- How to Make a Fill the Height of the Remaining Space
- Create HTML
- Create CSS
- Example of making a fill the remaining space with Flexbox:
- Here’s the result, same as before:
- Example of making a fill the remaining space with the position property:
- Example of making a fill the remaining space with the display set to «table»:
- Example of making a fill the remaining space with the calc() function:
- Body height: 100% not taking the entire html height [duplicate]
- Answer by Thaddeus Roberson
- The Modern Solution is Simplified
- Answer by Annika Ball
- Answer by Lucy Hayden
- Answer by Ansley Fischer
- Answer by Miller Stephenson
- Answer by Kimberly Lawrence
- Answer by Rocco Walter
- Answer by Alaric Rhodes
How to Make a Fill the Height of the Remaining Space
If you need the content to fill the height of the full screen, you’re in the right place.
In this snippet, we’ll demonstrate four methods of making a fill the height of the remaining space. So, let’s start!
1. The most usual solution to this problem is to use Flexbox. Let’s see how to use it. For this method, we’ll need the CSS flex property as a shorthand for the flex-grow, flex-shrink, and flex-basis properties.
Create HTML
- Use a and add three other ellements iinside.
- Add class attributes to the elements.
- Add elements inside the tag.
div class="box"> div class="row header"> p>header (sized to content) p> div> div class="row content"> p>content (fills remaining space) p> div> div class="row footer"> p>footer (fixed height) p> div> div>Create CSS
- Set the height and margin for the and elements.
- Set the display to “flex”, and add the flex-flow and height properties for the “box” class.
- Set the border for the “box.row”.
- Set the flex property for the “row header”, “row content”, and “row footer” classes, separately.
html, body < height: 100%; margin: 0; > .box < display: flex; flex-flow: column; height: 100%; > .box .row < border: 1px dotted #0313fc; > .box .row.header < flex: 0 1 auto; > .box .row.content < flex: 1 1 auto; > .box .row.footer < flex: 0 1 40px; >Example of making a fill the remaining space with Flexbox:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> style> html, body < height: 100%; margin: 0; > .box < display: flex; flex-flow: column; height: 100%; > .box .row < border: 1px dotted #0313fc; > .box .row.header < flex: 0 1 auto; > .box .row.content < flex: 1 1 auto; > .box .row.footer < flex: 0 1 40px; > style> head> body> div class="box"> div class="row header"> p>header (sized to content) p> div> div class="row content"> p>content (fills remaining space) p> div> div class="row footer"> p>footer (fixed height) p> div> div> body> html>Using flexbox, you can switch between rows and columns having either fixed dimensions, content-sized dimensions, or remaining space dimensions. In the example above, we demonstrated how to add an area with fixed height and set the content area for filling the remaining space.
Let’s extend our example and add a container div after the box div.
div class="box"> div class="box-container"> /* add this line */ div class="row header"> p>header (sized to content) p> div> div class="row content"> p>content (fills remaining space) p> div> div class="row footer"> p>footer (fixed height) p> div> div> /* end of box-container div */ div>As we see, our layout’s broken!
The solution’s pretty simple. We should change the default behaviour of div tags, which is setting the display to be a block-level element. We will use the display: contents , so the contents will determine the size of the element.
.box-container < display: contents; >Here’s the result, same as before:
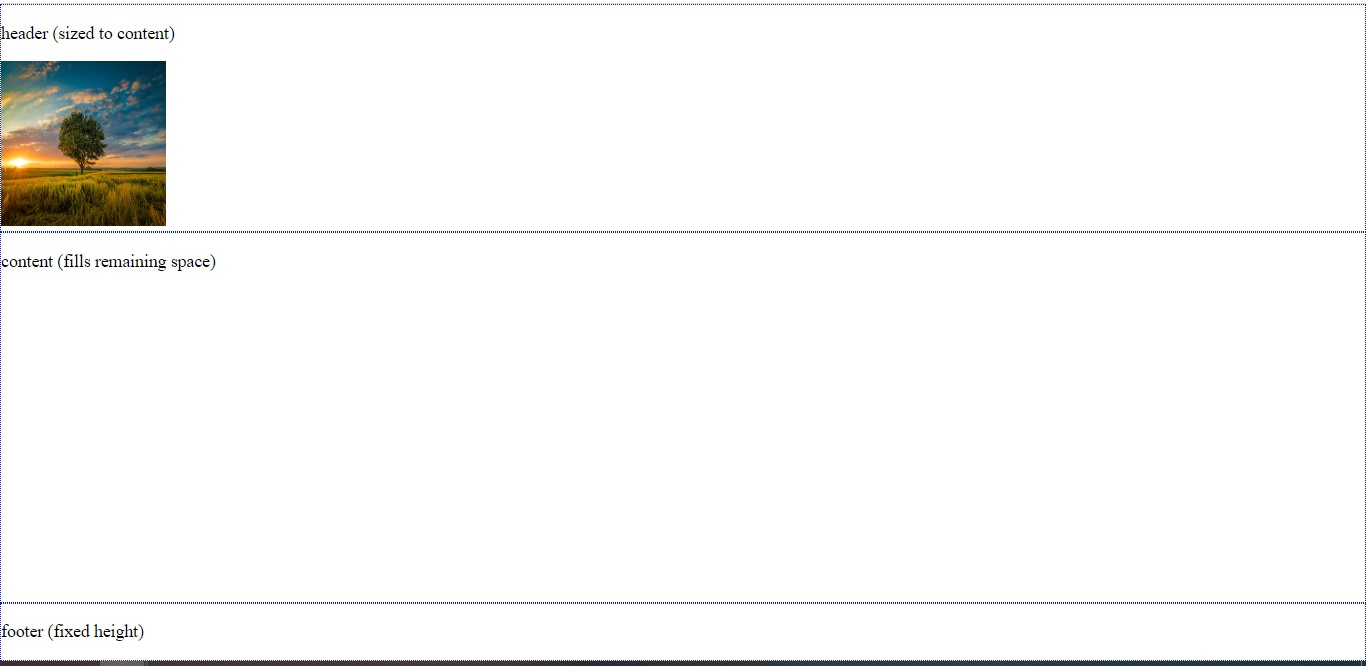
Let’s take a step further by adding an image in our box-container and seeing what happens.
