- 11 Examples of HTML div With Style, Class, id, background etc
- A few examples of using div tag
- The div style
- Example of style in div for setting font size and color
- A div background color demo
- A div background image example
- A div border demo
- A div width and height example
- An example of div with padding and margin
- The div Class and ID attributes
- The Class attribute of div
- CSS style in class attribute of div
- HTML Div – What is a Div Tag and How to Style it with CSS
- When to Use the div Tag
- 1. Use div in Web Layouts
- 2. Use div in CSS Art
- How to Style the div Tag
- 1. How to Apply Font Properties with div
- 2. How to Apply Color with the Div Tag
- 3. How to Style Texts with the Div Tag
- 4. How to Create a Shadow Effect with the Div Tag
- How to Use Multiple Div Elements without Getting Confused
- Conclusion
- Базовые CSS-стили различных элементов
- Базовая конструкция
- Тени
- Градиенты
- Закругленные углы
- Ссылки
- Input
11 Examples of HTML div With Style, Class, id, background etc
The div element defines the “division” in the HTML documents. The div tags are generally used to define the layout or sections of the web pages.
The div HTML tag is used to group HTML block elements like paragraphs, headings, and format those with style or CSS. Alternatively, you can say, the div is a container that encloses other HTML block-elements to format them with CSS.
Note: The block elements are those that occupy full available width. Also, these elements add a line before and after it.
To understand the difference between block Vs inline elements, see this example.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to use the div tag with the CSS class, id and style attributes along with using CSS to set the border, background color or image, font size, alignment etc. with examples.
A few examples of using div tag
The div style
The style is an attribute that allows applying inline CSS to the div or elements within the div. This is how you can use div style.
Following are a few examples of using HTML div style attribute.
Example of style in div for setting font size and color
The example below sets the font size and color of the text by using the style attribute in a div element.
A div background color demo
The following example shows how to set the background color with the style attribute. The background property of CSS, background-color is used to define the background color of div.
Applying background to div tag by class or id in CSS is explained below with examples.
A div background image example
The following example sets the background image of the div element. The background image is set in the style attribute by using the background-image property of CSS.
A div border demo
The example below shows how to apply the border to HTML div tag with the style attribute. The CSS border property is used to define the border.
As you can see, the border style is kept solid, the border color is black and thickness is 1 pixel.
A div width and height example
The example below shows how to set the height and width of the div element. The height and width are set in the style attribute of the div element. The div height is kept 100 while the width is 300.
An example of div with padding and margin
In the following example, we are using CSS padding and margin properties in the div tag. To learn more about padding and margin go to their respective chapters.
The div Class and ID attributes
Until now we have learned how to set different properties of div tag by using div attributes, especially the style attribute. We saw the examples of setting the div border, background color, and image, font size, and color with inline CSS.
Now let us work and see examples with div class and id and separate CSS rather inline by using the class and id attributes.
The Class attribute of div
The class is an attribute of the div tag that acts as an identifier in the document. For example, you can use div class name in the CSS to create a class for div element style. Similarly, you can refer that particular div by class name in jQuery etc.
CSS style in class attribute of div
You can create a class in CSS that contains style for multiple div tags. You have to give it the same name as in the class attribute. The same class name will be used in CSS style section (in the head tag of HTML) or external CSS. The class in CSS is starts with a dot(.) e.g. .divclass.
The following example will show you how to style a div tag with a class attribute. We will set the div height, width, background color, border, align properties – all in one CSS class.
HTML Div – What is a Div Tag and How to Style it with CSS
Kolade Chris
The HTML division tag, called «div» for short, is a special element that lets you group similar sets of content together on a web page. You can use it as a generic container for associating similar content.
The div tag is one of the most used tags and doesn’t seem to be going anywhere despite the introduction of semantic elements (these elements let you use several tags as a container).
In this tutorial, I will show you the various things you can do with the div tag, how you can use multiple divs the same HTML file without getting confused, and how to style it.
When to Use the div Tag
The div tag is multi-purpose – you can use it to do several things on a web page. You’ll mostly use it in web layouts and CSS art, but it’s super flexible.
Ultimately, you’ll almost always to use it to style whatever it contains or manipulate such things with JavaScript.
