- Built-in types (C++)
- Void type
- std::nullptr_t
- Boolean type
- Character types
- Floating-point types
- Integer types
- Integer type synonyms
- Sizes of built-in types
- C++ Float: 7 Examples to Learn
- What if the float is assigned to an int type variable
- Comparing float with double and long double variables
- Setting precision by setprecision() function example
- C++ size of double – Size of int c++ – C++ Program to Find Size of Int, Float, Char and double data types using sizeof operator
- C++ Program to Find Size of Int, Float, Char and double data types using sizeof operator
- C++ program to find size of variable using sizeof operator
- Find Size of int, float, double and char in Your System using C++ 1 min read
- Add comment
- Cancel reply
- You may also like
- C++ Programs (Code Explanation Line by Line)
- What are Bit Field Classes in C++
- Dynamic Memory Allocation for Array of Objects in C++
- What are the different types of storage classes in C/C++ programming
Built-in types (C++)
Built-in types (also called fundamental types) are specified by the C++ language standard and are built into the compiler. Built-in types aren’t defined in any header file. Built-in types are divided into three main categories: integral, floating-point, and void. Integral types represent whole numbers. Floating-point types can specify values that may have fractional parts. Most built-in types are treated as distinct types by the compiler. However, some types are synonyms, or treated as equivalent types by the compiler.
Void type
The void type describes an empty set of values. No variable of type void can be specified. The void type is used primarily to declare functions that return no values or to declare generic pointers to untyped or arbitrarily typed data. Any expression can be explicitly converted or cast to type void . However, such expressions are restricted to the following uses:
- An expression statement. (For more information, see Expressions.)
- The left operand of the comma operator. (For more information, see Comma Operator.)
- The second or third operand of the conditional operator ( ? : ). (For more information, see Expressions with the Conditional Operator.)
std::nullptr_t
The keyword nullptr is a null-pointer constant of type std::nullptr_t , which is convertible to any raw pointer type. For more information, see nullptr .
Boolean type
The bool type can have values true and false . The size of the bool type is implementation-specific. See Sizes of built-in types for Microsoft-specific implementation details.
Character types
The char type is a character representation type that efficiently encodes members of the basic execution character set. The C++ compiler treats variables of type char , signed char , and unsigned char as having different types.
Microsoft-specific: Variables of type char are promoted to int as if from type signed char by default, unless the /J compilation option is used. In this case, they’re treated as type unsigned char and are promoted to int without sign extension.
A variable of type wchar_t is a wide-character or multibyte character type. Use the L prefix before a character or string literal to specify the wide-character type.
Microsoft-specific: By default, wchar_t is a native type, but you can use /Zc:wchar_t- to make wchar_t a typedef for unsigned short . The __wchar_t type is a Microsoft-specific synonym for the native wchar_t type.
The char8_t type is used for UTF-8 character representation. It has the same representation as unsigned char , but is treated as a distinct type by the compiler. The char8_t type is new in C++20. Microsoft-specific: use of char8_t requires the /std:c++20 compiler option or later (such as /std:c++latest ).
The char16_t type is used for UTF-16 character representation. It must be large enough to represent any UTF-16 code unit. It’s treated as a distinct type by the compiler.
The char32_t type is used for UTF-32 character representation. It must be large enough to represent any UTF-32 code unit. It’s treated as a distinct type by the compiler.
Floating-point types
Floating-point types use an IEEE-754 representation to provide an approximation of fractional values over a wide range of magnitudes. The following table lists the floating-point types in C++ and the comparative restrictions on floating-point type sizes. These restrictions are mandated by the C++ standard and are independent of the Microsoft implementation. The absolute size of built-in floating-point types isn’t specified in the standard.
| Type | Contents |
|---|---|
| float | Type float is the smallest floating point type in C++. |
| double | Type double is a floating point type that is larger than or equal to type float , but shorter than or equal to the size of type long double . |
| long double | Type long double is a floating point type that is larger than or equal to type double . |
Microsoft-specific: The representation of long double and double is identical. However, long double and double are treated as distinct types by the compiler. The Microsoft C++ compiler uses the 4- and 8-byte IEEE-754 floating-point representations. For more information, see IEEE floating-point representation.
Integer types
The int type is the default basic integer type. It can represent all of the whole numbers over an implementation-specific range.
A signed integer representation is one that can hold both positive and negative values. It’s used by default, or when the signed modifier keyword is present. The unsigned modifier keyword specifies an unsigned representation that can only hold non-negative values.
A size modifier specifies the width in bits of the integer representation used. The language supports short , long , and long long modifiers. A short type must be at least 16 bits wide. A long type must be at least 32 bits wide. A long long type must be at least 64 bits wide. The standard specifies a size relationship between the integral types:
An implementation must maintain both the minimum size requirements and the size relationship for each type. However, the actual sizes can and do vary between implementations. See Sizes of built-in types for Microsoft-specific implementation details.
The int keyword may be omitted when signed , unsigned , or size modifiers are specified. The modifiers and int type, if present, may appear in any order. For example, short unsigned and unsigned int short refer to the same type.
Integer type synonyms
The following groups of types are considered synonyms by the compiler:
Microsoft-specific integer types include the specific-width __int8 , __int16 , __int32 , and __int64 types. These types may use the signed and unsigned modifiers. The __int8 data type is synonymous with type char , __int16 is synonymous with type short , __int32 is synonymous with type int , and __int64 is synonymous with type long long .
