Class ClassLoader
A class loader is an object that is responsible for loading classes. The class ClassLoader is an abstract class. Given the binary name of a class, a class loader should attempt to locate or generate data that constitutes a definition for the class. A typical strategy is to transform the name into a file name and then read a «class file» of that name from a file system.
Every Class object contains a reference to the ClassLoader that defined it.
Class objects for array classes are not created by class loaders, but are created automatically as required by the Java runtime. The class loader for an array class, as returned by Class.getClassLoader() is the same as the class loader for its element type; if the element type is a primitive type, then the array class has no class loader.
Applications implement subclasses of ClassLoader in order to extend the manner in which the Java virtual machine dynamically loads classes.
Class loaders may typically be used by security managers to indicate security domains.
In addition to loading classes, a class loader is also responsible for locating resources. A resource is some data (a » .class » file, configuration data, or an image for example) that is identified with an abstract ‘/’-separated path name. Resources are typically packaged with an application or library so that they can be located by code in the application or library. In some cases, the resources are included so that they can be located by other libraries.
The ClassLoader class uses a delegation model to search for classes and resources. Each instance of ClassLoader has an associated parent class loader. When requested to find a class or resource, a ClassLoader instance will usually delegate the search for the class or resource to its parent class loader before attempting to find the class or resource itself.
Class loaders that support concurrent loading of classes are known as parallel capable class loaders and are required to register themselves at their class initialization time by invoking the ClassLoader.registerAsParallelCapable method. Note that the ClassLoader class is registered as parallel capable by default. However, its subclasses still need to register themselves if they are parallel capable. In environments in which the delegation model is not strictly hierarchical, class loaders need to be parallel capable, otherwise class loading can lead to deadlocks because the loader lock is held for the duration of the class loading process (see loadClass methods).
Run-time Built-in Class Loaders
- Bootstrap class loader. It is the virtual machine’s built-in class loader, typically represented as null , and does not have a parent.
- Platform class loader. The platform class loader is responsible for loading the platform classes. Platform classes include Java SE platform APIs, their implementation classes and JDK-specific run-time classes that are defined by the platform class loader or its ancestors. The platform class loader can be used as the parent of a ClassLoader instance. To allow for upgrading/overriding of modules defined to the platform class loader, and where upgraded modules read modules defined to class loaders other than the platform class loader and its ancestors, then the platform class loader may have to delegate to other class loaders, the application class loader for example. In other words, classes in named modules defined to class loaders other than the platform class loader and its ancestors may be visible to the platform class loader.
- System class loader. It is also known as application class loader and is distinct from the platform class loader. The system class loader is typically used to define classes on the application class path, module path, and JDK-specific tools. The platform class loader is the parent or an ancestor of the system class loader, so the system class loader can load platform classes by delegating to its parent.
Normally, the Java virtual machine loads classes from the local file system in a platform-dependent manner. However, some classes may not originate from a file; they may originate from other sources, such as the network, or they could be constructed by an application. The method defineClass converts an array of bytes into an instance of class Class . Instances of this newly defined class can be created using Class.newInstance .
The methods and constructors of objects created by a class loader may reference other classes. To determine the class(es) referred to, the Java virtual machine invokes the loadClass method of the class loader that originally created the class.
For example, an application could create a network class loader to download class files from a server. Sample code might look like:
ClassLoader loader = new NetworkClassLoader(host, port); Object main = loader.loadClass("Main", true).newInstance(); . . . The network class loader subclass must define the methods findClass and loadClassData to load a class from the network. Once it has downloaded the bytes that make up the class, it should use the method defineClass to create a class instance. A sample implementation is:
class NetworkClassLoader extends ClassLoader < String host; int port; public Class findClass(String name) < byte[] b = loadClassData(name); return defineClass(name, b, 0, b.length); >private byte[] loadClassData(String name) < // load the class data from the connection . . . >>
Binary names
Any class name provided as a String parameter to methods in ClassLoader must be a binary name as defined by The Java Language Specification .
Examples of valid class names include:
"java.lang.String" "javax.swing.JSpinner$DefaultEditor" "java.security.KeyStore$Builder$FileBuilder$1" "java.net.URLClassLoader$3$1"
Any package name provided as a String parameter to methods in ClassLoader must be either the empty string (denoting an unnamed package) or a fully qualified name as defined by The Java Language Specification .
Внутренности JVM, Часть 1 — Загрузчик классов
В этой серии статей я расскажу о том, как работает Java Virtual Machine. Сегодня мы рассмотрим механизм загрузки классов в JVM.
Виртуальная машина Java — это сердце экосистемы Java-технологий. Она делает для Java-программ возможность реализации принципа «написано один раз, работает везде» (write once run everywhere). Как и другие виртуальные машины, JVM представляет собой абстрактный компьютер. Основная задача JVM — загружать class-файлы и выполнять содержащийся в них байт-код.