1. Use div in Web Layouts
You’ll primarily use the div tag to group similar content together so you can style it easily. A great example of this is using div to group different sections of a webpage together. You can put together the header, nav, sections, and footer of a page in an individual div tag so they can be styled together.
Later in this tutorial, I will take you through how to make a web layout with multiple div tags without getting confused.
Div itself does not have a direct effect on the presentation of the content unless you style it.
2. Use div in CSS Art
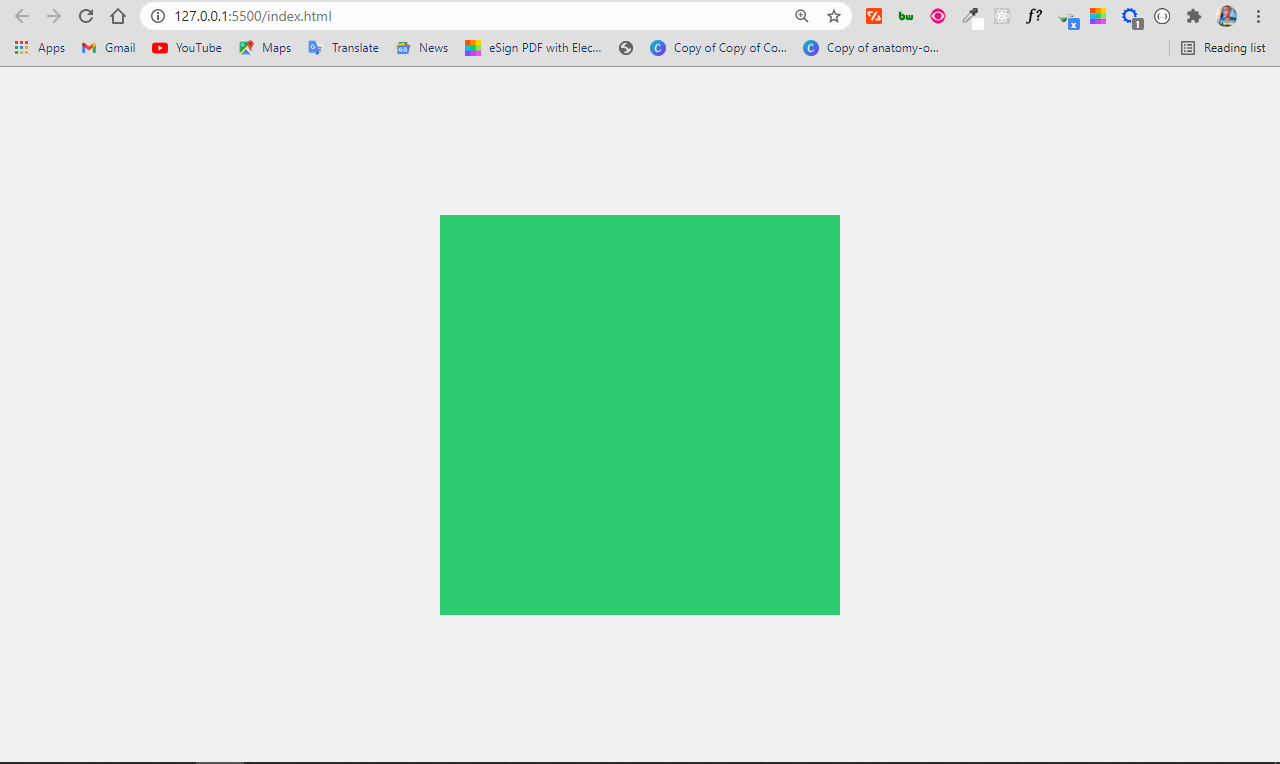
With the div tag, you can make various shapes and draw anything because it is easy to style.
To make a square with div tag, you first need to define an empty div tag and attach a class attribute to it in the HTML. In the CSS, select the div with the class attribute, then set an equal height and width for it.
