- How to Handle Error in Web.xml for Java web applications
- Sorry, the page you requested were not found.
- Related Java Error Handling Tutorials:
- Other Java Servlet Tutorials:
- About the Author:
- Add comment
- Comments
- Java web xml error page
- Resource not found!
- Обработка исключений
- Exception occurred while processing the request
- How to define Error page in Java Web Application — Servlet JSP Example
- Page-Specific Error page in JSP
- Error page in Java Web Application JSP Servlet
- Application wide Error page in Java web application
- 5 comments :
How to Handle Error in Web.xml for Java web applications
In Java web application development, error handling is required to build user-friendly and secured websites. In case of errors occurred, the user doesn’t have to see technical error details which they cannot understand. Instead, they should see a friendly page that tells them what happened. Also, it’s recommended to handle error properly to hide sensitive, technical information which can be exploited by hackers.
Java EE allows you to handle errors (by HTTP error codes and Java exception types) easily by putting some pieces of configuration in the web deployment descriptor document (the web.xml file). That means instead of showing the default error pages provided by the server, you can show your own error pages.
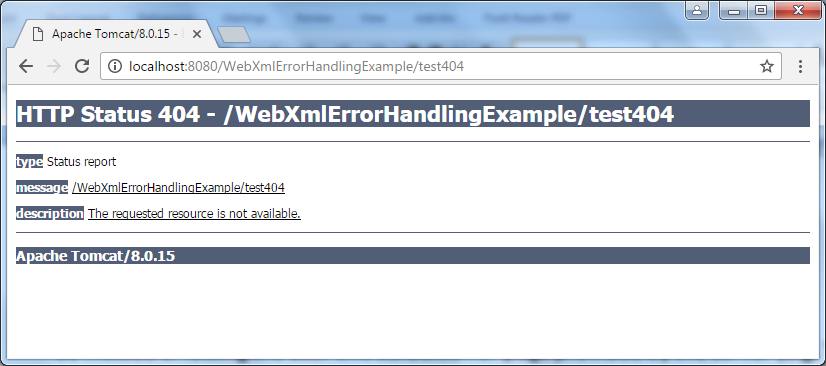
For example, putting the following declaration in the web.xml will override the handling of HTTP 404 error by the server:
With this declaration, if any 404 error occurred, your own error page is displayed to the user ( Error404.jsp page in the above example). Note that your custom error page is relative to the web application’s context root.
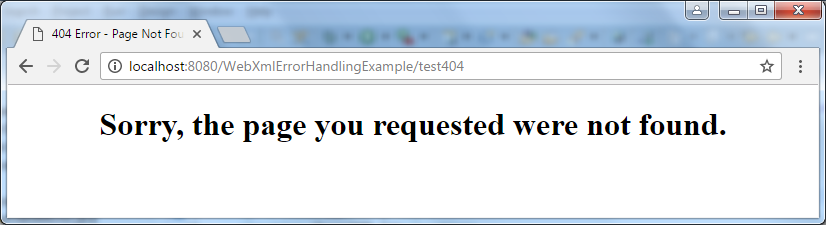
In your own error handling page, you can hide the technical information by showing only readable message to the user. For example, here’s the HTML code of the Error404.jsp page:
Sorry, the page you requested were not found.
You can show them a friendlier version like this:
You can add other elements to handle other error codes. For example, the following XML snippet declares the page that handles the HTTP 500 error:
Similarly, you can also declare JSP pages to handle exceptions thrown by the application. For example, the following XML code declares which page handles exceptions of type java.io.IOException :
java.io.IOException /IOException.jsp
You can also declare a generic exception page to catch all types of exception like this:
java.lang.Throwable /Exception.jsp
Here, if any exception occurred and it is not declared to be handled specifically in the web.xml , then the server will show the Exception.jsp page, because all exceptions are subtypes of the Throwable type.
Note that the most specific exception type is chosen if there are multiple matches. Consider the following declaration:
java.io.IOException /IOException.jsp java.lang.Throwable /Exception.jsp
In this case, if an IOException occurred, both the handlers match, but the handler for java.io.Exception is chosen because it is more specific than the one for java.lang.Throwable .
But if a ServletException occurred, the handler for java.lang.Throwable is chosen because there’s no specific handling for this exception.
That’s how to handle errors in web.xml for Java web applications. You can download the sample project in the attachment.
Related Java Error Handling Tutorials:
Other Java Servlet Tutorials:
About the Author:
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He started programming with Java in the time of Java 1.4 and has been falling in love with Java since then. Make friend with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos you YouTube.
Add comment
Comments
I have executed the above code. But in all the cases the result is «Sorry, the page you requested were not found.» Kindly clarify
CodeJava.net shares Java tutorials, code examples and sample projects for programmers at all levels.
CodeJava.net is created and managed by Nam Ha Minh — a passionate programmer.
Copyright © 2012 — 2023 CodeJava.net, all rights reserved.
Java web xml error page
Файл web.xml позволяет указать, какие страницы html или jsp будут отправляться пользователю при отправке статусных кодов ошибок. Для этого в web.xml применяется элемент .
Внутри этого элемента с помощью элемента указывается статусный код ошибки, который надо обработать. А элемент указывает на путь к странице html или jsp, которая будет отправляться пользователю.
Например, добавим в проект в папку WebContent новый файл 404.html со следующим кодом:
Resource not found!
