- HTML Tag
- Syntax
- Example of the HTML tag:
- Result
- Example of the HTML tag used with the CSS color and line-height properties:
- Attributes
- How to style tag?
- Common properties to alter the visual weight/emphasis/size of text in tag:
- Coloring text in tag:
- Text layout styles for tag:
- Other properties worth looking at for tag:
- Mastering CSS Properties for Body Element: Margin, Background, Font Family, and Height
- Background Properties
- Margin Properties
- Font Properties
- Height Properties
- Miscellaneous Properties
- Best Practices and Conclusion
- This is a heading
- Browser Support
- Global Attributes
- Event Attributes
- More Examples
- Example
- Hello world!
- Example
- Hello world!
- Example
- Hello world!
- Example
- Example
- Example
- Related Pages
- Default CSS Settings
- Example
- COLOR PICKER
- Report Error
- Thank You For Helping Us!
- : The Document Body element
- Attributes
- Examples
- Result
- Specifications
- Browser compatibility
- See also
- Found a content problem with this page?
- MDN
- Support
- Our communities
- Developers
HTML Tag
The tag defines a web page content (text, images, links, etc.). It is placed inside the element, after the element. In an HTML document, we can use only one tag.
Commonly, a list of content-specific CSS classes is placed within the element allowing JavaScript developers and designers to target pages easily. Even if these classes are not used, they won’t cause any problems.
Syntax
The
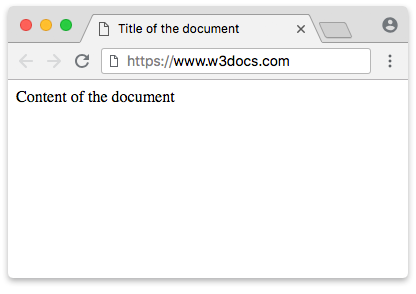
tag comes in pairs. The content is written between the opening () and closing () tags.Example of the HTML tag:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> head> body> p>Content of the document p> body> html>Result
Example of the HTML tag used with the CSS color and line-height properties:
html> html> head> title>Title of the document title> style> body < color: #444444; line-height: 1.5; > style> head> body> h1>HTML body tag example h1> p>Lorem ipsum, or lipsum as it is sometimes known, is dummy text used in laying out print, graphic or web designs. The passage is attributed to an unknown typesetter in the 15th century who is thought to have scrambled parts of Cicero's De Finibus Bonorum et Malorum for use in a type specimen book. p> body> html>Attributes
| Attribute | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| alink | color | Defines the color of the active link. Not used in HTML5. |
| background | URL | Defines the background image. Not used in HTML5. |
| bgcolor | color | Defines the background color. Not used in HTML5. |
| link | color | Defines the color of unvisited links. Not used in HTML5. |
| text | color | Defines the color of the text in a document. Not used in HTML5. |
| vlink | color | Defines the color of the visited link. Not used in HTML5. |
How to style tag?
Common properties to alter the visual weight/emphasis/size of text in tag:
- CSS font-style property sets the style of the font. normal | italic | oblique | initial | inherit.
- CSS font-family property specifies a prioritized list of one or more font family names and/or generic family names for the selected element.
- CSS font-size property sets the size of the font.
- CSS font-weight property defines whether the font should be bold or thick.
- CSS text-transform property controls text case and capitalization.
- CSS text-decoration property specifies the decoration added to text, and is a shorthand property for text-decoration-line, text-decoration-color, text-decoration-style.
Coloring text in tag:
- CSS color property describes the color of the text content and text decorations.
- CSS background-color property sets the background color of an element.
Text layout styles for tag:
- CSS text-indent property specifies the indentation of the first line in a text block.
- CSS text-overflow property specifies how overflowed content that is not displayed should be signalled to the user.
- CSS white-space property specifies how white-space inside an element is handled.
- CSS word-break property specifies where the lines should be broken.
Other properties worth looking at for tag:
- CSS text-shadow property adds shadow to text.
- CSS text-align-last property sets the alignment of the last line of the text.
- CSS line-height property specifies the height of a line.
- CSS letter-spacing property defines the spaces between letters/characters in a text.
- CSS word-spacing property sets the spacing between words.
Mastering CSS Properties for Body Element: Margin, Background, Font Family, and Height
Learn how to effectively use CSS properties for the body element such as margin, background, font family, and height. Improve your CSS development skills with this comprehensive guide.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is an essential component of web development. It is used to style and format HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) documents, making them visually appealing and user-friendly. CSS properties can be applied to different HTML elements, including the body element. In this article, we will focus on mastering CSS properties for the body element, specifically related to margin, background, font family, and height.