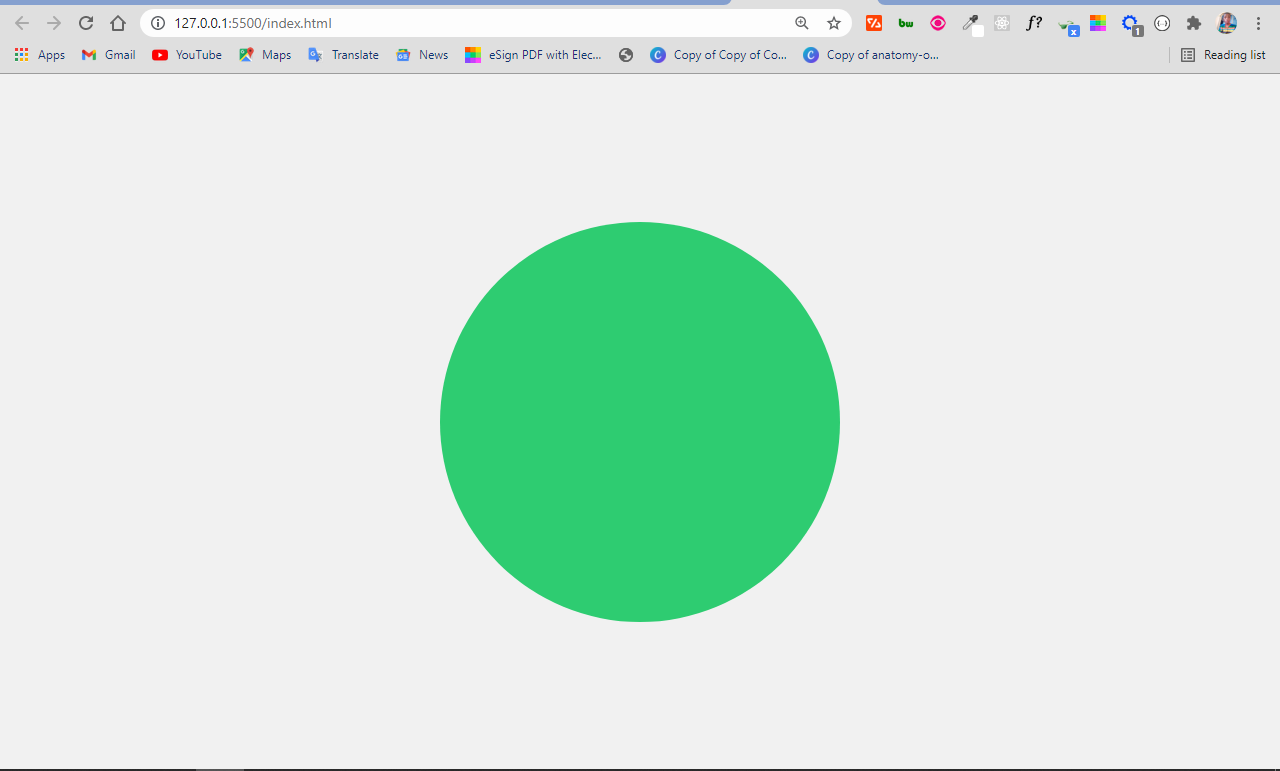
You can make a circle with the div tag by coding an empty div in the HTML, setting an equal height and width for it in the CSS, then a border-radius of 50%.
