- Attributeerror str object has no attribute decode python
- # AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’
- # You don’t need to call decode() on strings
- # Use a try/except statement to handle a possible AttributeError
- # Encoding a string vs Decoding a bytes object
- # Using bytes() and str() functions instead
- # All text in Python is Unicode
- # Additional Resources
- How to Fix “AttributeError: ‘Str’ Object Has no Attribute ‘Decode’” in Python?
- What is an AttributeError in Python?
- When the AttributeError: ‘Str’ Object Has no Attribute ‘Decode’ Occurs?
- What Are Encoding and Decoding?
- Reasons For the “AttributeError: ‘Str’ Object Has no Attribute ‘Decode’” Error in Python
- How to Fix the “AttributeError: ‘Str’ Object Has no Attribute ‘Decode’” Error in Python?
- Conclusion
- Attributeerror: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’ ( Solved )
- What is AttributeError ?
- Cause of the Attributeerror: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’
- Solution for the Attributeerror: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’
- Conclusion
- Attributeerror: ‘dict’ object has no attribute encode ( Solved )
- ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘contains’ ( Solved )
- AttributeError: str object has no attribute write ( Solved )
- Join our list
Attributeerror str object has no attribute decode python
Last updated: Jan 29, 2023
Reading time · 3 min
# AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’
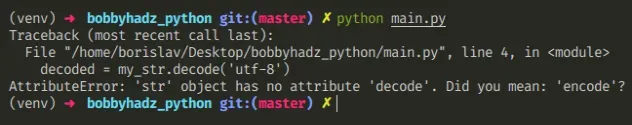
The Python «AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode'» occurs when we call the decode() method on a string that has already been decoded from bytes.
To solve the error, remove the call to the decode() method as the string is already decoded.
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
Copied!my_str = 'bobbyhadz.com' # ⛔️ AttributeError: 'str' object has no attribute 'decode'. Did you mean: 'encode'? decoded = my_str.decode('utf-8')
# You don’t need to call decode() on strings
The issue in the code sample is that we are trying to decode a string object.
Decoding is the process of converting a bytes object to a string and since we already have a string, we don’t have to call the decode() method on it.
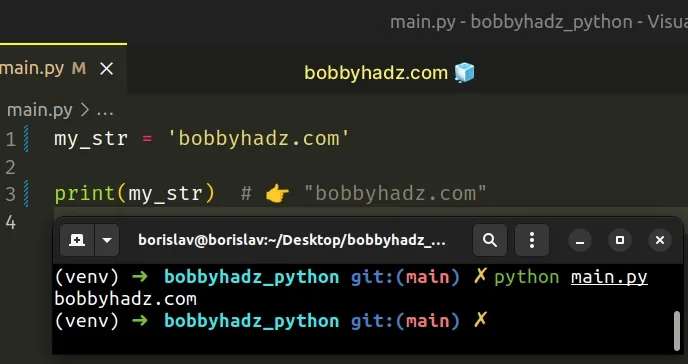
To solve the error, remove the call to the decode() method.
Copied!my_str = 'bobbyhadz.com' print(my_str) # 👉️ "bobbyhadz.com"
We don’t have to call the decode() method on strings because all strings in Python are already decoded.
# Use a try/except statement to handle a possible AttributeError
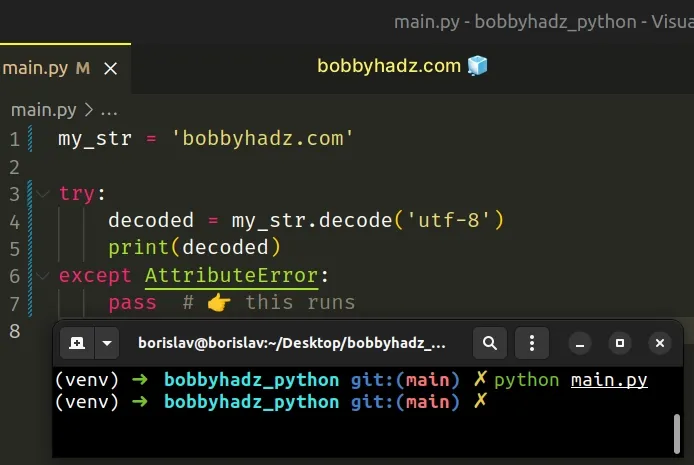
If you aren’t sure where you have a bytes object or a string, use a try/except statement to handle the possible AttributeError .
