- ZeroDivisionError: float division | Python
- ZeroDivisionError
- Handling ZeroDivisionError in Python
- Reproducing the error
- Wrap it in try except
- Check before you do the division
- Different Variation
- Error division by zero python
- # Table of Contents
- # ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero in Python
- # Checking if the value we are dividing by is not 0
- # Using a try/except statement to handle the error
- # Figure out where the variable got set to 0
- # Handling a number from user input with a try/except statement
- # Table of Contents
- # ZeroDivisionError: integer modulo by zero in Python
- # Figuring out where the variable got assigned a zero value
- # Check if the value is not 0 before using modulo
- # Using a try/except statement to handle the error
- # ZeroDivisionError: division by zero in Python
- # Checking if the value you are dividing by is not zero
- # Using a try/except statement to handle the error
- # Additional Resources
- How to Fix ZeroDivisionError in Python
- What Causes ZeroDivisionError
- Python ZeroDivisionError Example
- How to Fix ZeroDivisionError in Python
- Track, Analyze and Manage Errors With Rollbar
ZeroDivisionError: float division | Python
In mathematics, any non-zero number either positive or negative divided by zero is undefined because there is no value. The reason is that the result of a division by zero is undefined is the fact that any attempt at a definition leads to a contradiction.
ZeroDivisionError
The super class of ZeroDivisionError is ArithmeticError. ZeroDivisionError is a built-in Python exception thrown when a number is divided by 0. This means that the exception raised when the second argument of a division or modulo operation is zero. In Mathematics, when a number is divided by a zero, the result is an infinite number. It is impossible to write an Infinite number physically. Python interpreter throws «ZeroDivisionError» error if the result is infinite number. While implementing any program logic and there is division operation make sure always handle ArithmeticError or ZeroDivisionError so that program will not terminate.
Handling ZeroDivisionError in Python
Wrap it in try-except
The above code can be reduced to:
Reproducing the error
You can solve the ZeroDivisionError by the following ways:
Wrap it in try except
Check before you do the division
The above code can be reduced to:
Different Variation
In Python, the Zero Division Error:division by zero is thrown in various forms in different contexts. They are given below:
- ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
- ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero
- ZeroDivisionError: integer division or modulo by zero
- ZeroDivisionError: long division or modulo by zero
- ZeroDivisionError: complex division by zero
- SyntaxError- EOL while scanning string literal
- TypeError: Can’t convert ‘int’ object to str implicitly
- IndentationError: expected an indented block
- ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10
- IndexError: list index out of range : Python
- AttributeError: ‘module’ object has no attribute ‘main’
- UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment
- TypeError: string indices must be integers
- FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory
- Fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory
- ImportError: No module named requests | Python
- TypeError: ‘NoneType’ object is not iterable
- SyntaxError: unexpected EOF while parsing | Python
- zsh: command not found: python
- Unicodeescape codec can’t decode bytes in position 2-3
Error division by zero python
Last updated: Feb 16, 2023
Reading time · 6 min
# Table of Contents
# ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero in Python
The Python «ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero» occurs when we try to divide a floating-point number by 0 .
To solve the error, use an if statement to check if the number you are dividing by is not zero, or handle the error in a try/except block.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
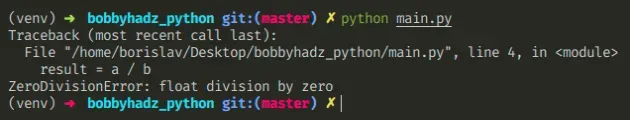
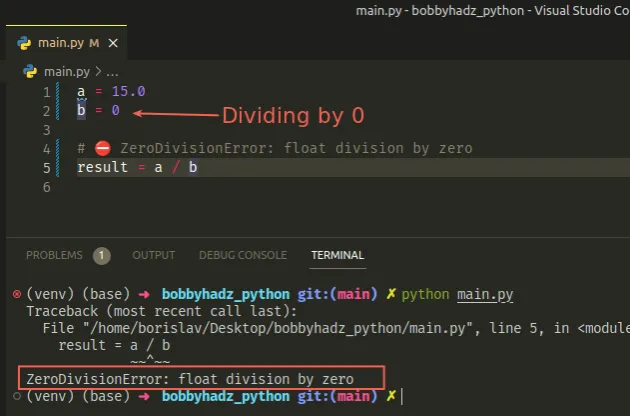
Copied!a = 15.0 b = 0 # ⛔️ ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero result = a / b
It’s unclear what value is expected when we divide by 0 , so Python throws an error.
