- CSS selectors
- Reference
- Combinators and seperators
- Selectors
- Terms
- Guides
- Related concepts
- Specifications
- See also
- Found a content problem with this page?
- CSS selectors
- What is a selector?
- Selector lists
- Types of selectors
- Type, class, and ID selectors
- CSS statements, rules, declaration blocks and selectors
- CSS statements
- Pictorial presentation of CSS statement
- CSS at rules
- CSS declaration blocks
- Pictorial presentation of CSS declaration block
- CSS selectors
- HTML and CSS code
CSS selectors
The CSS selectors module defines the patterns to select elements to which a set of CSS rules are then applied along with their specificity . The CSS selectors module provides us with more than 60 selectors and five combinators. Other modules provide additional pseudo-class selectors and pseudo-elements.
In CSS, selectors are patterns used to match, or select, the elements you want to style. Selectors are also used in JavaScript to enable selecting the DOM nodes to return as a NodeList .
Selectors, whether used in CSS or JavaScript, enable targeting HTML elements based on their type, attributes, current states, and even position in the DOM. Combinators allow you to be more precise when selecting elements by enabling selecting elements based on their relationship to other elements.
Reference
Combinators and seperators
Selectors
Terms
- Pseudo-class glossary term
- Functional pseudo-classes
- Combinators
- Simple selector
- Compound selector
- Complex selector
- Relative selector
- Selector list
- Specificity
Guides
Overview of the different types of simple selectors and various combinators defined in the CSS selectors and the CSS pseudo modules.
Explanation of the structure of CSS selectors and the terminologies introduced in the CSS selectors module, ranging from «simple selector» to «forgiving relative selector list».
Lists the pseudo-classes, selectors that allow the selection of elements based on state information that is not contained in the document tree, defined in the various CSS modules and HTML.
Learn how to use the :target pseudo-class to style the target element a URL’s fragment identifier.
Learn the different UI pseudo-classes available for styling forms in different states.
The selectors API enables using selectors in JavaScript to retrieve element nodes from the DOM.
Related concepts
- :popover-open pseudo-class
- CSS scoping module
- :host pseudo-class
- :host() pseudo-class
- :host-context() pseudo-class
- ::slotted pseudo-element
- ::after
- ::before
- ::file-selector-button
- ::first-letter
- ::first-line
- ::grammar-error
- ::marker
- ::placeholder
- ::selection
- ::spelling-error
- ::target-text
- ::part pseudo-element
- ::backdrop
- ::cue
- ::cue-region
Specifications
See also
Found a content problem with this page?
This page was last modified on Jul 21, 2023 by MDN contributors.
Your blueprint for a better internet.
CSS selectors
In CSS, selectors are used to target the HTML elements on our web pages that we want to style. There are a wide variety of CSS selectors available, allowing for fine-grained precision when selecting elements to style. In this article and its sub-articles we’ll run through the different types in great detail, seeing how they work.
Prerequisites: Basic computer literacy, basic software installed, basic knowledge of working with files, HTML basics (study Introduction to HTML), and an idea of how CSS works (study CSS first steps.) Objective: To learn how CSS selectors work in detail. What is a selector?
A CSS selector is the first part of a CSS Rule. It is a pattern of elements and other terms that tell the browser which HTML elements should be selected to have the CSS property values inside the rule applied to them. The element or elements which are selected by the selector are referred to as the subject of the selector.
In other articles you may have met some different selectors, and learned that there are selectors that target the document in different ways — for example by selecting an element such as h1 , or a class such as .special .
In CSS, selectors are defined in the CSS Selectors specification; like any other part of CSS they need to have support in browsers for them to work. The majority of selectors that you will come across are defined in the Level 3 Selectors specification and Level 4 Selectors specification, which are both mature specifications, therefore you will find excellent browser support for these selectors.
Selector lists
If you have more than one thing which uses the same CSS then the individual selectors can be combined into a selector list so that the rule is applied to all of the individual selectors. For example, if I have the same CSS for an h1 and also a class of .special , I could write this as two separate rules.
h1 color: blue; > .special color: blue; >I could also combine these into a selector list, by adding a comma between them.
White space is valid before or after the comma. You may also find the selectors more readable if each is on a new line.
In the live example below try combining the two selectors which have identical declarations. The visual display should be the same after combining them.
