Class File
The conversion of a pathname string to or from an abstract pathname is inherently system-dependent. When an abstract pathname is converted into a pathname string, each name is separated from the next by a single copy of the default separator character. The default name-separator character is defined by the system property file.separator , and is made available in the public static fields separator and separatorChar of this class. When a pathname string is converted into an abstract pathname, the names within it may be separated by the default name-separator character or by any other name-separator character that is supported by the underlying system.
A pathname, whether abstract or in string form, may be either absolute or relative. An absolute pathname is complete in that no other information is required in order to locate the file that it denotes. A relative pathname, in contrast, must be interpreted in terms of information taken from some other pathname. By default the classes in the java.io package always resolve relative pathnames against the current user directory. This directory is named by the system property user.dir , and is typically the directory in which the Java virtual machine was invoked.
The parent of an abstract pathname may be obtained by invoking the getParent() method of this class and consists of the pathname’s prefix and each name in the pathname’s name sequence except for the last. Each directory’s absolute pathname is an ancestor of any File object with an absolute abstract pathname which begins with the directory’s absolute pathname. For example, the directory denoted by the abstract pathname «/usr» is an ancestor of the directory denoted by the pathname «/usr/local/bin» .
- For UNIX platforms, the prefix of an absolute pathname is always «/» . Relative pathnames have no prefix. The abstract pathname denoting the root directory has the prefix «/» and an empty name sequence.
- For Microsoft Windows platforms, the prefix of a pathname that contains a drive specifier consists of the drive letter followed by «:» and possibly followed by «\\» if the pathname is absolute. The prefix of a UNC pathname is «\\\\» ; the hostname and the share name are the first two names in the name sequence. A relative pathname that does not specify a drive has no prefix.
Instances of this class may or may not denote an actual file-system object such as a file or a directory. If it does denote such an object then that object resides in a partition. A partition is an operating system-specific portion of storage for a file system. A single storage device (e.g. a physical disk-drive, flash memory, CD-ROM) may contain multiple partitions. The object, if any, will reside on the partition named by some ancestor of the absolute form of this pathname.
A file system may implement restrictions to certain operations on the actual file-system object, such as reading, writing, and executing. These restrictions are collectively known as access permissions. The file system may have multiple sets of access permissions on a single object. For example, one set may apply to the object’s owner, and another may apply to all other users. The access permissions on an object may cause some methods in this class to fail.
Instances of the File class are immutable; that is, once created, the abstract pathname represented by a File object will never change.
Interoperability with java.nio.file package
The java.nio.file package defines interfaces and classes for the Java virtual machine to access files, file attributes, and file systems. This API may be used to overcome many of the limitations of the java.io.File class. The toPath method may be used to obtain a Path that uses the abstract path represented by a File object to locate a file. The resulting Path may be used with the Files class to provide more efficient and extensive access to additional file operations, file attributes, and I/O exceptions to help diagnose errors when an operation on a file fails.
Creating class file java
Learn Latest Tutorials
Preparation
Trending Technologies
B.Tech / MCA
Javatpoint Services
JavaTpoint offers too many high quality services. Mail us on h[email protected], to get more information about given services.
- Website Designing
- Website Development
- Java Development
- PHP Development
- WordPress
- Graphic Designing
- Logo
- Digital Marketing
- On Page and Off Page SEO
- PPC
- Content Development
- Corporate Training
- Classroom and Online Training
- Data Entry
Training For College Campus
JavaTpoint offers college campus training on Core Java, Advance Java, .Net, Android, Hadoop, PHP, Web Technology and Python. Please mail your requirement at [email protected].
Duration: 1 week to 2 week
Like/Subscribe us for latest updates or newsletter 




What is class file in Java? Example
What is the class file in Java?
Class file in Java is compiled from of Java source file. When we compile a Java program written in a Java source file ended with a .java extension, it produces one more class file depending upon how many classes are declared and defined in that Java source file. One Java source file can only contain one public class, and its name must match with the name of the file like HelloWorld.java file can contain a public class whose name should be HelloWorld as shown below :
public class HelloWorld < public static void main(String. args)< System.out.println("I am inside java class HelloWorld"); > >
if you compile this Java file by
Class file details in Java
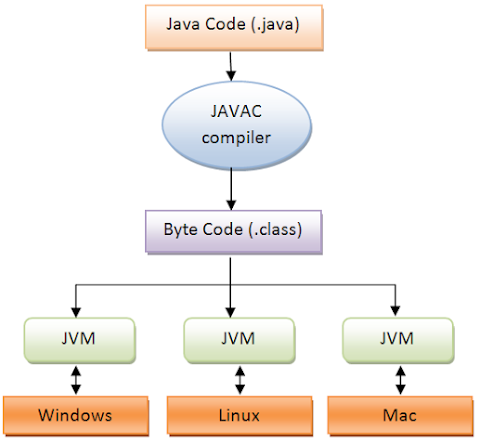
A class file in Java has a .class extension. It contains bytecode, which is instruction for Java Virtual Machine, which translates that bytecode into platform-specific machine level instruction based upon whether the Java program runs on Windows or Linux.