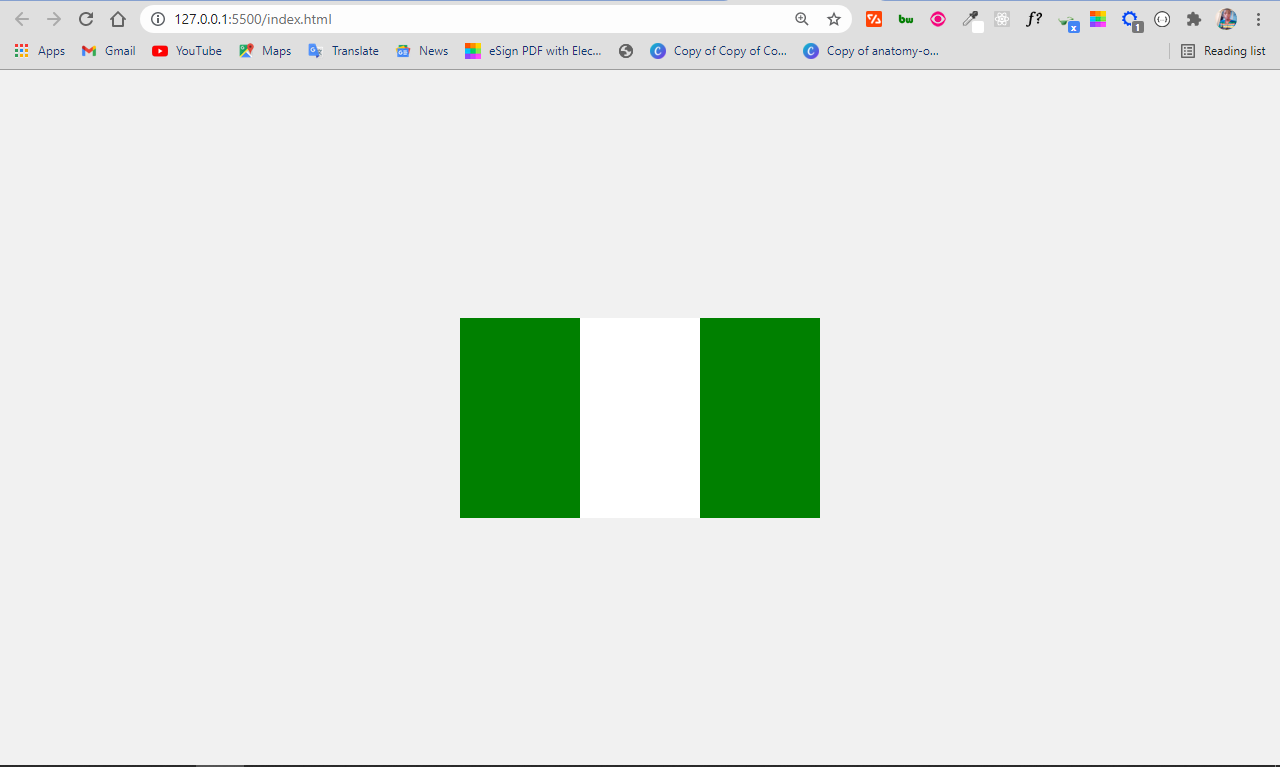
Making the Nigerian flag with the div tag is not that hard. The flag is a rectangular shape with the colors green, white, and green.
To make it, define 3 div tags and attach different classes, then style them appropriately in the CSS.
.naija-flag < display: flex; >.first-green < height: 100px; width: 60px; background-color: green; >.white < height: 100px; width: 60px; background-color: white; >.second-green
How to Style the div Tag
As we discussed above, the div tag is very easy to style. It’s one of the reasons why many developers use it to group similar content.
The div tag accepts almost all CSS properties without a problem. Let’s look at a few examples of that now.
1. How to Apply Font Properties with div
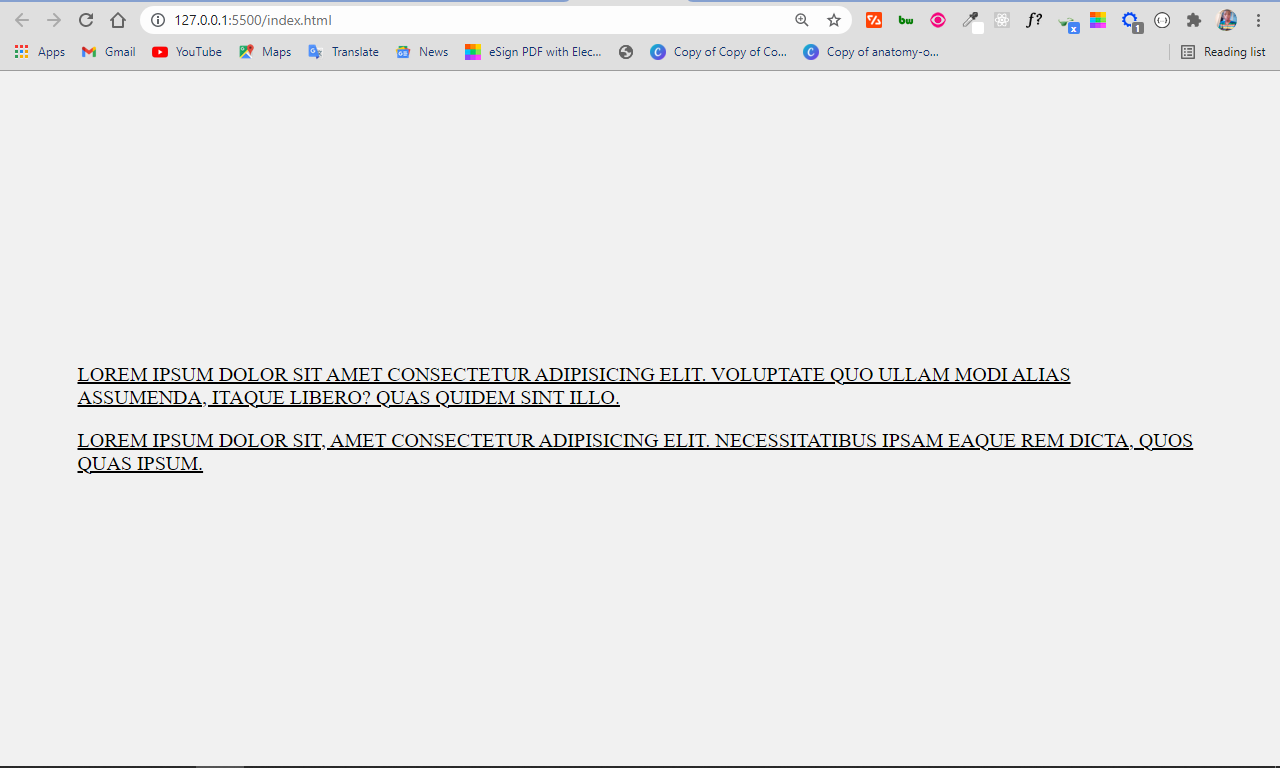
You can apply the CSS properties such as font-size , font-family , font-weight , and font-style on content grouped together with the div tag:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Voluptate quo ullam modi alias assumenda, itaque libero? Quas quidem sint illo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit, amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Necessitatibus ipsam eaque rem dicta, quos quas ipsum.
2. How to Apply Color with the Div Tag
You can apply the CSS color and background-color properties on content grouped together with the div tag:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Voluptate quo ullam modi alias assumenda, itaque libero? Quas quidem sint illo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit, amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Necessitatibus ipsam eaque rem dicta, quos quas ipsum.
3. How to Style Texts with the Div Tag
You can apply the CSS text-transform and text-decoration properties on a div tag like this:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Voluptate quo ullam modi alias assumenda, itaque libero? Quas quidem sint illo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit, amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Necessitatibus ipsam eaque rem dicta, quos quas ipsum.