Background Properties
The background property is used to set the background color or image of an element. The background-size property is used to set the size of an element’s background image. This property is used to scale the image to fit the container. It takes different values, such as “auto”, “cover”, and “contain”. For example, if we want to set the background image size to “cover”, we can use the following code:
body background-image: url("path/to/image.jpg"); background-size: cover; > Margin Properties
The margin property is used to create extra space around an element. It can be applied to all four sides of an element or to individual sides. There are different ways to apply margin to all four sides of an element, such as using the “margin” property or using the shorthand “margin-top”, “margin-right”, “margin-bottom”, and “margin-left” properties. For example, we can use the shorthand property to set the margin for all four sides of the body element:
Font Properties
The font-family property is used to set the font family for an element. It determines the typeface that will be used to display the text. It is important to select appropriate font families for different contexts. For example, if we want to set the font family for the body element, we can use the following code:
body font-family: Arial, sans-serif; > Height Properties
The height property is used to set the height of an element. There are different ways to set the height of an element, such as using the “height” property or using the “min-height” and “max-height” properties. For example, if we want to set the height of the body element to 100%, we can use the following code:
Miscellaneous Properties
There are other CSS properties that can be applied to the body element, such as text-align and line-height. The text-align property is used to set the horizontal alignment of text. It can be inherited from a parent element in CSS. For example, if we want to inherit the text-align property from a parent element, we can use the following code:
The line-height property is used to set the height of a line of text. It is important to use best practices for setting line-height in CSS. For example, if we want to set the line-height for the body element to 1.5, we can use the following code:
Best Practices and Conclusion
In CSS development, it is important to use shorthand properties and best practices to optimize the code and ensure consistency across the website. We have discussed how to apply CSS properties to the body element, specifically related to margin, background, font family, and height. We have also looked at other miscellaneous properties that can be applied to the body element, such as text-align and line-height. By mastering these CSS properties, you can create visually appealing and user-friendly websites. Remember to use best practices and optimize your code for the best performance.
This is a heading
This is a paragraph.
The element contains all the contents of an HTML document, such as headings, paragraphs, images, hyperlinks, tables, lists, etc.
Note: There can only be one element in an HTML document.
Browser Support
Global Attributes
Event Attributes
More Examples
Example
Add a background image to a document (with CSS):
Hello world!
Visit W3Schools.com!
Example
Set the background color of a document (with CSS):
Hello world!
Visit W3Schools.com!
Example
Set the color of text in a document (with CSS):
Hello world!
This is some text.
Visit W3Schools.com!
Example
Set the color of unvisited links in a document (with CSS):
Example
Set the color of active links in a document (with CSS):
Example
Set the color of visited links in a document (with CSS):
Related Pages
Default CSS Settings
Most browsers will display the element with the following default values:
Example
body <
display: block;
margin: 8px;
>
COLOR PICKER
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, do not hesitate to send us an e-mail:
Thank You For Helping Us!
Your message has been sent to W3Schools.
Top Tutorials
Top References
Top Examples
Get Certified
W3Schools is optimized for learning and training. Examples might be simplified to improve reading and learning. Tutorials, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content. While using W3Schools, you agree to have read and accepted our terms of use, cookie and privacy policy.
: The Document Body element
The HTML element represents the content of an HTML document. There can be only one element in a document.
Attributes
This element includes the global attributes.
Color of text for hyperlinks when selected. Do not use this attribute! Use the CSS color property in conjunction with the :active pseudo-class instead.
URI of an image to use as a background. Do not use this attribute! Use the CSS background property on the element instead.
Background color for the document. Do not use this attribute! Use the CSS background-color property on the element instead.
The margin of the bottom of the body. Do not use this attribute! Use the CSS margin-bottom property on the element instead.
The margin of the left of the body. Do not use this attribute! Use the CSS margin-left property on the element instead.
Color of text for unvisited hypertext links. Do not use this attribute! Use the CSS color property in conjunction with the :link pseudo-class instead.
Function to call after the user has printed the document.
Function to call when the user requests printing of the document.
Function to call when the document is about to be unloaded.
Function to call when the document loses focus.
Function to call when the document fails to load properly.
Function to call when the document receives focus.
Function to call when the fragment identifier part (starting with the hash ( ‘#’ ) character) of the document’s current address has changed.
Function to call when the preferred languages changed.
Function to call when the document has finished loading.
Function to call when the document has received a message.
Function to call when network communication has failed.
Function to call when network communication has been restored.
Function to call when the user has navigated session history.
Function to call when the user has moved forward in undo transaction history.
Function to call when the document has been resized.
Function to call when the storage area has changed.
Function to call when the user has moved backward in undo transaction history.
Function to call when the document is going away.
The margin of the right of the body. Do not use this attribute! Use the CSS margin-right property on the element instead.
Foreground color of text. Do not use this attribute! Use CSS color property on the element instead.
The margin of the top of the body. Do not use this attribute! Use the CSS margin-top property on the element instead.
Color of text for visited hypertext links. Do not use this attribute! Use the CSS color property in conjunction with the :visited pseudo-class instead.
Examples
html lang="en"> head> title>Document titletitle> head> body> p> The code><body>code> HTML element represents the content of an HTML document. There can be only one code><body>code> element in a document. p> body> html>
Result
Specifications
Browser compatibility
BCD tables only load in the browser
See also
Found a content problem with this page?
This page was last modified on Jun 13, 2023 by MDN contributors.
Your blueprint for a better internet.
MDN
Support
Our communities
Developers
Visit Mozilla Corporation’s not-for-profit parent, the Mozilla Foundation.
Portions of this content are ©1998– 2023 by individual mozilla.org contributors. Content available under a Creative Commons license.