When you group selectors in this way, if any selector is syntactically invalid, the whole rule will be ignored.
In the following example, the invalid class selector rule will be ignored, whereas the h1 would still be styled.
h1 color: blue; > ..special color: blue; >When combined however, neither the h1 nor the class will be styled as the entire rule is deemed invalid.
Types of selectors
There are a few different groupings of selectors, and knowing which type of selector you might need will help you to find the right tool for the job. In this article’s subarticles we will look at the different groups of selectors in more detail.
Type, class, and ID selectors
This group includes selectors that target an HTML element such as an .
It also includes selectors which target a class:
CSS statements, rules, declaration blocks and selectors
In this tutorial, we have discussed CSS statements, rules, declaration blocks and selectors.
CSS statements
A CSS stylesheet is made up of CSS statements which describe presentations for HTML or XML web documents.
If you look at the example bellow,
then, in this stylesheet, «background-color: #FDD017; «, » color: #003366;«, » font-weight: bold; «; » width: 500px;«, » padding: 5px;» all these are CSS statements.
Pictorial presentation of CSS statement
There are two kinds of CSS statement : at rules and rule sets.
CSS at rules
A CSS rule set ( also called «rule» ) comprises of a selector followed by a declaration block ( properties and values wrapped by curly braces ).
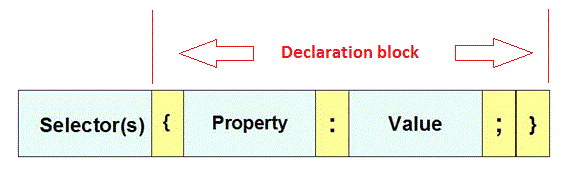
CSS declaration blocks
A declaration block contains CSS properties and their respective values enclosed in curly braces. A pair of property and value ends with a semicolon ( ; ).
Pictorial presentation of CSS declaration block
CSS selectors
CSS Selectors select HTML elements in an HTML page. Properties and values written against CSS selectors assign styles, i.e. presentational features to the HTML elements.
Look at the example bellow :
here, » p » is a selector. Since p refers to p element ( paragraph ) , so if this stylesheet is implemented on an HTML page, all paragraph elements will look like as described against p, in the stylesheet.
Besides elements names the selector can be a group of elements, a document identifier, i.e. class or id and some other types of pseudo-elements or pseudo elements.
Bellow we have given code and result, if the above stylesheet is attached to an HTML element :
HTML and CSS code
pLorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Nam egestas placerat venenatis. Donec rhoncus ipsum et nibh congue convallis. Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Vivamus lacinia arcu vitae enim tempus scelerisque. Praesent laoreet sagittis lorem, viverra accumsan lectus vulputate scelerisque. Donec placerat sem quis augue feugiat tincidunt. Etiam consequat malesuada diam et pharetra. Aliquam ac nibh id lacus molestie scelerisque eget nec lectus. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Donec condimentum magna fringilla mi sodales sit amet dignissim metus molestie. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Integer semper congue sem, eu condimentum felis vulputate vitae.
Suspendisse semper luctus sagittis. Sed sollicitudin, nunc laoreet tempus volutpat, lectus neque faucibus leo, quis dignissim dolor ipsum vitae libero. Donec adipiscing neque vitae erat feugiat sollicitudin. In rhoncus urna vel lorem dictum ultrices. Vivamus volutpat rhoncus tellus, sit amet feugiat orci scelerisque placerat. Proin viverra massa quis nulla mattis vel aliquam lacus auctor. In at ipsum mauris. Morbi tincidunt enim tempus nunc sollicitudin et convallis tellus molestie. Aliquam tempus felis vitae urna malesuada elementum. Nunc pharetra diam et dui semper eleifend. Cum sociis natoque penatibus et magnis dis parturient montes, nascetur ridiculus mus. Nam at magna orci, sed volutpat eros. Integer dictum volutpat turpis in dictum. Donec tristique fringilla nibh, id cursus nulla aliquet commodo. Pellentesque elit est, tincidunt non pharetra eget, elementum quis est. Donec feugiat sem ullamcorper dui viverra lacinia. Fusce tempus adipiscing egestas
We have discussed different types of selectors and their usage in our CSS Selectors Tutorials.
Previous: CSS syntax
Next: CSS commentsFollow us on Facebook and Twitter for latest update.