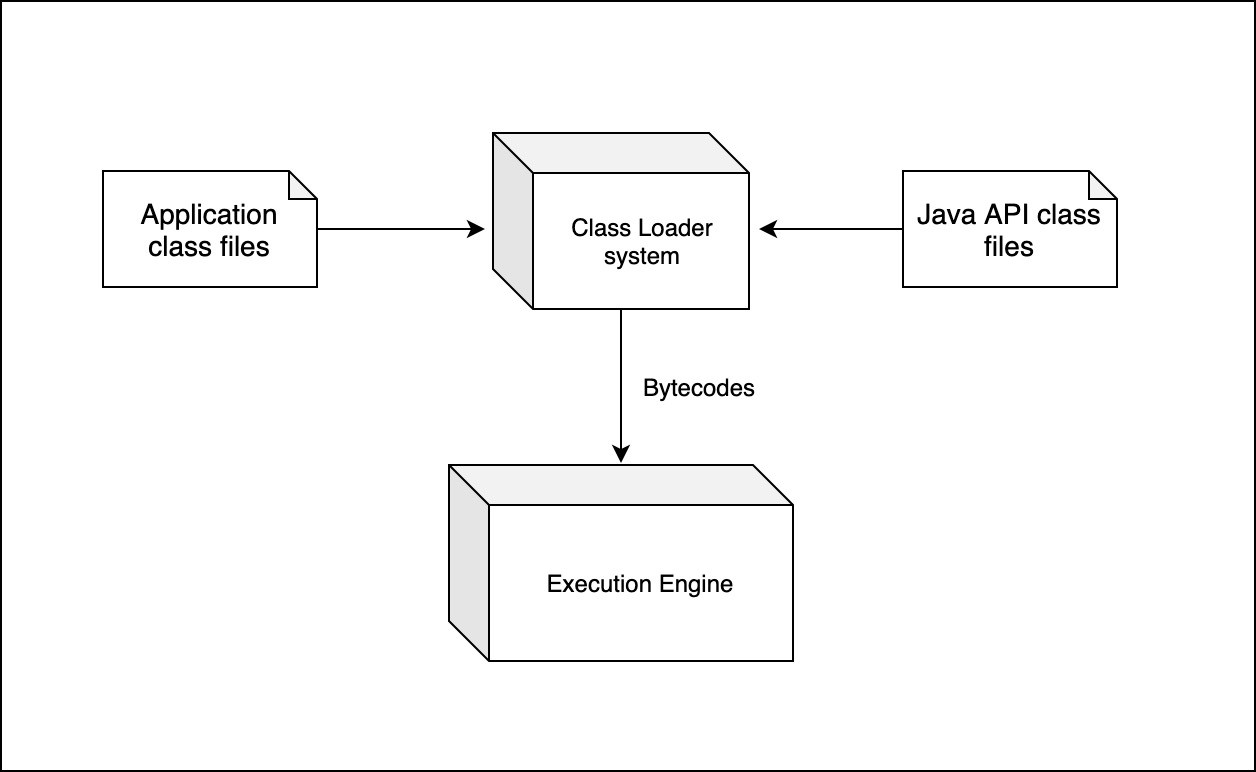
В состав JVM входят различные компоненты, такие как загрузчик классов (Classloader), сборщик мусора (Garbage Collector) (автоматическое управление памятью), интерпретатор, JIT-компилятор, компоненты управления потоками. В этой статье рассмотрим загрузчик классов (Class loader).
Загрузчик классов загружает class-файлы как для вашего приложения, так и для Java API. В виртуальную машину загружаются только те class-файлы Java API, которые действительно требуются при выполнении программы.
Байт-код выполняется подсистемой исполнения (execution engine).
Что такое загрузка классов?
Загрузка классов — это поиск и загрузка типов (классов и интерфейсов) динамически во время выполнения программы. Данные о типах находятся в бинарных class-файлах.
Этапы загрузки классов
Подсистема загрузчика классов отвечает не только за поиск и импорт бинарных данных класса. Она также выполняет проверку правильности импортируемых классов, выделяет и инициализирует память для переменных класса, помогает в разрешении символьных ссылок. Эти действия выполняются в следующем порядке:
- Загрузка (loading) — поиск и импорт бинарных данных для типа по его имени, создание класса или интерфейса из этого бинарного представления.
- Связывание, линковка (linking) — выполнение верификации, подготовки и, необязательного, разрешения:
- Верификация (verification) — проверка корректности импортируемого типа.
- Подготовка (preparation) — выделение памяти для статических переменных класса и инициализация памяти значениями по умолчанию.
- Разрешение (resolution) — преобразование символьных ссылок типов в прямые ссылки.