In fact, this combination of a class file, bytecode, and JVM makes Java achieves platform independence. If anyone asks what is byte code in Java, is it machine instruction? You can answer them that it’s just meant for JVM and not for a machine.
When you run a Java program as described in this step-by-step tutorial for running a java program using the java command, we provide the name of the class file which contains the main method in Java.
JVM first loads that file and executes the main method, which is the entry point of the Java application. Remember java compiler or javac command is used to create a class file from the java source file, and the java command is used to run a Java program stored in a class file.
Since the class file contains bytecode in hex format and the class file format is well-documented, anyone can temper with the class file and break Java security grantees. To prevent that every Java class file is verified by Verifier after loading during Byte code verification process and Verifier rejects the class file which violates constraints of Java programming language.
That’s all on the Class file in Java, and how to create a class file in Java. In short Class, a file is a binary file that contains bytecode, and a Java compiler is used to create a Class file in Java. This is one of the key concepts in Java as it allows Java programs to remain platform-independent. This means you can run the same JAR file of your Java application in Mac, Windows, and Linux without any additional change.
Thanks for reading this article so far. If you find my explanation of Java’s class files, please share them with your friends and colleagues. If you have any questions or doubts, please ask.
Java Class File
A Java class file is a file containing Java bytecode and having .class extension that can be executed by JVM. A Java class file is created by a Java compiler from .java files as a result of successful compilation. As we know that a single Java programming language source file (or we can say .java file) may contain one class or more than one class. So if a .java file has more than one class then each class will compile into a separate class files.
For Example: Save this below code as Test.java on your system.
For Compiling:
After compilation there will be 3 class files in corresponding folder named as:
A single class file structure contains attributes that describe a class file.
Representation of Class File Structure
Elements of class file are as follows:
- magic_number: The first 4 bytes of class file are termed as magic_number. This is a predefined value which the JVM use to identify whether the .class file is generated by valid compiler or not. The predefined value will be in hexadecimal form i.e. 0xCAFEBABE.
Now let’s see what happen when JVM will not find valid magic number. Suppose we have a .java file named as Sample.java as follows and follow step by step process on your system.
// class Declaration class Sample < public static void main(String[] args) < System.out.println("Magic Number"); >> Step 1: Compile using javac Sample.java
Step 2: Now open the Sample.class file. It will looks like following.
Step 3: Now erase at least single symbol from this Sample.class file from starting of file and save it.
Step 4: Now try to run this using java Sample command and see the magic i.e. you will get run time exception (See the highlighted text in below image):
Note: This can vary depending on how much you remove the .class file data.
Note: Lower version compiler generated .class file can be executed by high version JVM but higher version compiler generated .class file cannot be executed by lower version JVM. If we will try to execute we will get run time exception.
This demonstration is for Windows OS as follows:
Step 1: Open a command prompt window and try to check java compiler version and JVM version using following commands respectively (Highlighted text in image are the commands)
Output for 1.8 version will be:
Step 2: Now check with another version which may be higher or lower than already installed.thisDownload link.
And install this to your PC or laptops and note the installation address.
Step 3: Open a second command prompt window and set the path of bin folder of installed jdk installed during 2nd step. And check for Java compiler version ad JVM version.
Step 4: Now on 1st command prompt compile the any valid .java file. For example: See above Sample.java file. Compile it as:
Step 5: Now on 2nd command prompt window try to run the above compiled code class file and see what happen. There is a run time exception which I have highlighted in below image.
Note: Internally jdk 1.5 version means 49.0 and 1.6 means 50.0 and 1.7 means 51.0 etc. class file version where the digits before the decimal point represent the major_version and digits after decimal point represents the minor_version.
- constant_pool_count: It represents the number of the constants present in the constant pool (When a Java file is compiled, all references to variables and methods are stored in the class’s constant pool as a symbolic reference).
- constant_pool[]: It represents the information about constants present in constant pool file.
- access_flags: It provide the information about the modifiers which are declared to the class file.
- this_class: It represents fully qualified name of the class file.
- super_class: It represents fully qualified name of the immediate super class of current class. Consider above Sample.java file. When we will compile it, then we can say this_class will be Sample class and super_class will be Object class.
- interface_count: It returns the number of interfaces implemented by current class file.
- interface[]: It returns interfaces information implemented by current class file.
- fields_count: It represents the number of fields (static variable) present in current class file.
- fields[]: It represent fields (static variable) information present in current class file.
- method_count: It represents number of methods present in current class file.
- method[]: It returns information about all methods present in current class file.
- attributes_count: It returns the number of attributes (instance variables) present in current class file.
- attributes[]: It provides information about all attributes present in current class file.