Sizes of built-in types
Most built-in types have implementation-defined sizes. The following table lists the amount of storage required for built-in types in Microsoft C++. In particular, long is 4 bytes even on 64-bit operating systems.
| Type | Size |
|---|---|
| bool , char , char8_t , unsigned char , signed char , __int8 | 1 byte |
| char16_t , __int16 , short , unsigned short , wchar_t , __wchar_t | 2 bytes |
| char32_t , float , __int32 , int , unsigned int , long , unsigned long | 4 bytes |
| double , __int64 , long double , long long , unsigned long long | 8 bytes |
See Data type ranges for a summary of the range of values of each type.
For more information about type conversion, see Standard conversions.
C++ Float: 7 Examples to Learn
You can see, the double variable type shows 8 while float type variables display 4 size (in byets).
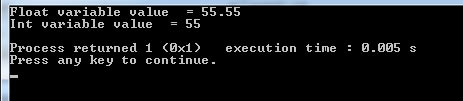
What if the float is assigned to an int type variable
Suppose, we have a float type variable with a value in decimal points. We assign its value to another variable of int type. See what it displays:
So, the result is not an error. In fact, int type variable yielded a truncated value and this is before the decimal part.
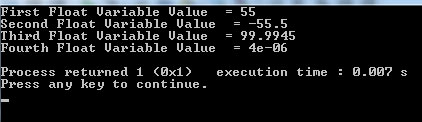
Comparing float with double and long double variables
Let us assign values with big precision to float, double, and long double variables (Since all can store floating-point values).
Our compiler allows six digits, so it outputs the same. The result may vary depending on the compiler.
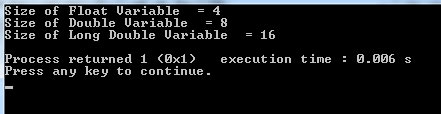
So what about all three variable sizes in bytes?
So, it’s 4 for float, 8 for double, and 16 for the long double variable.
Note that, a long double can also take 12 bytes – it depends on the operating system.
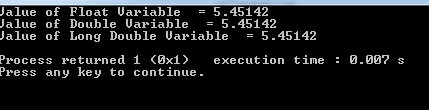
Setting precision by setprecision() function example
As we have seen in the above example, the compiler allowed only six digits. We can set the precision by using the setprecision() function.
This is defined in the iomanip header file that you have to include in the CPP file, in order to use it.
In the example, we have used the same values for float, double and long double variables.
The precision is set as 11 by using the setprecision function.
See the code and output:
C++ size of double – Size of int c++ – C++ Program to Find Size of Int, Float, Char and double data types using sizeof operator
Size of int c++: In the previous article, we have discussed C++ Program to Find Average of Numbers Using Arrays. In this article, we will see C++ Program to Find Size of Int, Float, Char and double data types using sizeof operator.
C++ Program to Find Size of Int, Float, Char and double data types using sizeof operator
- Write a program in C++ to find the size of variables in run time using size of operator.
- How to find the size of Integer, Character, floating point and Double data type variables in C++.
C++ program to find size of variable using sizeof operator
C++ size of double: In this program, we will use sizeof operator to find the size of variable at run-time. The size of variable is system dependent. Hence, the output of below program may differ depending upon the system configurations.
sizeof Operator
The sizeof is a compile time operator not a standard library function. The sizeof is a unary operator which returns the size of passed variable or data type in bytes.
As we know, that size of basic data types in C++ is system dependent, So we can use sizeof operator to dynamically determine the size of variable at run time.
/* * C++ Program to find Size of char, int, float, and double * in Your System uisng sizeof operator */ #include using namespace std; int main() < // Printing size of Basic Data Types cout
Size of a Character Variable (char) = 1 bytes Size of an Integer Variable (int) = 4 bytes Size of a Floating Point Variable (float) = 4 bytes Size of Double Variable (double) = 8 bytes
Start writing code in C++ language by referring to Simple C++ Program Examples available here. These examples are helpful to get an idea on the format, function used in every basic program.
Find Size of int, float, double and char in Your System using C++ 1 min read
To find the size of variable, sizeof operator is used.
his program declares 4 variables of type int, float, double and char. Then, the size of each variable is evaluated using sizeof operator.
Add comment
Cancel reply
You may also like
C++ Programs (Code Explanation Line by Line)
C++ is a high-level, general-purpose programming language developed by Bjarne Stroustrup in 1983. It is an extension of the C language and is widely used for developing operating systems, system software, and various.
What are Bit Field Classes in C++
A field or member inside a class which allows programmers to save memory are known as bit fields. As we know a integer variable occupies 32 bits (on a 32-bit machine). If we only want to store two values like 0 and 1.
Dynamic Memory Allocation for Array of Objects in C++
Table of Contents Toggle Dynamic memory allocation for array of objectsObjects As Function Arguments Dynamic memory allocation for array of objects In the previous topic memory for array of objects was static as the.
What are the different types of storage classes in C/C++ programming
In C programming, there are four storage classes: Automatic storage class: Variables declared within a function or block are automatically allocated memory from the stack and are known as automatic variables. They are.