When we divide a number by 0 , the result tends towards infinity.
# Checking if the value we are dividing by is not 0
One way to solve the error is to check if the value we are dividing by is not 0 .
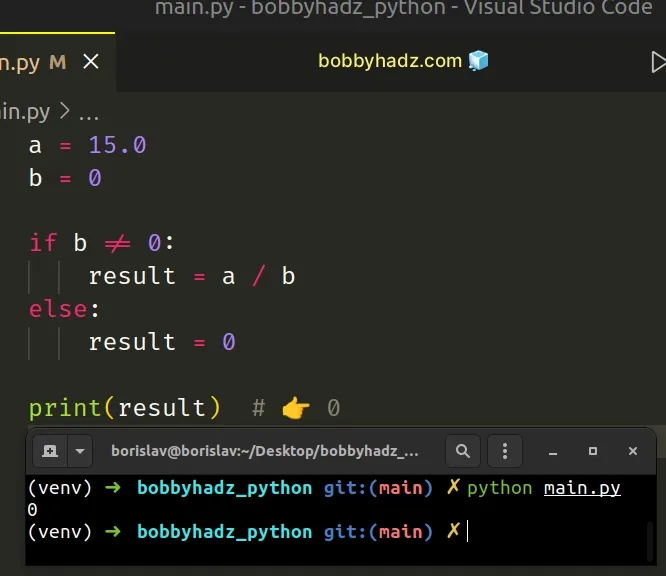
Copied!a = 15.0 b = 0 if b != 0: result = a / b else: result = 0 print(result) # 👉️ 0
We check if the b variable doesn’t store a 0 value and if it doesn’t, we divide a by b .
Otherwise, we set the result variable to 0 . Note that this could be any other value that suits your use case.
If setting the result variable to 0 if b is equal to 0 suits your use case, you can shorten this to a single line.
Copied!a = 15.0 b = 0 result = b and a / b print(result) # 👉️ 0
The expression x and y first evaluates x , and if x is falsy, its value is returned, otherwise, y is returned.
Since 0 is a falsy value, it gets returned if the b variable in the example stores a 0 value, otherwise, the result of dividing a by b is returned.
# Using a try/except statement to handle the error
Alternatively, you can use a try/except statement.
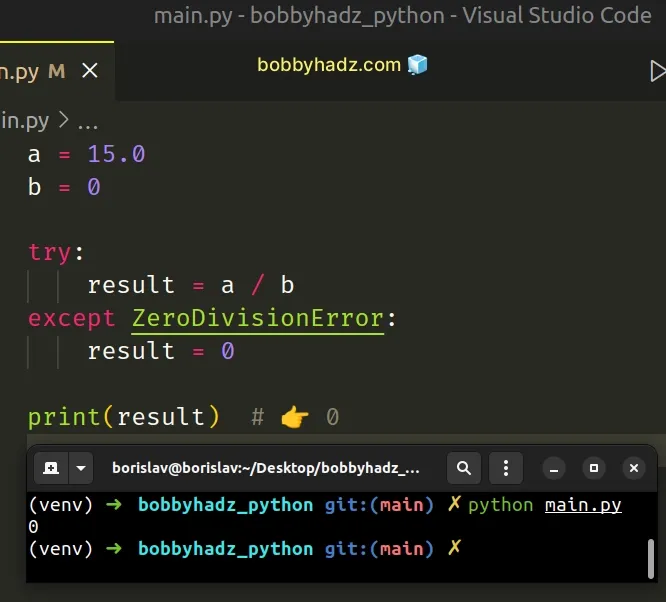
Copied!a = 15.0 b = 0 try: result = a / b except ZeroDivisionError: result = 0 print(result) # 👉️ 0
We try to divide a by b and if we get a ZeroDivisionError , the except block sets the result variable to 0 .
# Figure out where the variable got set to 0
The best way to solve the error is to figure out where the variable gets assigned a 0 and check whether that’s the expected behavior.