Copied!my_str = 'bobbyhadz.com' try: decoded = my_str.decode('utf-8') print(decoded) except AttributeError: pass # 👉️ this runs
We try to decode the value and if it doesn’t have a decode() attribute (it’s not a bytes object), we handle the AttributeError .
You can also extract the logic into a reusable function.
Copied!def decode(string): try: decoded = string.decode('utf-8') return decoded except AttributeError: return string result = decode('bobbyhadz.com') print(result) # 👉️ bobbyhadz.com result = decode(b'bobbyhadz.com') print(result) # 👉️ bobbyhadz.com
Encoding is the process of converting a string to a bytes object and decoding is the process of converting a bytes object to a string .
# Encoding a string vs Decoding a bytes object
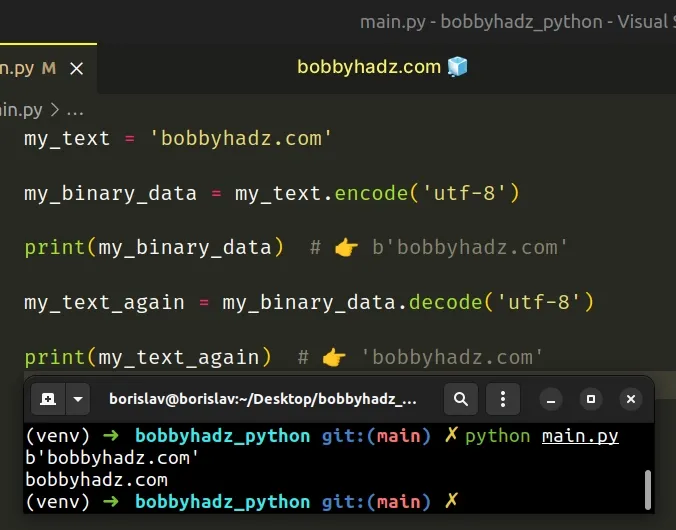
You can use the str.encode() method to go from str to bytes and bytes.decode() to go from bytes to str .
Copied!my_text = 'bobbyhadz.com' my_binary_data = my_text.encode('utf-8') print(my_binary_data) # 👉️ b'bobbyhadz.com' my_text_again = my_binary_data.decode('utf-8') print(my_text_again) # 👉️ 'bobbyhadz.com'
The str.encode() method is the opposite of bytes.decode() and returns a bytes representation of the Unicode string, encoded in the requested encoding.
# Using bytes() and str() functions instead
You can also use bytes(s, encoding=. ) and str(b, encoding=. ) .
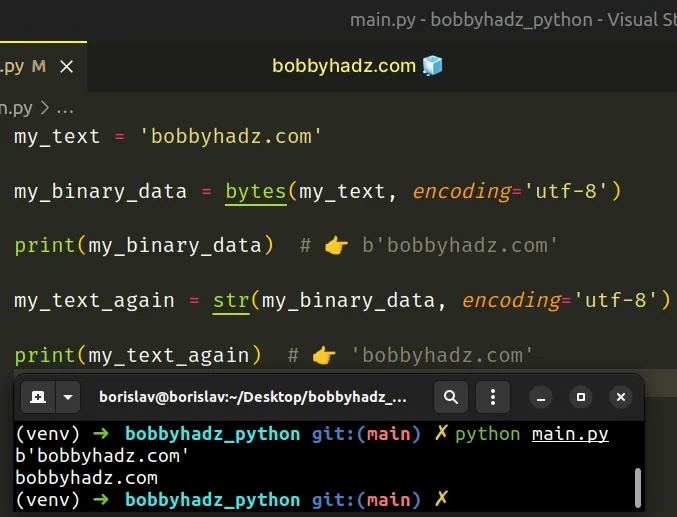
Copied!my_text = 'bobbyhadz.com' my_binary_data = bytes(my_text, encoding='utf-8') print(my_binary_data) # 👉️ b'bobbyhadz.com' my_text_again = str(my_binary_data, encoding='utf-8') print(my_text_again) # 👉️ 'bobbyhadz.com'
The str class returns a string version of the given object. If an object is not provided, the class returns an empty string.
