; >@Override public String getHDD() < return this.hdd; >@Override public String getCPU() < return this.cpu; >> package com.journaldev.design.model; public class Server extends Computer < private String ram; private String hdd; private String cpu; public Server(String ram, String hdd, String cpu)< this.ram=ram; this.hdd=hdd; this.cpu=cpu; >@Override public String getRAM() < return this.ram; >@Override public String getHDD() < return this.hdd; >@Override public String getCPU() < return this.cpu; >> Factory Class for Each subclass
First of all we need to create a Abstract Factory interface or abstract class. ComputerAbstractFactory.java
package com.journaldev.design.abstractfactory; import com.journaldev.design.model.Computer; public interface ComputerAbstractFactory
Notice that createComputer() method is returning an instance of super class Computer . Now our factory classes will implement this interface and return their respective sub-class. PCFactory.java
package com.journaldev.design.abstractfactory; import com.journaldev.design.model.Computer; import com.journaldev.design.model.PC; public class PCFactory implements ComputerAbstractFactory < private String ram; private String hdd; private String cpu; public PCFactory(String ram, String hdd, String cpu)< this.ram=ram; this.hdd=hdd; this.cpu=cpu; >@Override public Computer createComputer() < return new PC(ram,hdd,cpu); >> package com.journaldev.design.abstractfactory; import com.journaldev.design.model.Computer; import com.journaldev.design.model.Server; public class ServerFactory implements ComputerAbstractFactory < private String ram; private String hdd; private String cpu; public ServerFactory(String ram, String hdd, String cpu)< this.ram=ram; this.hdd=hdd; this.cpu=cpu; >@Override public Computer createComputer() < return new Server(ram,hdd,cpu); >> Now we will create a consumer class that will provide the entry point for the client classes to create sub-classes. ComputerFactory.java
package com.journaldev.design.abstractfactory; import com.journaldev.design.model.Computer; public class ComputerFactory < public static Computer getComputer(ComputerAbstractFactory factory)< return factory.createComputer(); >> Notice that its a simple class and getComputer method is accepting ComputerAbstractFactory argument and returning Computer object. At this point the implementation must be getting clear. Let’s write a simple test method and see how to use the abstract factory to get the instance of sub-classes. TestDesignPatterns.java
package com.journaldev.design.test; import com.journaldev.design.abstractfactory.PCFactory; import com.journaldev.design.abstractfactory.ServerFactory; import com.journaldev.design.factory.ComputerFactory; import com.journaldev.design.model.Computer; public class TestDesignPatterns < public static void main(String[] args) < testAbstractFactory(); >private static void testAbstractFactory() < Computer pc = com.journaldev.design.abstractfactory.ComputerFactory.getComputer(new PCFactory("2 GB","500 GB","2.4 GHz")); Computer server = com.journaldev.design.abstractfactory.ComputerFactory.getComputer(new ServerFactory("16 GB","1 TB","2.9 GHz")); System.out.println("AbstractFactory PC Config::"+pc); System.out.println("AbstractFactory Server Config::"+server); >> AbstractFactory PC Config::RAM= 2 GB, HDD=500 GB, CPU=2.4 GHz AbstractFactory Server Config::RAM= 16 GB, HDD=1 TB, CPU=2.9 GHz Here is the class diagram of abstract factory design pattern implementation.
Abstract Factory Design Pattern Benefits
- Abstract Factory design pattern provides approach to code for interface rather than implementation.
- Abstract Factory pattern is “factory of factories” and can be easily extended to accommodate more products, for example we can add another sub-class Laptop and a factory LaptopFactory.
- Abstract Factory pattern is robust and avoid conditional logic of Factory pattern.
Abstract Factory Design Pattern Examples in JDK
- javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory#newInstance()
- javax.xml.transform.TransformerFactory#newInstance()
- javax.xml.xpath.XPathFactory#newInstance()
Abstract Factory Design Pattern Video Tutorial
I recently uploaded a video on YouTube for abstract factory design pattern. In the video, I discuss when and how to implement an abstract factory pattern. I have also discussed what is the difference between the factory pattern and abstract factory design pattern. https://youtu.be/BPkYkyVWOaw
You can download the examples code from my GitHub Project.
Thanks for learning with the DigitalOcean Community. Check out our offerings for compute, storage, networking, and managed databases.