Примечание — загрузчик классов, помимо загрузки классов, также отвечает за поиск ресурсов. Ресурс — это некоторые данные (например, “.class” файл, данные конфигурации, изображения), которые идентифицируются с помощью абстрактного пути, разделенного символом «/». Ресурсы обычно упаковываются вместе с приложением или библиотекой для того, чтобы их можно было использовать в коде приложения или библиотеки.
Механизм загрузки классов в Java
Примечание переводчика — в данном разделе описано поведение для java < 9, в java 9+ произошли небольшие изменения, которые описаны ниже.
В Java используется модель делегирования загрузки классов. Основная идея состоит в том, что у каждого загрузчика классов есть “родительский” загрузчик. Когда происходит загрузка класса, то загрузчик “делегирует” поиск класса своему родителю, перед тем как искать класс самостоятельно.
Модель делегирования загрузчиков классов представляет собой граф загрузчиков, которые передают друг другу запросы на загрузку. Корнем в этом графе является bootstrap-загрузчик. Загрузчики классов создаются с одним родителем, которому они могут делегировать загрузку, и осуществляют поиск класса в следующих местах:
Класс загружается тем загрузчиком, который ближе всего к корню, поскольку право первому загрузить класс всегда предоставляется загрузчику-родителю. Это позволяет загрузчику видеть только классы, загруженные самостоятельно, его родителем или предками. Он не может видеть классы, загруженные дочерними загрузчиками.
В Java SE Platform API исторически было определено два загрузчика классов:
Bootstrap class loader (базовый, первичный загрузчик) — загружает классы из bootstrap classpath.
System class loader (системный загрузчик) — родительский класс для новых загрузчиков классов и, как правило, загрузчик классов, используемый для загрузки и запуска приложения.
Загрузчики классов JDK 9+
Application class loader — обычно используется для загрузки классов приложения из classpath. Также это загрузчик по умолчанию для некоторых модулей JDK, которые содержат утилиты или экспортируют API утилит. (Примечание переводчика: например, jdk.jconsole , jdk.jshell и др)
Platform class loader — загружает выбранные (на основе безопасности / разрешений) модули Java SE и JDK. Например, java.sql.
Bootstrap class loader — загружает основные модули Java SE и JDK.
Эти три встроенных загрузчика классов работают вместе следующим образом:
- Application class loader сначала ищет именованные модули, определенные для всех встроенных загрузчиков. Если для одного из этих загрузчиков определен подходящий модуль, то этот загрузчик загружает класс. Если в именованном модуле, определенном для одного из этих загрузчиков, класс не найден, тогда application class loader делегирует его родителю. Если класс не найден родителем, то application class loader ищет его в classpath. Классы, найденные в classpath, загружаются как члены безымянного модуля этого загрузчика.
- Platform class loader выполняет поиск именованных модулей, определенных для всех встроенных загрузчиков. Если подходящий модуль определен для одного из этих загрузчиков, тогда этот загрузчик загружает класс. Если в именованном модуле, определенном для одного из этих загрузчиков, класс не найден, тогда platform class loader делегирует его родителю.
- Bootstrap class loader выполняет поиск именованных модулей, определенных для него самого. Если класс не найден в именованном модуле, определенном для bootstrap-загрузчика, тогда bootstrap-загрузчик ищет файлы и каталоги, добавленные в bootstrap classpath, с помощью параметра -Xbootclasspath/a (позволяет добавить файлы и каталоги к bootstrap classpath). Классы, найденные в bootstrap classpath, загружаются как члены безымянного модуля этого загрузчика.
package ru.deft.homework; import java.sql.Date; public class BuiltInClassLoadersDemo < public static void main(String[] args) < BuiltInClassLoadersDemo demoObject = new BuiltInClassLoadersDemo(); ClassLoader applicationClassLoader = demoObject.getClass().getClassLoader(); printClassLoaderDetails(applicationClassLoader); // java.sql classes are loaded by platform classloader java.sql.Date now = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); ClassLoader platformClassLoder = now.getClass().getClassLoader(); printClassLoaderDetails(platformClassLoder); // java.lang classes are loaded by bootstrap classloader ClassLoader bootstrapClassLoder = args.getClass().getClassLoader(); printClassLoaderDetails(bootstrapClassLoder); >private static void printClassLoaderDetails(ClassLoader classLoader) < // bootstrap classloader is represented by null in JVM if (classLoader != null) < System.out.println("ClassLoader name : " + classLoader.getName()); System.out.println("ClassLoader class : " + classLoader.getClass().getName()); >else < System.out.println("Bootstrap classloader"); >> >Запустив этот код на установленном у меня Amazon Corretto 11.0.3, получим следующий результат:
ClassLoader name : app ClassLoader class : jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader ClassLoader name : platform ClassLoader class : jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$PlatformClassLoader Bootstrap classloader