4. How to Create a Shadow Effect with the Div Tag
You can create a shadow effect with the div tag with the box-shadow property:
Before paying to learn programming, checkout freeCodeCamp.org
The HTML, CSS, and JavaScript curricula would take you from zero to hero in web development.
There is a Python curriculum that will get you a considerable knowledge in Python
And an upcoming Data Science curriculum.
What’s happening in the CSS above?
I was able to create the shadow effect with the CSS box-shadow property.
- The first value (2px) represents the offset on the x-axis (offset-x)
- The second (another 2px) represents the offset on the y-axis (offset-y)
- The next 20px is for the blur-radius, that is, how blurry you want the shadow to be.
- The 23px value is the spread radius (how far you want the shadow to spread)
- The last value is the shadow color – in this case, #7fecad.
The output looks like this:
How to Use Multiple Div Elements without Getting Confused
Div tags are commonly used to group similar content together. In older and even some newer web pages, you’ll find divs all around, despite the fact that semantic tags are recommended for accessibility and better SEO.
Since div tags are still very common, I recommend applying class and id attributes to them so you can manipulate individual div elements with those attributes.
I will walk you through how to put this into practice by making a basic web layout.
The first section you’ll want to make is the header, containing the logo and navbar:
Before styling the navbar, I made some CSS resets to make things align correctly and display nicely:
* < margin: 0; padding: 0; box-sizing: border-box; >.hero, .about, .services, .contact
In the code snippet above:
- I removed the default margin and padding
- I set a maximum width for the main sections so they don’t go all across for better UX
- I set a margin at the bottom of each section to give them some space
- I set a margin 0 at the top and bottom, auto on the left and right to center them.