The syntax for using the bytes class is the same, except that a b prefix is added.
Ever since Python 3, the language uses the concepts of text and binary data instead of Unicode strings and 8-bit strings.
# All text in Python is Unicode
All text in Python is Unicode, however, encoded Unicode is represented as binary data.
You can use the str type to store text and the bytes type to store binary data.
In Python 3 you can no longer use u’. ‘ literals for Unicode text because all strings are now Unicode.
However, you must use b’. ‘ literals for binary data.
A good way to start debugging is to print(dir(your_object)) and see what attributes a string has.
Here is an example of what printing the attributes of a string looks like.
Copied!my_string = 'bobbyhadz.com' # [ 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', # 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isascii', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', # 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', # 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'removeprefix', 'removesuffix', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', # 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', # 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill'] print(dir(my_string))
If you pass a class to the dir() function, it returns a list of names of the class’s attributes, and recursively of the attributes of its bases.
If you try to access any attribute that is not in this list, you would get the «AttributeError: str object has no attribute error».
Since decode() is not a method implemented by strings, the error is caused.
If the error persists, follow the instructions in my AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘X in Python article.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
I wrote a book in which I share everything I know about how to become a better, more efficient programmer.
How to Fix “AttributeError: ‘Str’ Object Has no Attribute ‘Decode’” in Python?
In this post, we will discuss what an AttributeError is. When does the AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’ occur? What is the ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’ ? And how to fix it, so without further ado, let’s get right into the topic.
Table of Contents
What is an AttributeError in Python?
AttributeError occurs when you reference an attribute of a module that doesn’t exist. These attributes can be a method or a variable in Python. Now let’s see an example to understand this error.
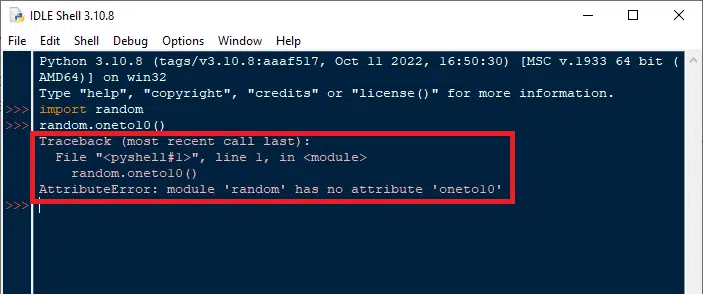
If we import random package and use its attribute randint with two parameters, 1 and 10 , to show a random number in the range of 1 to 10.
# import random import random print (random.randint(1,10))
This program doesn’t have any error because randint is an attribute of the random package, but if we write.
import random random.oneto10()
For our general guide catering to discussing what the AttributeError in Python is and general fixes for how one can resolve it, you can find it here.
When the AttributeError: ‘Str’ Object Has no Attribute ‘Decode’ Occurs?
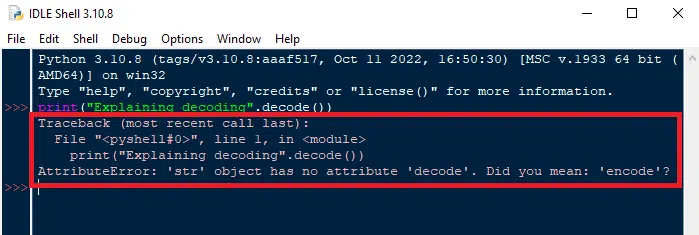
The leading cause of the AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’ is that decode is not an attribute of the str object . Decoding comes after encoding. If we call decode without encoding, it causes an error. For example, if we try to decode a string.
print("Explaining decoding".decode()) Before moving toward a solution, we must understand decode and encode and how we can use them in our program.
What Are Encoding and Decoding?
Encoding is converting strings into bytes. On the other hand, decoding means converting back bytes into strings. We use encode() for encoding and decode() for decoding in Python. The encode() method takes two parameters encoding type and errors .