Here are some common ways you might get a zero value unexpectedly.
Copied!print(int()) # 👉️ 0 print(int(0.9)) # 👉️ 0
You might also get a zero value if you multiply any number by 0 .
Copied!num_1 = 5 num_2 = num_1 * 0 print(num_2) # 👉️ 0
Make sure you haven’t assigned the result of multiplying a number by 0 to a variable.
# Handling a number from user input with a try/except statement
If you need to take a number from user input, use a try/except statement to handle the potential ZeroDivisionError .
Copied!num_1 = 15.0 try: num_2 = int(input('Enter a number: ')) result = num_1 / num_2 print(f'The result of the division is: result>') except (ZeroDivisionError, ValueError): print('Specify a positive integer value')
If the user passes an invalid integer, a ValueError is raised and is then handled by the except block.
Similarly, if the user enters 0 , a ZeroDivisionError is raised and is handled by the except block.
Otherwise, the result of the division gets printed in the try block.
# Table of Contents
# ZeroDivisionError: integer modulo by zero in Python
The Python «ZeroDivisionError: integer division or modulo by zero» occurs when we use the modulo % operator with an integer and a zero.
To solve the error, figure out where the 0 comes from and correct the assignment.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
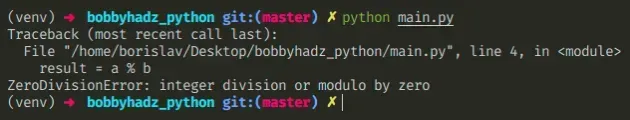
Copied!a = 6 b = 0 # ⛔️ ZeroDivisionError: integer division or modulo by zero # ZeroDivisionError: integer modulo by zero result = a % b
We tried using the modulo % operator with a zero.
It’s unclear what value is expected when we divide by 0 , so Python throws an error.
When we divide a number by 0 , the result tends towards infinity.
# Figuring out where the variable got assigned a zero value
The best way to solve the error is to figure out where the 0 value comes from and correct the assignment.
Here are some unexpected sources of 0 .
Copied!import random print(int()) # 👉️ 0 print(int(0.9)) # 👉️ 0 print(random.randint(0, 10)) # 👉️ 0 print(list(range(0, 5))) # 👉️ [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
If you use the random.randint() method or the range() class, make sure to start from 1 , and not from 0 .
Copied!import random print(random.randint(1, 10)) # 👉️ 4 # 👇️ [1, 2, 3, 4] print(list(range(1, 5)))
# Check if the value is not 0 before using modulo
You can also conditionally check if the variable doesn’t store a 0 value before using the modulo operator.
Copied!a = 6 b = 0 if b != 0: result = a % b else: # 👇️ this runs print('b is equal to 0')
The if statement checks if the b variable doesn’t store a 0 value before using the modulo % operator.
# Using a try/except statement to handle the error
Alternatively, you can use a try/except statement.
Copied!a = 6 b = 0 try: result = a % b print(result) except ZeroDivisionError: pass
We use the modulo operator and if we get a ZeroDivisionError , the except block is run.
You can set the result variable to a value that suits your use case in the except block or simply pass.
The modulo (%) operator returns the remainder from the division of the first value by the second.
Copied!print(10 % 2) # 👉️ 0 print(10 % 4) # 👉️ 2
If the value on the right-hand side is zero, the operator raises a ZeroDivisionError exception.
The left and right-hand side values may also be floating point numbers.
If the left-hand side value is a float and the right-hand side value is 0 , you would get a «ZeroDivisionError: float modulo» error.
Copied!# ⛔️ ZeroDivisionError: float modulo print(10.5 % 0) # 👉️ 0
# ZeroDivisionError: division by zero in Python
The Python «ZeroDivisionError: division by zero» occurs when we try to divide a number by 0 .