To style the navbar appropriately, I will grab the container div tag with its class attribute, header . I’ll give it a display of flex , alongside some other properties to lay it out nicely. I will also grab the div wrapped around the navbar ( ul element) by its class and lay it out with Flexbox.
For the remaining sections apart from the footer, the HTML and stylings are generic:
Hero Section
About Us
Our Services
Contact Us
© 2021 All Rights Reserved
.hero < background-color: #eee; height: 200px; >.hero h1 < display: flex; align-items: center; justify-content: center; line-height: 6; >.about < background-color: #eee; height: 200px; >.about h1 < display: flex; align-items: center; justify-content: center; line-height: 6; >.services < background-color: #eee; height: 200px; >.services h1 < display: flex; align-items: center; justify-content: center; line-height: 6; >.contact < background-color: #eee; height: 200px; >.contact h1 < display: flex; align-items: center; justify-content: center; line-height: 6; >.footer < background-color: #777; height: 40px; >.footer p
I gave the individual sections a greyish background color and a height of 200px. I positioned the h1 tags inside in their centers with Flexbox and applied a line height of 1.5 to each of them.
Finally, I gave the footer a deeper grey background color to make it distinct, and centered the content in it with a line height of 1.7.
The resulting layout looks like this:
Conclusion
The HTML div tag is commonly used among web developers everywhere.
Just keep in mind that you should usually use semantic HTML in place of the div tag unless none of them (the semantic tags) really match the content to group together. This is because semantic tags are better for accessibility and SEO.
In short, the div tag remains useful and isn’t going anywhere anytime soon, so feel free to use it when necessary.
Thank you for reading and have a nice time.
Базовые CSS-стили различных элементов
В этом топике представлены лаконичные базовые стили для различных элементов: кнопок, ссылок, форм, теней, градиентов, которые можно использовать в своих проектах. Да и просто разобраться в принципах работы таких конструкций проще на несложных примерах.
Базовая конструкция
В примерах базовая конструкция блока выглядит так:
Тени
Блок отбрасывает тень в разные стороны:
.drop-shadow < background: #9479fa; >.drop-shadow.top < box-shadow: 0 -4px 2px -2px rgba(0,0,0,0.4) >.drop-shadow.right < box-shadow: 4px 0 2px -2px rgba(0,0,0,0.4) >.drop-shadow.bottom < box-shadow: 0 4px 2px -2px rgba(0,0,0,0.4) >.drop-shadow.left
div[class*="emphasize-"] < background: #69D2E7; >.emphasize-dark < box-shadow: 0 0 5px 2px rgba(0,0,0,.35) >.emphasize-light < box-shadow: 0 0 0 10px rgba(255,255,255,.25) >.emphasize-inset < box-shadow: inset 0 0 7px 4px rgba(255,255,255,.5) >.emphasize-border
div[class*="embossed"] < background: #8ec12d; color: #333; text-shadow: 0 1px 1px rgba(255,255,255,0.9); >.embossed-light < border: 1px solid rgba(0,0,0,0.05); box-shadow: inset 0 1px 0 rgba(255,255,255,0.7); >.embossed-heavy