The general syntax of encoding
encode(encoding, errors)
Encode () has two parameters, and both are optional. If we don’t pass the encoding type, then the default type for encoding is utf-8 . Encoding tells encoding types, for example, utf-8 , ascii , utf-16, etc.
myStr = “Encode Example”.encode('utf-8', 'strict') print (myStr) We use the decode() method for decoding. This method also takes two parameters.
The general syntax of decoding:
myStr = “Encode Example”.encode('utf-8', 'strict') print (myStr.decode('utf-8', 'strict')) Reasons For the “AttributeError: ‘Str’ Object Has no Attribute ‘Decode’” Error in Python
The following are the reasons why this error occurs.
- The Python version is not upgraded.
- You are decoding a string that is already decoded.
- Use decoding without using encoding.
- The specified object cannot access the decode() method.
How to Fix the “AttributeError: ‘Str’ Object Has no Attribute ‘Decode’” Error in Python?
To ignore the “ AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’” in your Python code, you must first check if you are using the python 2.x versions, then upgrade it to 3.x.
Still, if you are facing the AttributeError, you are not encoding the string. You have to encode the string first then you can decode it.
Let’s understand this concept using a practical example.
# how to use the decode function #intialize a string you want to encode and decode myStr = "how to use decode function" #encoding of myStr variable into bytes myStr = myStr.encode('utf-16', 'strict') print ("Encoded Bytes") print (myStr) print ("Decoded String") #decode bytes into a string print (myStr.decode('utf-16','strict')) Encoded Bytes b'\xff\xfeh\x00o\x00w\x00 \x00t\x00o\x00 \x00u\x00s\x00e\x00 \x00d\x00e\x00c\x00o\x00d\x00e\x00 \x00f\x00u\x00n\x00c\x00t\x00i\x00o\x00n\x00' Decoded String how to use the decode function
Conclusion
To summarize the article on how to fix the AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’, we’ve discussed what in encoding and decoding in Python. In addition to that, we’ve talked about why the AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’ occurs and how to fix it.
The main reasons for this error would be that we didn’t upgrade to version 3 or we are decoding already decoded bytes. All the reasons and situations are explained clearly.
Congratulations 🥳! To successfully make your python program free from AttributeError: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’ error.
A quick question, how to decode a collection of ASCII bytes in Python?
Attributeerror: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’ ( Solved )
In most of the cases in the python programming language, you work with the string. In the latest version of the Python language which is 3. xx, all the strings are already decoded. You will get the error Attributeerror: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode‘ if you try to call the decode() method on the strings.
In this entire tutorial, you will know why this Attributeerror comes and what you can do to solve these issues.
What is AttributeError ?
As you already know there are many inbuilt functions provided by python. If you are using these methods with invalid datatype then the python interpreter throws the AttribureError.
Let’s understand with an example. Suppose I am using the python append() method. This method accepts variables of a list type. But if you pass the string variable to it then you will get the AttributeError.
Cause of the Attributeerror: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’
The main cause of the Attributeerror: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’ is that you are already decoding the decoded strings. Decoding is the process of converting bytes object to str and encoding is the process of converting str to a bytes object.
Let’s take an example and understand it. I am using the python 3. xx version and decoding the sample string.
Run the below lines of code.
Output
Solution for the Attributeerror: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’
The solution to this error is that you don’t have to decode the string. It’s because if you are using the python 3. xx version all the strings are already decoded. However, if in any case you want to decode then you have to first encode to ‘utf-8’ or any format then you have to cast the string or first encode the string and then decode it.
Decoding string using cast
Output
Decoding String through encoding
Conclusion
An error Attributeerror: ‘str’ object has no attribute ‘decode’ comes when you are decoding already decoded strings. If you are getting this error then it’s obvious that you are using the python 2. xx versions. Therefore upgrade the python to 3. xx version.
I hope you have liked this tutorial, if you have any doubts then you can contact us for more help. You can also read the blow article on similar line to strengthen the knowledge.
Attributeerror: ‘dict’ object has no attribute encode ( Solved )
‘str’ object has no attribute ‘contains’ ( Solved )
AttributeError: str object has no attribute write ( Solved )
Data Science Learner Team
Join our list
Subscribe to our mailing list and get interesting stuff and updates to your email inbox.
We respect your privacy and take protecting it seriously
Thank you for signup. A Confirmation Email has been sent to your Email Address.