head> title>Title of the document title> style> html, body < height: 100%; margin: 0; > .box < display: flex; flex-flow: column; height: 100%; > .box .row < border: 1px dotted #0313fc; > .box .row.header < flex: 0 1 auto; > .box .row.content < flex: 1 1 auto; > .box .row.footer < flex: 0 1 40px; > .box-container < display: contents; > style> head> body> div class="box"> div class="box-container"> div class="row header"> p>header (sized to content) p> img src="https://img.freepik.com/free-photo/wide-angle-shot-single-tree-growing-clouded-sky-during-sunset-surrounded-by-grass_181624-22807.jpg" height="150px" width="150px" /> div> div class="row content"> p>content (fills remaining space) p> div> div class="row footer"> p>footer (fixed height) p> div> div> div> body>It seems like it’s still working, great! So all we had to do was to place display: contents to our box-container div .
2. Another way of making a fill the remaining space is to use the CSS position property. Just set the position to “absolute” to stretch the .
Example of making a fill the remaining space with the position property:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> style> html, body < height: 100%; width: 100%; margin: 0; > #fixed-height < height: 100px; background-color: #57c975; > #remaining-height < background-color: #d9deda; position: absolute; top: 100px; bottom: 0; width: 100%; > style> head> body> div id="fixed-height"> Fixed height div> div id="remaining-height"> Remaining height div> body> html>3. The next method of making a fill the remaining space is using tables. By setting the display property to “table”, we can distribute the given space. When we set a fixed height for one element, the other will use the remaining space.
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> style> html, body < height: 100%; width: 100%; margin: 0; > #fixed-height < height: 100px; background-color: #57c975; > #remaining-height < background-color: #d9deda; position: absolute; top: 100px; bottom: 0; width: 100%; > style> head> body> div id="fixed-height"> Fixed height div> div id="remaining-height"> Remaining height div> body> html>Example of making a fill the remaining space with the display set to «table»:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> style> html, body, #outer < height: 100%; width: 100%; margin: 0; > #outer < display: table; > #fixed-height < height: 100px; background-color: #ebcaca; display: table-row; > #remaining-height < background-color: #ebe6e6; display: table-row; > style> head> body> div id="outer"> div id="fixed-height"> Fixed height div> div id="remaining-height"> Remaining height div> div> body> html>4. The last method is to use the CSS calc() function. In this way, we can assign a height calculated from the total height minus the height of the other element.
Example of making a fill the remaining space with the calc() function:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> style> html, body < height: 100%; width: 100%; margin: 0; > #fixed-height < height: 100px; background-color: #ebcaca; > #remaining-height < background-color: #ebe6e6; height: calc(100% - 100px); > style> head> body> div id="fixed-height"> Fixed height div> div id="remaining-height"> Remaining height div> body> html>Body height: 100% not taking the entire html height [duplicate]
Try setting the height of the html element to 100% as well. ,Body looks to its parent (HTML) for how to scale the dynamic property, so the HTML element needs to have its height set as well. ,As an alternative to setting both the html and body element’s heights to 100%, you could also use viewport-percentage lengths., 57 ok I found out! it works if I add html,body 😀 – bodyofheat Jul 11 ’11 at 19:32
Try setting the height of the html element to 100% as well.