To solve the error, use an if statement to check if the number you are dividing by is not zero, or handle the error in a try/except block.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
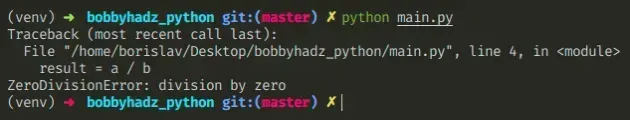
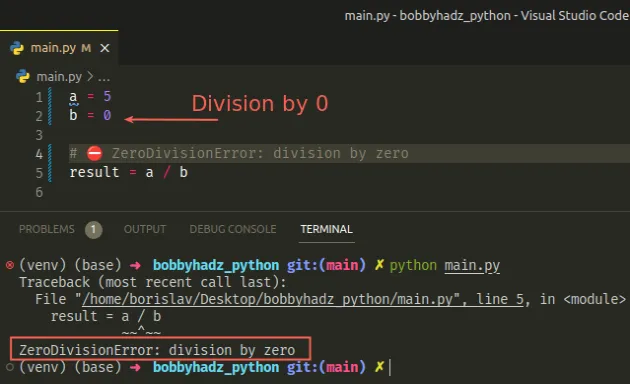
Copied!a = 5 b = 0 # ⛔️ ZeroDivisionError: division by zero result = a / b
It’s unclear what value is expected when we divide by 0 , so Python throws an error.
When we divide a number by 0 , the result tends towards infinity.
# Checking if the value you are dividing by is not zero
One way to solve the error is to check if the value we are dividing by is not 0 .
Copied!a = 5 b = 0 if b != 0: result = a / b else: result = 0 print(result) # 👉️ 0
We check if the b variable doesn’t store a 0 value and if it doesn’t, we divide a by b .
Otherwise, we set the result variable to 0 . Note that this could be any other value that suits your use case.
If setting the result variable to 0 , if b is equal to 0 suits your use case, you can shorten this to a single line.
Copied!a = 5 b = 0 result = b and a / b print(result) # 👉️ 0
The expression x and y first evaluates x , and if x is falsy, its value is returned, otherwise, y is returned.
Since 0 is a falsy value, it gets returned if the b variable in the example stores a 0 value, otherwise the result of dividing a by b is returned.
# Using a try/except statement to handle the error
Alternatively, you can use a try/except statement.
Copied!a = 5 b = 0 try: result = a / b except ZeroDivisionError: result = 0 print(result) # 👉️ 0
The try/except block is known as «asking for forgiveness, rather than permission».
We try to divide a by b and if we get a ZeroDivisionError , the except block sets the result variable to 0 .
The best way to solve the error is to figure out where the variable gets assigned a 0 and check whether that’s the expected behavior.
Here are some common ways you might get a zero value unexpectedly.
Copied!print(int()) # 👉️ 0 print(int(0.9)) # 👉️ 0
You might also get a zero value by multiplying a number by 0 .
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
I wrote a book in which I share everything I know about how to become a better, more efficient programmer.
How to Fix ZeroDivisionError in Python
In Python, a ZeroDivisionError is raised when a division or modulo operation is attempted with a denominator or divisor of 0.
What Causes ZeroDivisionError
A ZeroDivisionError occurs in Python when a number is attempted to be divided by zero. Since division by zero is not allowed in mathematics, attempting this in Python code raises a ZeroDivisionError .
Python ZeroDivisionError Example
Here’s an example of a Python ZeroDivisionError thrown due to division by zero:
In this example, a number a is attempted to be divided by another number b , whose value is zero, leading to a ZeroDivisionError :
File "test.py", line 3, in print(a/b) ZeroDivisionError: division by zero How to Fix ZeroDivisionError in Python
The ZeroDivisionError can be avoided using a conditional statement to check for a denominator or divisor of 0 before performing the operation.
The code in the earlier example can be updated to use an if statement to check if the denominator is 0:
a = 10 b = 0 if b == 0: print("Cannot divide by zero") else: print(a/b) Running the above code produces the correct output as expected:
A try-except block can also be used to catch and handle this error if the value of the denominator is not known beforehand:
try: a = 10 b = 0 print(a/b) except ZeroDivisionError as e: print("Error: Cannot divide by zero") Surrounding the code in try-except blocks like the above allows the program to continue execution after the exception is encountered:
Error: Cannot divide by zero Track, Analyze and Manage Errors With Rollbar
Managing errors and exceptions in your code is challenging. It can make deploying production code an unnerving experience. Being able to track, analyze, and manage errors in real-time can help you to proceed with more confidence. Rollbar automates error monitoring and triaging, making fixing Python errors easier than ever. Try it today!