В файле web.xml определим следующее содержимое:
В данном случае элемент error-code указывает, что мы будем обрабатывать ошибки со статусным кодом 404 (то есть такие ошибки, которые подразумевают отсутствие ресурса на сервере). А элемент location указывает, что в случае обращения к несуществующему ресурсу пользователю будет отправляться страница 404.html.
Обработка исключений
Кроме настройки обработки стандартных ошибок протокола http,типа 404 или 403, файл web.xml позволяет настроить обработку исключений, которые могут возникнуть при обработке запроса. Для этого в web.xml применяется элемент
Например, добавим в проект в папку WebContent новый файл error.jsp и определим в нем следующий код:
Exception occurred while processing the request
Type:
Message:
Данная страница jsp будет отображать информацию об исключении. Через глобальный объект pageContext в страницу передается контекст. Если при обработке запроса возникло какое-нибудь исключение, то метод pageContext.getException() возвратит это исключение в виде объекта Exception. И далее мы можем исследовать этот объект и вызывать его методы, например, получить тип исключения и сообщение об исключении.
Симитируем с сервлете какое-нибудь исключение:
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; @WebServlet("/hello") public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet < protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException < int x = 0; int y = 8 / x; >> В данном случае мы получаем ошибку деления на нуль, которая представлена типом java.lang.ArithmeticException.
Теперь определим следующий файл web.xml:
java.lang.Throwable /error.jsp
Элемент exception-type указывает, что обрабатываться будут исключения типа java.lang.Throwable. Поскольку это базовый класс для всех типов исключений, то фактически мы будем обрабатывать все исключения. Хотя можно конкретизировать тип исключения, например, указать тот же java.lang.ArithmeticException.
Элемент location определяет страницу, которая отправляется пользователю при возникновении исключении. В данном случае это error.jsp.
В итоге при обращении к сервлету будет сгенерировано исключение, и мы увидим информацию о нем:
How to define Error page in Java Web Application — Servlet JSP Example
There are two ways to define the Error page in Java web application written using Servlet and JSP. The first way is page wise error page which is defined on each jsp page and if there is any unhandled exception thrown from that page, the corresponding error page will be displayed. The second approach is an application-wide general or default error page which is shown if any Exception is thrown from any Servlet or JSP and there is no page-specific error page defined.
In this java tutorial we will see both approaches to declare error page in JSP and when should we use page specific error page and when should we choose to generate a default application-wide error page in Java web application.
This is in continuation of my earlier post on Servlet and JSP like the top 10 Servlet interview questions and the top 10 JSP interview questions . If you have’ read them yet, you can also read them to learn about essential Servlet and JSP concepts.
Page-Specific Error page in JSP
Every JSP page has an attribute called «errorpage» on page directive, by using this attribute you can define an error page for any particular JSP. After that, if any unhandled Exception is thrown from that JSP, this error page will be invoked. In order to make any JSP page as an error page, you need to use «isErrorPage» attribute of the page directive and mark it true.
For example, in the below JSP pages, error.jsp is an error page that can be used to display custom error messages if any unhandled exception is thrown from login.jsp (because it is defined as error page for login.jsp)
//error.jsp %@ page isErrorPage="true"%> //login.jsp %@ page errorPage="error.jsp"%>
This is a preferred way of showing error messages in Java web applications if you have custom error messages based on JSP and it also supersedes any application-wide error page defined in web.xml. You can also join these Servlet and JSP courses to learn more about page directives in JSP.
Error page in Java Web Application JSP Servlet
Application wide Error page in Java web application
There is another way to define error pages in java web applications written using servlet and JSP. This is called an application-wide error page or default/general error page because it’s applicable to the whole web application instead of any particular servlet or JSP. Its recommended practice for every Java web application to have a default error page in addition to page-specific error pages.
This error page is defined in web.xml by using tag < error-page >. < error-page >allows you to define custom error messages based upon HTTP error code or any Java Exception. you can define a default error message for all exceptions by specifying < exception-type >as java.lang.Throwable and it would be applicable to all exceptions are thrown from any Servlet or JSP from web application. here is an example of declaring default error page in Java web application based on HTTP Error code and Java Exception type.
java.lang.Throwable /error.htm error-page> error-code>500error-code>/internal-server-error.htm error-page> error-page> error-code>404error-code>/page-not-found-error.htm error-page>
That’s all on how to define the custom error page in Java application both page-specific and an application-wide default error page. An important point to note is that page-specific error pages take precedence over application-wide default error pages defined in web.xml.
5 comments :
Hi Javin
Please let us to see hole content for each post in google reader. like before!
In my country blogspot is filtered and unfortunately I can not see the hole content of each post in google reader.
Thanks in advance.
There is a severe issue with using «errorpage» «isErrorpage» and declaring error page in web.xml file, it doesn’t display properly in Internet Explorer at least version 6 and 7, instead it shows it own IE error page for page 404 and internal server error 500. better approach is using Spring exception handling and defining default error view for Spring’s Exception handler. in this way you will get consistent behavior over all browser because error page will not be treated as error page instead it will be treated as another jsp page.I have spent lot of time to figure out this bug with IE6, you may save your precious time. Also there is another theory that IE and chrome will display its own error page if size of error page will be less than 512 bytes. I have tested this but in my case even if size was more than 512 bytes it was still showing «Internal server error-500» Only solution which worked was Using Spring Exception handling.
I think best way to handle page not found error (Error code 404) and Internal Server Error(Error code 500) is to use Spring framework. Spring MVC provides Exception handling mechanism which can be setup in dispatcher-servlet.xml file and it can have different error pages for different Exception type and can have a default one as well but I am not sure if supports error code as well.