However the content of body will probably need to change dynamically. Setting min-height to 100% will accomplish this goal.
Answer by Thaddeus Roberson
The image above is taken from a page with the following CSS: ,For a responsive full page height, set the body element min-height to 100vh.,Setting min-height to 100% on both elements does not allow the body element to fill the page like you might expect. If you check the computed style values in dev tools, the body element has a height of zero. ,However, with no width value provided for the HTML element, setting the width of the body element to 100% results in full page width.
It is not uncommon to see CSS properties applied to both the HTML and body elements like this:
The image above is taken from a page with the following CSS:
For years, the answer was the following:
The Modern Solution is Simplified
A CSS reset removes this. Otherwise, setting the width to 100% before removing the margins will cause the body element to overflow. Here’s the CSS reset I use:
Answer by Annika Ball
I have been struggling to understand this scenario,The html element ignores min-height: 100%.,So that when there is no content on the page, the html and body take 100% of the height of page. And if there is content in body, these should change their height according to content height. ,Thanks to @Alohci for correcting me on the interpretation of the spec.
Answer by Lucy Hayden
The browser will calculate and select a height for the specified element.,The min-height and max-height properties override height.,Defines the height as a percentage of the containing block’s height.,The height CSS property specifies the height of an element. By default, the property defines the height of the content area. If box-sizing is set to border-box, however, it instead determines the height of the border area.
/* values */ height: 120px; height: 10em; /* value */ height: 75%; /* Keyword values */ height: max-content; height: min-content; height: fit-content(20em); height: auto; /* Global values */ height: inherit; height: initial; height: revert; height: unset; Answer by Ansley Fischer
Browsers feature a default margin, padding and borders to HTML elements. And the worst part is it’s different for each browser!,Yeah unfortunately the vh unit is almost useless on iOS Safari. I believe the trick is to use height: 100% on html element and then pass that down to the body and any container with flex or grid.,By setting both and its child to 100% height, we achieve the full size.,This is a «blanket» solution that would cover all margin and padding variations for any browser you might have.
/* override browser default */ html, body < margin: 0; padding: 0; >/* use viewport-relative units to cover page fully */ body < height: 100vh; width: 100vw; >/* include border and padding in element width and height */ * < box-sizing: border-box; >/* full-sized container that fills up the page */ div < height: 100%; width: 100%; /* example padding, font-size, background, etc */ padding: 10px; font-size: 20px; background-color: lightskyblue; >Answer by Miller Stephenson
Tell me if it worked or not.,Try to set also the containers between the body and the map container to 100%. That’s what is in the answer.,If you check in inspect of the browser, you can see that there are a few containers between the body and the main container:,In addition to Container widget, i also add another CSS rule to MainContent:
SyntaxEditor Code Snippet
Answer by Kimberly Lawrence
Negative values like height: -100px are not accepted. The height property does not apply to non-replaced inline elements including table columns and column groups.,The height property in CSS defines specifies the content height of boxes and accepts any of the length values.,The “content” area is defined as the padding and border in addition to the height/width or size the content itself takes up.,And how is the height calculated if the height of the containing block is specified and the containing block is absolutely positioned?
Negative values like height: -100px are not accepted. The height property does not apply to non-replaced inline elements including table columns and column groups.
Answer by Rocco Walter
I’ve observed some strange behavior that started around iOS 12.2 and continues through iOS 13.x. If you load even a very simple web page into Safari that contains a div with a 100% height, then the result is correct and you get a full-screen div. If you rotate the device to landscape then it resizes and the div still fills the screen. But when you rotate it back to portrait, an empty white area appears at the bottom of the screen, and there doesn’t appear to be a way to make it go away.,I am also experiencing this issue in my applicaiton. The div that is shortened is in the middle of the screen, creating a white gap, im thinking it’s the 100%. Only an issue on iOS devices. ,I suspect this has to do with the change Apple made around the iOS 12.2 timeframe, where when a phone is rotated to portrait, the URL bar shrinks and the navigation bar is hidden. When this happens, the content area is in effect larger than it was before, but it’s like CSS doesn’t know about it, so a height of 100% represents the height as if the URL bar was larger and the nav bar was present.,Viewing that page on an iPhone with iOS 12.2+ will look fine, so rotate to landscape and then rotate back to portrait. A white area will appear at the bottom. I’m told that on larger-style iPhones, this only occurs if it is the only tab open — otherwise, iOS never hides the navigation bar. On my 6s, it happens every time.
Answer by Alaric Rhodes
You can also use utilities to set the width and height relative to the viewport.,You can also use max-width: 100%; and max-height: 100%; utilities as needed.,Relative to the viewport,Easily make an element as wide or as tall with our width and height utilities.
Width 25% Width 50% Width 75% Width 100% Width auto