Градиенты
div[class*="gradient"] < background-color: #DEB8A0; box-shadow: 0 0 0 1px #a27b62; >.gradient-light-linear < background-image: linear-gradient(rgba(255,255,255,.5), rgba(255,255,255,0)); >.gradient-dark-linear
Закругленные углы
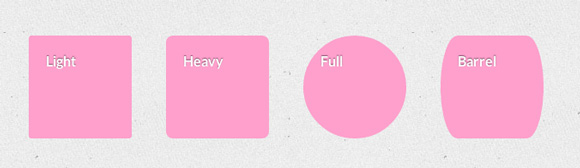
div[class*="rounded"] < background: #fca1cc; >.light-rounded < border-radius: 3px; >.heavy-rounded < border-radius: 8px; >.full-rounded < border-radius: 50%; >.barrel-rounded < border-radius: 20px/60px; >Ссылки
Несколько примеров стилей для ссылки в тексте:
.inline-link-1 < display: inline-block; margin: 0 0.2em; padding: 3px; background: #97CAF2; border-radius: 2px; transition: all 0.3s ease-out; /* Font styles */ text-decoration: none; font-weight: bold; color: white; >.inline-link-1:hover < background: #53A7EA >.inline-link-1:active < background: #C4E1F8 >.inline-link-1:visited
.inline-link-2 < display: inline-block; border-bottom: 2px dashed rgba(0,0,0,0.9); /* Font styles */ text-decoration: none; color: #777; >.inline-link-2:hover < border-bottom-style: dotted; >.inline-link-2:active < border-bottom-style: solid; >.inline-link-2:visited
.inline-link-3 < display: inline-block; position: relative; padding-left: 6px; /* Font styles */ text-decoration: none; color: #6AB3EC; text-shadow: 0 1px 1px rgba(255,255,255,0.9); >.inline-link-3:hover < color: #3C9CE7; >.inline-link-3:before < content: "\25BA"; font-size: 80%; display: inline-block; padding-right: 3px; pointer-events: none; >.inline-link-3:hover:before
.metro.three-d < position: relative; box-shadow: 1px 1px #53A7EA, 2px 2px #53A7EA, 3px 3px #53A7EA; transition: all 0.1s ease-in; >.metro.three-d:active
.bordered-link < display: inline-block; padding: 8px; border: 3px solid #FCB326; border-radius: 6px; box-shadow: 0 2px 1px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2), inset 0 2px 1px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2); /* Font styles */ text-decoration: none; font-size: 14px; text-transform: uppercase; color: #222; >.bordered-link:hover < border-color: #FDD68B >.bordered-link:active
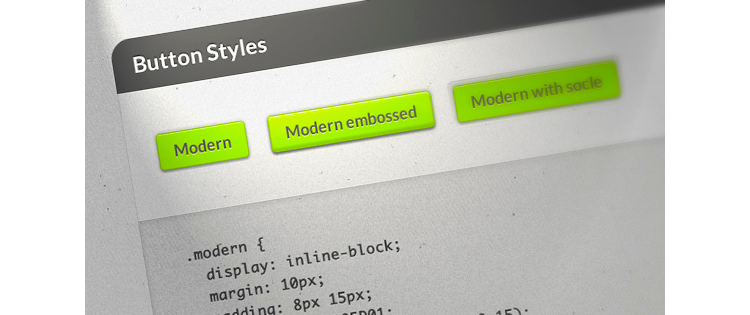
.embossed-link < box-shadow: inset 0 3px 2px rgba(255,255,255,.22), inset 0 -3px 2px rgba(0,0,0,.17), inset 0 20px 10px rgba(255,255,255,.12), 0 0 4px 1px rgba(0,0,0,.1), 0 3px 2px rgba(0,0,0,.2); >.modern.embossed-link < box-shadow: inset 0 1px 0 rgba(255,255,255,0.5), 0 2px 2px rgba(0,0,0,0.3), 0 0 4px 1px rgba(0,0,0,0.2), inset 0 3px 2px rgba(255,255,255,.22), inset 0 -3px 2px rgba(0,0,0,.15), inset 0 20px 10px rgba(255,255,255,.12), 0 0 4px 1px rgba(0,0,0,.1), 0 3px 2px rgba(0,0,0,.2); >.modern.embossed-link:active
Input
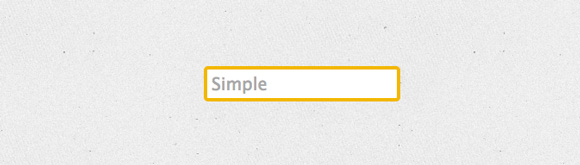
Добавляет border-radius по клику:
.simple-input < display: block; padding: 5px; border: 4px solid #F1B720; border-radius: 5px; color: #333; transition: all 0.3s ease-out; >.simple-input:hover < border-radius: 8px >.simple-input:focus
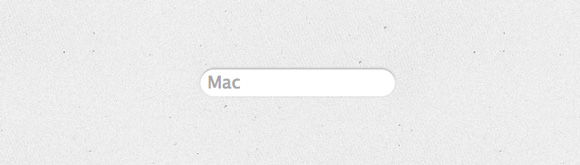
Вместо формы ввода просто линия: